Abstract
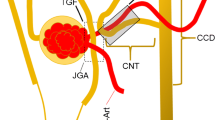
Within each nephro-vascular unit, the tubule returns to the vicinity of its own glomerulus. At this site, there are specialised tubular cells, the macula densa cells, which sense changes in tubular fluid composition and transmit information to the glomerular arterioles resulting in alterations in glomerular filtration rate and blood flow. Work over the last few years has characterised the mechanisms that lead to the detection of changes in luminal sodium chloride and osmolality by the macula densa cells. These cells are true “sensor cells” since intracellular ion concentrations and membrane potential reflect the level of luminal sodium chloride concentration. An unresolved question has been the nature of the signalling molecule(s) released by the macula densa cells. Currently, there is evidence that macula densa cells produce nitric oxide via neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) through cyclooxygenase 2 (COX 2)-microsomal prostaglandin E synthase (mPGES). However, both of these signalling molecules play a role in modulating or regulating the macula-tubuloglomerular feedback system. Direct macula densa signalling appears to involve the release of ATP across the basolateral membrane through a maxi-anion channel in response to an increase in luminal sodium chloride concentration. ATP that is released by macula densa cells may directly activate P2 receptors on adjacent mesangial cells and afferent arteriolar smooth muscle cells, or the ATP may be converted to adenosine. However, the critical step in signalling would appear to be the regulated release of ATP across the basolateral membrane of macula densa cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barajas L (1979) Anatomy of the juxtaglomerular apparatus. Am J Physiol 237:F333–F343
Schafer JA, Troutman SL, Andreoli TE (1974) Volume reabsorption, transepithelial potential differences, and ionic permeability properties in mammalian superficial proximal straight tubules. J Gen Physiol 64:582–607
Burg MB, Green N (1973) Function of the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. Am J Physiol 224:659–668
Rocha AS, Kudo LH (1982) Water, urea, sodium, chloride, and potassium transport in the in vitro isolated perfused papillary collecting duct. Kidney Int 22:485–491
Barajas L, Salido EC, Liu L, Powers KV (1995) The juxtaglomerular apparatus: a morphologic perspective. In: Laragh JH et al (eds) Hypertension: pathophysiology, diagnosis and management. Raven, New York, pp 1335–1348
Komlosi P, Fintha A, Bell PD (2005) Renal cell-to-cell communication via extracellular ATP. Physiology (Bethesda) 20:86–90
Bell PD, St John PL, Speyer M, Abrahamson DR (1992) Permeability of the macula densa basement membrane area to high molecular weight molecules. Ren Physiol Biochem 15:89–98
Iijima K, Moore LC, Goligorsky MS (1991) Syncytial organization of cultured rat mesangial cells. Am J Physiol 260:F848–F855
Peti-Peterdi J (2006) Calcium wave of tubuloglomerular feedback. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 291:F473–F480
Pricam C, Humbert F, Perrelet A, Orci L (1974) Gap junctions in mesangial and lacis cells. J Cell Biol 63:349–354
Goligorsky MS, Iijima K, Krivenko Y, Tsukahara H, Hu Y, Moore LC (1997) Role of mesangial cells in macula densa to afferent arteriole information transfer. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 24:527–531
Navar LG and Bell PD (2004) Romancing the macula densa at UAB. Kidney Int Suppl :S34-S40
Ullrich KJ, Schmidt-Nielsen B, O'Dell R, Pehling G, Gottschalk CW, Lassiter WE, Mylle M (1963) Micropuncture study of composition of proximal and distal tubular fluid in rat kidney. Am J Physiol 204:527–531
