Abstract
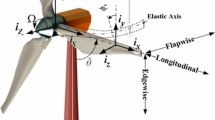
In this paper, aeroelastic stability analysis of hingeless helicopter blades in frequency domain is studied. In this regard, the nonlinear structural beam model of Hodges–Dowell and an unsteady aerodynamic model based on Greenberg theory and using Loewy aerodynamic function are considered to construct the aeroelastic model. Then, the concept of optimum equivalent linear frequency response function (OELF) is implemented to derive the aeroelastic FRF by coupling the aerodynamic and structural FRFs. Finally, for stability analysis, the efficient and simple criterion of condition number (CN) of aeroelastic OELF is applied. The comparison of the obtained results against those in the literature shows the capability of the OELF and condition number criterion for capturing the instability boundaries of a complex, nonlinear, aeroelastic system such as helicopter blades.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(A_{i}-O_{ij}\) :
-
Modal integrals
- \(c\) :
-
Blade chord
- \({C}'(k)\) :
-
Loewy’s lift deficiency function
- \(C_{l_\alpha }, C_{d_0}\) :
-
Lift coefficient and profile drag coefficient, respectively
- \(H\) :
-
FRF/OELF
- \(k\) :
-
Reduced frequency
- \(k_A\) :
-
Radius of gyration of blade cross-section
- \(k_m \) :
-
Mass radius of gyration of blade cross-section
- K:
-
\({k_A^2}/{k_m^2}\)
- \(L_\nu , L_w\) :
-
Dimensionless generalized aerodynamic forces per unit length
- \(M_\phi \) :
-
Dimensionless aerodynamic pitching moment per unit length
- \(S_{ ff} \) :
-
Power spectral density of excitation
- \(S_{x_n f} \) :
-
Cross-spectral density of excitation and response
- \(\bar{{V}}_{i}\) :
-
Induced flow velocity
- \(u, v, w\) :
-
Displacements in the \(x\), \(y\), \(z\) directions, respectively
- \(V_j, W_j, \Phi _{j} \) :
-
Generalized coordinates
- \(x, y, z\) :
-
Undeformed coordinate system
- \(\gamma \) :
-
Lock number
- \(\delta _{ij} \) :
-
Kronecker delta
- \(\theta , \theta _f \) :
-
Collective pitch angle and collective angle of instability of linearized aeroelastic system, respectively
- \(\alpha _{j}, \beta _{j}, \gamma _{j} \) :
-
Constants related to mode shapes
- \(\beta _{pc} \) :
-
Precone angle
- \(\kappa \) :
-
Dimensionless torsional rigidity
- \(\Lambda _1, \Lambda _2 \) :
-
Dimensionless bending stiffnesses
- \(\mu , \mu _1, \mu _2 \) :
-
Dimensionless mass radius of gyration
- \(\sigma \) :
-
Solidity
- \(\varphi \) :
-
Elastic torsion deflection
- \(\omega \) :
-
Frequency
- \(\bar{(\,)}\) :
-
Non-dimensional parameter
- \(\left( \,\right) _0, \Delta \left( \, \right) \) :
-
Equilibrium and perturbation components of generalized coordinates
- \(\left( \, \right) ^{\prime }\) :
-
\(\frac{\partial }{\partial x}\)
-
 :
: -
\(\frac{\partial }{\partial t}\)
References
Hodges, D.: A simplified algorithm for determining the stability of linear systems. AIAA J. 15, 424–425 (1977)
Hodges, D., Ormiston, R.: Stability of elastic bending and torsion of uniform cantilever rotor blades in hover with variable structural coupling. NASA TN D-8192 (1976)
Shahverdi, H., Nobari, A., Behbehani-Nejad, M., Haddadpour, H.: Aeroelastic analysis of helicopter rotor blade in hover using an efficient reduced-order aerodynamic model. J. Fluids Struct. 25, 1243–1257 (2009)
Friedmann, P., Tong, P.: Dynamic nonlinear elastic stability of helicopter rotor blades in hover and in forward flight. NASA CR-114485 (1972)
Sivaneri, T., Chopra, I.: Dynamic stability of a rotor blade using finite element analysis. AIAA J. 20, 716–723 (1982)
Bielawa, L.: Rotary Wing Structural Dynamics and Aeroelasticity. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Washington, DC (1992)
Hodges, D., Dowell, E.: Nonlinear equation of motion for the elastic bending and tortion of twisted nonuniform rotor blades. NASA TN D-7818 (1974)
Lee, I., Cho, M.: Aeroelastic stability of hingeless rotor blade in hover using large deflection theory. AIAA J. 32, 1472–1477 (1994)
Roknizadeh, S.A.S., Nobari, A.S., Mohagheghi, M., Shahverdi, H.: Stability analysis of aeroelastic systems based on aeroelastic frequency response function and condition number. Aircr. Eng. Aerosp. Technol. 84, 299–310 (2012)
Roknizadeh, S.A.S., Nobari, A., Shahverdi, H.: A new frequency domain based approach for a nonlinear aeroelasticity analysis. J. Fluids Struct. 43, 220–230 (2013)
Kashani, H., Nobari, A.: Identification of dynamic characteristics of nonlinear joint based on the optimum equivalent linear frequency function. J. Sound Vib. 329, 1460–1479 (2010)
Hodges, D.H., Pierce, G.A.: Introduction to Structural Dynamics and Aeroelasticity. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2001)
Greenberg, J.: Airfoil in sinusoidal motion in a pulsating stream. NACA TN 1326 (1947)
Sadati, S., Nobari, A., Naraghi, T.: Identification of a nonlinear joint in an elastic structure using optimum equivalent linear frequency response function. Acta Mech. 223, 1507–1516 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roknizadeh, S.A.S., Nobari, A.S. & Shahverdi, H. Nonlinear aeroelastic stability analysis of hingeless helicopter rotor blades using FRF coupling and condition number. Nonlinear Dyn 82, 289–297 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-015-2157-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-015-2157-3


 :
: