Abstract
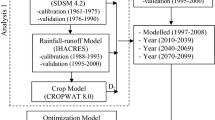
Increases in greenhouse gases caused by human activities have raised global temperature. Global warming affects water resources systems and the hydrologic cycle and may impact the performance of water resource systems. Water resources managers face challenges balancing conflicting goals in reservoir operation given the uncertainties introduced by climatic change. The HadCM3 climate model is used in this paper to estimate temperature and precipitation for early (2025–2039), middle (2055–2069) and late (2085–2099) periods of the 21st century under the A2 greenhouse gases emission scenario. The estimated temperature and precipitation from the climate model are input to a calibrated hydrologic model (IHACRES) to simulate inflow in a river basin draining to the Karoon-4 reservoir in Iran. A meta-heuristic multi-objective optimization algorithm (NSGA-II) is used in conjunction to predicted hydrologic variables to optimize dynamic operation rules in the Karoon-4 reservoir. The Karoon4 reservoir is operated non-adaptively and adaptively under climatic change. Our results show that adaptive reservoir management increases the reliability and reduces the vulnerability associated with hydropower generation in early, middle, and late simulation periods of the 21st century. These findings establish the importance of factoring in climatic change and considering adaptive strategies in future reservoir operations.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi M, Bozorg Haddad O, Marino MA (2014) Extraction of flexible multi-objective real-time reservoir operation rules. Water Resour Manag 28(1):131–147
Ashofteh PS, Bozorg Haddad O, Marino MA (2013a) Climate change impact on reservoir performance indexes in agricultural water supply. J Irrig Drain Eng 139(2):85–97
Ashofteh PS, Bozorg Haddad O, Marino MA (2013b) Scenario assessment of streamflow simulation and its transition probability in future periods under climate change. Water Resour Manag 27(1):255–274
Boyer C, Chaumont D, Chartier I, Roy AG (2010) Impact of climate change on the hydrology of St. Lawrence tributaries. J Hydrol 384(1–2):65–83
Bozorg Haddad O, Mariño MA (2011) Optimum operation of wells in coastal aquifers. Proc Inst Civ Eng : Water Manag 164(3):135–146
Bozorg Haddad O, Adams BJ, Mariño MA (2008) Optimum rehabilitation strategy of water distribution systems using the HBMO algorithm. J Water Supply: Res Technol - AQUA 57(5):327–350
Bozorg Haddad O, Moradi-Jalal M, Mirmomeni M, Kholghi MKH, Mariño MA (2009) Optimal cultivation rules in multi-crop irrigation areas. Irrig Drain 58(1):38–49
Bozorg Haddad O, Mirmomeni M, Zarezadeh Mehrizi M, Mariño MA (2010a) Finding the shortest path with honey-bee mating optimization algorithm in project management problems with constrained/unconstrained resources. Comput Optim Appl 47(1):97–128
Bozorg Haddad O, Mirmomeni M, Mariño MA (2010b) Optimal design of stepped spillways using the HBMO algorithm. Civ Eng Environ Syst 27(1):81–94
Bozorg Haddad O, Afshar A, Mariño MA (2011a) Multireservoir optimisation in discrete and continuous domains. Proc Inst Civ Eng : Water Manag 164(2):57–72
Bozorg Haddad O, Moradi-Jalal M, Mariño MA (2011b) Design-operation optimisation of run-of-river power plants. Proc Inst Civ Eng : Water Manag 164(9):463–475
Deb K, Partap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan T (2002) A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGAII. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 6(2):182–197
Diaz-Nieto J, Wibly RL (2005) A comparison of statistical downscaling and climate change factor methods: impacts on low flows in the River Thames, United Kingdom. Clim Chang 63(2–3):245–268
Eum HL, Simonovic SP (2010) Integrated reservoir management system for adaptation to climate change: The Nakdong river basin in Korea. Water Resour Manag 24(13):3397–3417
Fallah-Mehdipour E, Bozorg Haddad O, Mariño MA (2011a) MOPSO algorithm and its application in multipurpose multireservoir operations. J Hydroinf 13(4):794–811
Fallah-Mehdipour E, Bozorg Haddad O, Beygi S, Mariño MA (2011b) Effect of utility function curvature of Young’s bargaining method on the design of WDNs. Water Resour Manag 25(9):2197–2218
Fallah-Mehdipour E, Bozorg Haddad O, Mariño MA (2012a) Real-time operation of reservoir system by genetic programming. Water Resour Manag 26(14):4091–4103
Fallah-Mehdipour E, Bozorg Haddad O, Rezapour Tabari MM, Mariño MA (2012b) Extraction of decision alternatives in construction management projects: application and adaptation of NSGA-II and MOPSO. Expert Sys Appl 39(3):2794–2803
Fallah-Mehdipour E, Bozorg Haddad O, Mariño MA (2013a) Developing reservoir operational decision rule by genetic programming. J Hydroinf 15(1):103–119