Bell PD, Lapointe JY, Peti-Peterdi J (2003) Macula densa cell signaling. Annu Rev Physiol 65:481–500
Bell PD, Lapointe JY (1997) Characteristics of membrane transport processes of macula densa cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 24:541–547
Bell PD, Navar LG (1982) Relationship between tubulo-glomerular feedback responses and perfusate hypotonicity. Kidney Int 22:234–239
Bell PD, Navar LG (1979) Stop-flow pressure feedback responses during reduced renal vascular resistance in the dog. Am J Physiol 237:F204–F209
Bell PD, Thomas C, Williams RH, Navar LG (1978) Filtration rate and stop-flow pressure feedback responses to nephron perfusion in the dog. Am J Physiol 234:F154–F165
Castrop H, Schweda F, Mizel D, Huang Y, Briggs J, Kurtz A, Schnermann J (2004) Permissive role of nitric oxide in macula densa control of renin secretion. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 286:F848–F857
Schnermann J, Davis JM, Wunderlich P, Levine DZ, Horster M (1971) Technical problems in the micropuncture determination of nephron filtration rate and their functional implications. Pflugers Arch 329:307–320
Schnermann J, Ploth DW, Hermle M (1976) Activation of tubulo-glomerular feedback by chloride transport. Pflugers Arch 362:229–240
Schnermann J (1998) Juxtaglomerular cell complex in the regulation of renal salt excretion. Am J Physiol 274:R263–R279
Schnermann J, Briggs JP (2000) Function of the juxtaglomerular apparatus: control of glomerular hemodynamics and renin secretion. In: Seldin DW et al (eds) The Kidney Physiology & Pathophysiology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadephia, pp 945–980
Barajas L, Powers K, Carretero O, Scicli AG, Inagami T (1986) Immunocytochemical localization of renin and kallikrein in the rat renal cortex. Kidney Int 29:965–970
Peti-Peterdi J, Fintha A, Fuson AL, Tousson A, Chow RH (2004) Real-time imaging of renin release in vitro. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287:F329–F335
Schweda F, Wagner C, Kramer BK, Schnermann J, Kurtz A (2003) Preserved macula densa-dependent renin secretion in A1 adenosine receptor knockout mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284:F770–F777
Bell PD, Lapointe JY, Cardinal J, Chang YS (1991) Transport pathways in macula densa cells. Kidney Int Suppl 32:S59–S64
Laamarti MA, Lapointe JY (1997) Determination of NH4+/NH3 fluxes across apical membrane of macula densa cells: a quantitative analysis. Am J Physiol 273:F817–F824
Lapointe JY, Laamarti A, Bell PD (1998) Ionic transport in macula densa cells. Kidney Int Suppl 67:S58–S64
Komlosi P, Fintha A, Bell PD (2006) Unraveling the relationship between macula densa cell volume and luminal solute concentration/osmolality. Kidney Int 70:865–871
Bell PD, Lapointe JY, Cardinal J (1989) Direct measurement of basolateral membrane potentials from cells of the macula densa. Am J Physiol 257:463–468
Laamarti MA, Bell PD, Lapointe JY (1998) Transport and regulatory properties of the apical Na-K-2Cl cotransporter of macula densa cells. Am J Physiol 275:703–709
Lapointe JY, Laamarti A, Hurst AM, Fowler BC, Bell PD (1995) Activation of Na:2Cl:K cotransport by luminal chloride in macula densa cells. Kidney Int 47:752–757
Lapointe JY, Bell PD, Cardinal J (1990) Direct evidence for apical Na+:2Cl−:K+ cotransport in macula densa cells. Am J Physiol 258:F1466–F1469
Lapointe JY, Bell PD, Hurst AM, Cardinal J (1991) Basolateral ionic permeabilities of macula densa cells. Am J Physiol 260:F856–F860
Hurst AM, Lapointe JY, Laamarti A, Bell PD (1994) Basic properties and potential regulators of the apical K+ channel in macula densa cells. J Gen Physiol 103:1055–1070
Fowler BC, Chang YS, Laamarti A, Higdon M, Lapointe JY, Bell PD (1995) Evidence for apical sodium proton exchange in macula densa cells. Kidney Int 47:746–751
