Abstract
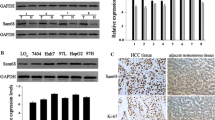
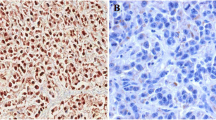
SEPT4 belongs to the Septin family with multiple functions in cell division, cytoskeletal organization and other processes. This study aims to investigate the relationship between SEPT4_i1 isoform and human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We showed that over-expression of SEPT4_i1 in HCC cells was able to sensitize cells to serum starvation-induced apoptosis. By contrast, knockdown of SEPT4_i1 expression in HCC cells was able to rescue cells from apoptosis induced by serum deprivation and to promote cell growth. Expressional analysis of SEPT4_i1 in tumor tissues further revealed that SEPT4_i1 was significantly down-regulated in human HCC tissues. Taken together, these data suggests a tumor suppressor role of SEPT4_i1 in HCC through regulating HCC cell apoptosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- KD:
-
Kilodalton
References
Kartmann B, Roth D (2001) Novel roles for mammalian septins: from vesicle trafficking to oncogenesis. J Cell Sci 114(Pt 5):839–844
Kinoshita M, Field CM, Coughlin ML, Straight AF, Mitchison TJ (2002) Self- and actin-templated assembly of Mammalian septins. Dev Cell 3(6):791–802
Faty M, Fink M, Barral Y (2002) Septins: a ring to part mother and daughter. Curr Genet 41(3):123–131
Hartwell LH (1971) Genetic control of the cell division cycle in yeast. IV. Genes controlling bud emergence and cytokinesis. Exp Cell Res 69(2):265–276
Spiliotis ET, Kinoshita M, Nelson WJ (2005) A mitotic septin scaffold required for Mammalian chromosome congression and segregation. Science 307(5716):1781–1785
Kinoshita M, Kumar S, Mizoguchi A, Ide C, Kinoshita A, Haraguchi T, Hiraoka Y, Noda M (1997) Nedd5, a mammalian septin, is a novel cytoskeletal component interacting with actin-based structures. Genes Dev 11(12):1535–1547
Hsu SC, Hazuka CD, Roth R, Foletti DL, Heuser J, Scheller RH (1998) Subunit composition, protein interactions, and structures of the mammalian brain sec6/8 complex and septin filaments. Neuron 20(6):1111–1122
Nagata K, Kawajiri A, Matsui S, Takagishi M, Shiromizu T, Saitoh N, Izawa I, Kiyono T, Itoh TJ, Hotani H (2003) Filament formation of MSF-A, a mammalian septin, in human mammary epithelial cells depends on interactions with microtubules. J Biol Chem 278(20):18538–18543
Kremer BE, Adang LA, Macara IG (2007) Septins regulate actin organization and cell-cycle arrest through nuclear accumulation of NCK mediated by SOCS7. Cell 130(5):837–850
Kim DS, Hubbard SL, Peraud A, Salhia B, Sakai K, Rutka JT (2004) Analysis of mammalian septin expression in human malignant brain tumors. Neoplasia 6(2):168–178
Jia ZF, Huang Q, Kang CS, Yang WD, Wang GX, Yu SZ, Jiang H, Pu PY (2010) Overexpression of septin 7 suppresses glioma cell growth. J Neurooncol 98(3):329–340
Larisch S, Yi Y, Lotan R, Kerner H, Eimerl S, Tony Parks W, Gottfried Y, Birkey Reffey S, de Caestecker MP, Danielpour D (2000) A novel mitochondrial septin-like protein, ARTS, mediates apoptosis dependent on its P-loop motif. Nat Cell Biol 2(12):915–921
Ihara M, Kinoshita A, Yamada S, Tanaka H, Tanigaki A, Kitano A, Goto M, Okubo K, Nishiyama H, Ogawa O (2005) Cortical organization by the septin cytoskeleton is essential for structural and mechanical integrity of mammalian spermatozoa. Dev Cell 8(3):343–352
Kissel H, Georgescu MM, Larisch S, Manova K, Hunnicutt GR, Steller H (2005) The Sept4 septin locus is required for sperm terminal differentiation in mice. Dev Cell 8(3):353–364
Blaser S, Horn J, Wurmell P, Bauer H, Strumpell S, Nurden P, Pagenstecher A, Busse A, Wunderle D, Hainmann I (2004) The novel human platelet septin SEPT8 is an interaction partner of SEPT4. Thromb Haemost 91(5):959–966
Kinoshita A, Kinoshita M, Akiyama H, Tomimoto H, Akiguchi I, Kumar S, Noda M, Kimura J (1998) Identification of septins in neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Pathol 153(5):1551–1560
Ihara M, Tomimoto H, Kitayama H, Morioka Y, Akiguchi I, Shibasaki H, Noda M, Kinoshita M (2003) Association of the cytoskeletal GTP-binding protein Sept4/H5 with cytoplasmic inclusions found in Parkinson’s disease and other synucleinopathies. J Biol Chem 278(26):24095–24102
Shehadeh L, Mitsi G, Adi N, Bishopric N, Papapetropoulos S (2009) Expression of Lewy body protein septin 4 in postmortem brain of Parkinson’s disease and control subjects. Mov Disord 24(2):204–210
Tanaka M, Tanaka T, Kijima H, Itoh J, Matsuda T, Hori S, Yamamoto M (2001) Characterization of tissue- and cell-type-specific expression of a novel human septin family gene, Bradeion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 286(3):547–553
Garber ME, Troyanskaya OG, Schluens K, Petersen S, Thaesler Z, Pacyna-Gengelbach M, van de Rijn M, Rosen GD, Perou CM, Whyte RI (2001) Diversity of gene expression in adenocarcinoma of the lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(24):13784–13789
Hallstrom TC, Mori S, Nevins JR (2008) An E2F1-dependent gene expression program that determines the balance between proliferation and cell death. Cancer Cell 13(1):11–22
Gottfried Y, Rotem A, Lotan R, Steller H, Larisch S (2004) The mitochondrial ARTS protein promotes apoptosis through targeting XIAP. EMBO J 23(7):1627–1635
Xie H, Surka M, Howard J, Trimble WS (1999) Characterization of the mammalian septin H5: distinct patterns of cytoskeletal and membrane association from other septin proteins. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 43(1):52–62
Iwaisako K, Hatano E, Taura K, Nakajima A, Tada M, Seo S, Tamaki N, Sato F, Ikai I, Uemoto S (2008) Loss of Sept4 exacerbates liver fibrosis through the dysregulation of hepatic stellate cells. J Hepatol 49(5):768–778
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Makoto Kinoshita (Kyoto University, Graduate School of Medicine, Japan) for providing pFLAG–SEPT4_i1 plasmid. We also thank Dr. Jinhu Guo (Sun Yat-Sen University) for helpful discussion. This project was supported by 863 projects of China (2006AA020501), the Project of the Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Commission (03dz14086) and the National Natural Science foundation of China (30024001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, S., Liu, M., Wu, Y. et al. Involvement of SEPT4_i1 in hepatocellular carcinoma: SEPT4_i1 regulates susceptibility to apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol Biol Rep 39, 4519–4526 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1242-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1242-z