Fallah-Mehdipour E, Bozorg Haddad O, Mariño MA (2013b) Extraction of multicrop planning rules in a reservoir system: application of evolutionary algorithms. J Irrig Drain Eng 139(6):490–498
Hay LE, Wibly RL, Leavesley GH (2000) A comparison of delta change and downscaled GCM scenarios for three mountainous basins in the United States. J Am Water Resour Assoc 36(2):387–397
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Chage (2000) Emission Scenarios. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (2014) Climate change 2014: impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability. the 5th assessment report. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Jakeman AJ, Hornberger GM (1993) How much complexity is warranted in a rainfall-runoff model? Water Resour Res 29(8):2637–2649
Jiang T, Chen YD, Xu C, Chen X, Chen X, Singh VP (2007) Comparison of hydrological impacts of climate change simulated by six hydrological models in the Dongjiang Basin, South China. J Hydrol 336(3):316–333
Karimi-Hosseini A, Bozorg Haddad O, Mariño MA (2011) Site selection of raingauges using entropy methodologies. Proc Inst Civ Eng : Water Manag 164(7):321–333
Lee SY, Fitzgerald CJ, Hamlet AF, Burges SJ (2011) Daily time-step refinement of optimized flood control rule curves for a global warming scenario. J Water Resour Plan Manag 137(4):309–317
Loáiciga HA (2002) Reservoir design and operation with variable lake hydrology. J Water Resour Plan Manag 128(6):399–405
Loáiciga HA (2004) Analytic game-theoretic approach to groundwater management. J Hydrol 297:22–33
Loáiciga HA, Valdes JB, Vogel R, Garvey J, Schwarz H (1996) Global warming and the hydrologic cycle. J Hydrol 174(1–2):83–128
Loáiciga HA, Maidment D, Valdes JB (2000) Climate change impacts in a regional karst aquifer, Texas, USA. J Hydrol 227:173–194
Majone B, Bovolo CI, Bellin A, Blenkinsop S, Fowler HJ (2012) Modeling the impacts of future climate change on water resources for the Gállego river basin (Spain). Water Resour Res 48(1), W01512
Minville M, Brissette F, Leconte R (2008) Uncertainty of the impact of climate change on the hydrology of a nordic watershed. J Hydrol 358(1–2):70–83
Minville M, Brissette F, Krau S, Leconte R (2009) Adaptation to climate change in the management of a canadian water-resources system exploited for hydropower. Water Resour Manag 23(14):2965–2986
Mitchell TD (2003) Pattern scaling: an examination of the accuracy of the technique for describing future climates. Clim Chang 60(3):217–242
Muzik I (2001) Sensitivity of hydrologic systems to climate change. Can Water Resour J 26(2):233–253
Noory H, Liaghat AM, Parsinejad M, Bozorg Haddad O (2012) Optimizing irrigation water allocation and multicrop planning using discrete PSO algorithm. J Irrig Drain Eng 138(5):437–444
Orouji H, Bozorg Haddad O, Fallah-Mehdipour E, Mariño MA (2013) Estimation of Muskingum parameter by meta-heuristic algorithms. Proc Inst Civ Eng : Water Manag 166(6):315–324
Pope VD, Gallani ML, Rowntree PR, Stratton RA (2000) The impact of new physical parameterizations in the Hadley Centre climate model: HadAM3. Climate Dynamic 16(2–3):123–146
Seifollahi-Aghmiuni S, Bozorg Haddad O, Omid MH, Mariño MA (2011) Long-term efficiency of water networks with demand uncertainty. Proc Inst Civ Eng : Water Manag 164(3):147–159
Seifollahi-Aghmiuni S, Bozorg Haddad O, Omid MH, Mariño MA (2013) Effects of pipe roughness uncertainty on water distribution network performance during its operational period. Water Resour Manag 27(5):1581–1599
Shokri A, Bozorg Haddad O, Mariño MA (2013) Algorithm for increasing the speed of evolutionary optimization and its accuracy in multi-objective problems. Water Resour Manag 27(7):2231–2249
Shokri A, Bozorg Haddad O, Mariño MA (2014) Multi-objective quantity–quality reservoir operation in sudden pollution. Water Resour Manag 28(2):567–586
Wilby RL, Harris I (2006) A framework for assessing uncertainties in climate change impacts: low-flow scenarios for the River Thames, UK. Water Resour Res 42(2), WR004065
Young HP (1993) An evolutionary model of bargaining. J Econ Theory 59(1):145–168
Yu PS, Yang TC, Wu CK (2002) Impact of climate change on water resources in southern Taiwan. J Hydrol 260(1–4):161–175
Zhou Y, Guo S (2013) Incorporating ecological requirement into multipurpose reservoir operating rule curves for adaptation to climate change. J Hydrol 498:153–164
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadi, M., Haddad, O.B. & Loáiciga, H.A. Adaptive Reservoir Operation Rules Under Climatic Change. Water Resour Manage 29, 1247–1266 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0871-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0871-0