Boulay G, Zhu X, Peyton M, Jiang M, Hurst R, Stefani E, Birnbaumer L (1997) Cloning and expression of a novel mammalian homolog of Drosophila transient receptor potential (Trp) involved in calcium entry secondary to activation of receptors coupled by the Gq class of G protein. J Biol Chem 272:29672–29680
Peti-Peterdi J, Bebok Z, Lapointe JY, Bell PD (2002) Novel regulation of cell [Na(+)] in macula densa cells: apical Na(+) recycling by H-K-ATPase. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 282:F324–F329
Bell PD, Lapointe JY, Sabirov R, Hayashi S, Peti-Peterdi J, Manabe K, Kovacs G, Okada Y (2003) Macula densa cell signaling involves ATP release through a maxi anion channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:4322–4327
Uchida S (2000) Physiological role of CLC-K1 chloride channel in the kidney. Nephrol Dial Transplant 15(Suppl 6):14–15
Uchida S, Sasaki S (2005) Function of chloride channels in the kidney. Annu Rev Physiol 67:759–778
Ren Y, Yu H, Wang H, Carretero OA, Garvin JL (2001) Nystatin and valinomycin induce tubuloglomerular feedback. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 281:F1102–F1108
Peti-Peterdi J, Morishima S, Bell PD, Okada Y (2002) Two-photon excitation fluorescence imaging of the living juxtaglomerular apparatus. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 283:F197–F201
Peti-Peterdi J, Bell PD (1999) Cytosolic [Ca2+] signaling pathway in macula densa cells. Am J Physiol 277:F472–F476
Bell PD, Navar LG (1982) Cytoplasmic calcium in the mediation of macula densa tubulo-glomerular feedback responses. Science 215:670–673
Ren Y, Liu R, Carretero OA, Garvin JL (2003) Increased intracellular Ca++ in the macula densa regulates tubuloglomerular feedback. Kidney Int 64:1348–1355
Thurau K, Valtin H, Schnermann J (1968) Kidney. Annu Rev Physiol 30:441–524
Navar LG, Inscho EW, Majid SA, Imig JD, Harrison-Bernard LM, Mitchell KD (1996) Paracrine regulation of the renal microcirculation. Physiol Rev 76:425–536
Skott O, Briggs JP (1987) Direct demonstration of macula densa-mediated renin secretion. Science 237:1618–1620
Bell PD, Peti-Peterdi J (1999) Angiotensin II stimulates macula densa basolateral sodium/hydrogen exchange via type 1 angiotensin II receptors. J Am Soc Nephrol 10(Suppl 11):S225–S229
Kovacs G, Peti-Peterdi J, Rosivall L, Bell PD (2002) Angiotensin II directly stimulates macula densa Na-2Cl-K cotransport via apical AT(1) receptors. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 282:F301–F306
Navar LG (1998) Integrating multiple paracrine regulators of renal microvascular dynamics. Am J Physiol 274:F433–F444
Navar LG, Imig JD, Zou L, Wang CT (1997) Intrarenal production of angiotensin II. Semin Nephrol 17:412–422
Persson PB (2003) Renin: origin, secretion and synthesis. J Physiol 552:667–671
Schnermann J, Briggs JP (1990) Restoration of tubuloglomerular feedback in volume-expanded rats by angiotensin II. Am J Physiol 259:F565–F572
Schnermann JB, Traynor T, Yang T, Huang YG, Oliverio MI, Coffman T, Briggs JP (1997) Absence of tubuloglomerular feedback responses in AT1A receptor- deficient mice. Am J Physiol 273:315–320
Vallon V (2003) Tubuloglomerular feedback in the kidney: insights from gene-targeted mice. Pflugers Arch 445:470–476
Bachmann S, Bosse HM, Mundel P (1995) Topography of nitric oxide synthesis by localizing constitutive NO synthases in mammalian kidney. Am J Physiol 268:F885–F898
Deng A, Wead LM, Blantz RC (2004) Temporal adaptation of tubuloglomerular feedback: Effects of COX-2. Kidney Int 66:2348–2353
Fischer E, Schnermann J, Briggs JP, Kriz W, Ronco PM, Bachmann S (1995) Ontogeny of NO synthase and renin in juxtaglomerular apparatus of rat kidneys. Am J Physiol 268:F1164–F1176
Harris RC (2002) Cyclooxygenase-2 and the kidney: functional and pathophysiological implications. J Hypertens Suppl 20:S3–S9
Kovacs G, Komlosi P, Fuson A, Peti-Peterdi J, Rosivall L, Bell PD (2003) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase: its role and regulation in macula densa cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:2475–2483
Liu R, Persson AE (2004) Angiotensin II stimulates calcium and nitric oxide release from Macula densa cells through AT1 receptors. Hypertension 43:649–653
Liu R, Carretero OA, Ren Y, Garvin JL (2005) Increased intracellular pH at the macula densa activates nNOS during tubuloglomerular feedback. Kidney Int 67:1837–1843
Ollerstam A, Persson AE (2002) Macula densa neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Cardiovasc Res 56:189–196
Paliege A, Mizel D, Medina C, Pasumarthy A, Huang YG, Bachmann S, Briggs JP, Schnermann JB, Yang T (2004) Inhibition of nNOS expression in the macula densa by COX-2 derived prostaglandin E2. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287:F152–F159
Ren YL, Garvin JL, Carretero OA (2000) Role of macula densa nitric oxide and cGMP in the regulation of tubuloglomerular feedback. Kidney Int 58:2053–2060
Tojo A, Onozato ML, Fukuda S, Asaba K, Kimura K, Fujita T (2004) Nitric oxide generated by nNOS in the macula densa regulates the afferent arteriolar diameter in rat kidney. Med Electron Microsc 37:236–241
Wang H, Carretero OA, Garvin JL (2002) Nitric oxide produced by THAL nitric oxide synthase inhibits TGF. Hypertension 39:662–666
Wilcox CS, Deng X, Welch WJ (1998) NO generation and action during changes in salt intake: roles of nNOS and macula densa. Am J Physiol 274:R1588–R1593
Wilcox CS, Welch WJ, Murad F, Gross SS, Taylor G, Levi R, Schmidt HH (1992) Nitric oxide synthase in macula densa regulates glomerular capillary pressure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:11993–11997
Liu R, Pittner J, Persson AE (2002) Changes of cell volume and nitric oxide concentration in macula densa cells caused by changes in luminal NaCl concentration. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:2688–2696
Wilcox CS, Welch WJ (1996) TGF and nitric oxide: effects of salt intake and salt-sensitive hypertension. Kidney Int Suppl 55:S9–S13
Peti-Peterdi J, Komlosi P, Fuson AL, Guan Y, Schneider A, Qi Z, Redha R, Rosivall L, Breyer MD, Bell PD (2003) Luminal NaCl delivery regulates basolateral PGE2 release from macula densa cells. J Clin Invest 112:76–82
Yang T, Park JM, Arend L, Huang Y, Topaloglu R, Pasumarthy A, Praetorius H, Spring K, Briggs JP, Schnermann J (2000) Low chloride stimulation of prostaglandin E2 release and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in a mouse macula densa cell line. J Biol Chem 275:37922–37929
Cheng HF, Wang JL, Zhang MZ, McKanna JA, Harris RC (2000) Nitric oxide regulates renal cortical cyclooxygenase-2 expression. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 279:F122–F129
Harris RC, McKanna JA, Akai Y, Jacobson HR, Dubois RN, Breyer MD (1994) Cyclooxygenase-2 is associated with the macula densa of rat kidney and increases with salt restriction. J Clin Invest 94:2504–2510
Harris RC, Breyer MD (2001) Physiological regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 in the kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 281:F1–F11
Fuson AL, Komlosi P, Unlap TM, Bell PD, Peti-Peterdi J (2003) Immunolocalization of a microsomal prostaglandin E synthase in rabbit kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 285:F558–F564
Inscho EW (2009) ATP, P2 receptors and the renal microcirculation. Pur. Sig., doi:10.1007/s11302-009-9147-1
Inscho EW, Cook AK, Mui V, Miller J (1998) Direct assessment of renal microvascular responses to P2-purinoceptor agonists. Am J Physiol 274:718–727
Inscho EW, Carmines PK, Navar LG (1991) Juxtamedullary afferent arteriolar responses to P1 and P2 purinergic stimulation. Hypertension 17:1033–1037
Inscho EW (2001) P2 receptors in regulation of renal microvascular function. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 280:F927–F944
Inscho EW, Schroeder AC, Deichmann PC, Imig JD (1999) ATP-mediated Ca2+ signaling in preglomerular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol 276:F450–F456
Inscho EW, Cook AK, Navar LG (1996) Pressure-mediated vasoconstriction of juxtamedullary afferent arterioles involves P2-purinoceptor activation. Am J Physiol 271:F1077–F1085
Majid DS, Inscho EW, Navar LG (1999) P2 purinoceptor saturation by adenosine triphosphate impairs renal autoregulation in dogs. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:492–498
Inscho EW, Cook AK, Imig JD, Vial C, Evans RJ (2003) Physiological role for P2X1 receptors in renal microvascular autoregulatory behavior. J Clin Invest 112:1895–1905
Osswald H, Nabakowski G, Hermes H (1980) Adenosine as a possible mediator of metabolic control of glomerular filtration rate. Int J Biochem 12:263–267
Casellas D, Moore LC (1990) Autoregulation and tubuloglomerular feedback in juxtamedullary glomerular arterioles. Am J Physiol 258:F660–F669
Inscho EW, Cook AK, Imig JD, Vial C, Evans RJ (2004) Renal autoregulation in P2X knockout mice. Acta Physiol Scand 181:445–453
Navar LG, Burke TJ, Robinson RR, Clapp JR (1974) Distal tubular feedback in the autoregulation of single nephron glomerular filtration rate. J Clin Invest 53:516–525
Navar LG, Bell PD, Burke TJ (1982) Role of a macula densa feedback mechanism as a mediator of renal autoregulation. Kidney Int Suppl 12:S157–S164
Loutzenhiser R, Griffin K, Williamson G, Bidani A (2006) Renal autoregulation: new perspectives regarding the protective and regulatory roles of the underlying mechanisms. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 290:R1153–R1167
Nishiyama A, Navar LG (2002) Response to J. Schnermann: adenosine mediates tubuloglomerular feedback. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 283:Ra278–Ra280
Nishiyama A, Navar LG (2002) ATP mediates tubuloglomerular feedback. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 283:R273–R275
Nishiyama A, Majid DS, Walker MIII, Miyatake A, Navar LG (2001) Renal interstitial atp responses to changes in arterial pressure during alterations in tubuloglomerular feedback activity. Hypertension 37:753–759
Nishiyama A, Majid DS, Taher KA, Miyatake A, Navar LG (2000) Relation between renal interstitial ATP concentrations and autoregulation-mediated changes in renal vascular resistance. Circ Res 86:656–662
Burnstock G (1997) The past, present and future of purine nucleotides as signalling molecules. Neuropharmacology 36:1127–1139
Baricordi OR, Ferrari D, Melchiorri L, Chiozzi P, Hanau S, Chiari E, Rubini M, di Virgilio F (1996) An ATP-activated channel is involved in mitogenic stimulation of human T lymphocytes. Blood 87:682–690
Schwiebert EM, Zsembery A (2003) Extracellular ATP as a signaling molecule for epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1615:7–32
Schwiebert EM (2001) ATP release mechanisms, ATP receptors and purinergic signalling along the nephron. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 28:340–350
Hovater MB, Olteanu D, Hanson EL, Cheng NL, Siroky B, Fintha A, Komlosi P, Liu W, Satlin LM, Bell PD, Yoder BK, Schwiebert EM (2008) Loss of apical monocilia on collecting duct principal cells impairs ATP secretion across the apical cell surface and ATP-dependent and flow-induced calcium signals. Purinergic Signal 4:155–170
Hanss B, Leal-Pinto E, Bruggeman LA, Copeland TD, Klotman PE (1998) Identification and characterization of a cell membrane nucleic acid channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:1921–1926
McCulloch F, Chambrey R, Eladari D, Peti-Peterdi J (2005) Localization of connexin 30 in the luminal membrane of cells in the distal nephron. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 289:F1304–F1312
Egan ME (2002) CFTR-associated ATP transport and release. Methods Mol Med 70:395–406
Schnermann J, Marver D (1986) ATPase activity in macula densa cells of the rabbit kidney. Pflugers Arch 407:82–86
Komlosi P, Banizs B, Fintha A, Steele SL, Zhang ZR, Bell PD (2008) Oscillating cortical thick ascending limb cells at the juxtaglomerular apparatus. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:1940–1946
Gunter TE, Yule DI, Gunter KK, Eliseev RA, Salter JD (2004) Calcium and mitochondria. FEBS Lett 567:96–102
Liu R, Bell PD, Peti-Peterdi J, Kovacs G, Johansson A, Persson AE (2002) Purinergic receptor signaling at the basolateral membrane of macula densa cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:1145–1151
Bell PD, Lapointe JY, Sabirov R, Hayashi S, Peti-Peterdi J, Manabe K, Kovacs G, Okada Y (2003) Macula densa cell signaling involves ATP release through a maxi anion channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:4322–4327
Okada SF, O'neal WK, Huang P, Nicholas RA, Ostrowski LE, Craigen WJ, Lazarowski ER, Boucher RC (2004) Voltage-dependent Anion Channel-1 (VDAC-1) Contributes to ATP Release and Cell Volume Regulation in Murine Cells. J Gen Physiol 124:513–526
Hazama A, Fan HT, Abdullaev I, Maeno E, Tanaka S, Ando-Akatsuka Y, Okada Y (2000) Swelling-activated, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-augmented ATP release and Cl− conductances in murine C127 cells. J Physiol 523(Pt 1):1–11
Sabirov RZ, Dutta AK, Okada Y (2001) Volume-dependent ATP-conductive large-conductance anion channel as a pathway for swelling-induced ATP release. J Gen Physiol 118:251–266
Sabirov RZ, Sheiko T, Liu H, Deng D, Okada Y, Craigen WJ (2006) Genetic demonstration that the plasma membrane maxianion channel and voltage-dependent anion channels are unrelated proteins. J Biol Chem 281:1897–1904
Sabirov RZ, Prenen J, Tomita T, Droogmans G, Nilius B (2000) Reduction of ionic strength activates single volume-regulated anion channels (VRAC) in endothelial cells. Pflugers Arch 439:315–320
Toma I, Bansal E, Meer EJ, Kang JJ, Vargas SL, Peti-Peterdi J (2008) Connexin 40 and ATP-dependent intercellular calcium wave in renal glomerular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 294:R1769–R1776
Komlosi P, Peti-Peterdi J, Fuson AL, Fintha A, Rosivall L, Bell PD (2004) Macula densa basolateral ATP release is regulated by luminal [NaCl] and dietary salt intake. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 286:F1054–F1058
Gutierrez AM, Lou X, Erik A, Persson G, Ring A (1999) Ca2+ response of rat mesangial cells to ATP analogues. Eur J Pharmacol 369:107–112
Kishore BK, Isaac J, Fausther M, Tripp SR, Shi H, Gill PS, Braun N, Zimmermann H, Sevigny J, Robson SC (2005) Expression of NTPDase1 and NTPDase2 in murine kidney: relevance to regulation of P2 receptor signaling. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 288:F1032–F1043
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease (DK-32032) and by a Scientist Development Award from the American Heart Association and a VA Merit Grant. We thank Ms. Barbara Harris for administrative assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bell, P.D., Komlosi, P. & Zhang, ZR. ATP as a mediator of macula densa cell signalling. Purinergic Signalling 5, 461–471 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-009-9148-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-009-9148-0