Abstract
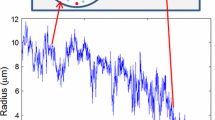
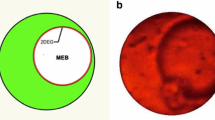
Multielectron bubbles (MEBs) are cavities in liquid helium containing a layer of electrons pinned to the inner surface of the bubbles. Previous experimental work carried out with MEBs in bulk helium-4 above the lambda point showed MEBs can contain vapor, which condenses in a time approximately proportional to the volume of the bubble, and this observation was further confirmed by numerical simulations. In the present work, we describe experiments where the MEBs are held against a solid substrate. We found the rate of vapor condensation and therefore the speed of collapse of the bubble to be orders of magnitude faster compared to MEBs in bulk. We discuss a numerical model and the associated difficulties to explain this difference.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.T. Sommer, Liquid helium as a barrier to electrons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 12, 271–273 (1964)
P. Leiderer, Electrons at the surface of quantum systems. J. Low Temp. Phys. 87, 247–278 (1992)
C.C. Grimes, Electrons in surface states on liquid helium. Surf. Sci. 73, 379–395 (1978)
A. Volodin, M. Khaikin, V. Edel’man, Development of instability and bubblon production on charged surface of helium. JETP Lett. 26, 11 (1977)
J. Tempere, I.F. Silvera, J.T. Devreese, Multielectron bubbles in helium as a paradigm for studying electrons on surfaces with curvature. Surf. Sci. Rep. 62, 159–217 (2007)
U. Albrecht, P. Leiderer, Multielectron bubbles in liquid helium. Eur. Lett. 3, 705–710 (1987)
J. Fang, A.E. Dementyev, J. Tempere, I.F. Silvera, Novel methods to create multielectron bubbles in superfluid helium. Rev. Sci. Instrum. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3553030
V. Vadakkumbatt, E.M. Joseph, A. Pal, A. Ghosh, Surface instabilities and generation of multielectron bubbles under pulsed electric fields. J. Low Temp. Phys. 171, 239–244 (2013)
E.M. Joseph, V. Vadakkumbatt, A. Pal, A. Ghosh, High speed imaging of generation and collapse of multielectron bubbles in liquid helium. J. Low Temp. Phys. 175, 78–84 (2014)
V. Vadakkumbatt, A. Ghosh, Fission of Multielectron bubbles in liquid helium under electric fields. J. Low Temp. Phys. 187, 369–375 (2017)
U. Albrecht, P. Leiderer, Unexpected hydrodynamic behavior of multielectron bubbles in liquid helium I. J. Low Temp. Phys. 86, 131–138 (1992)
V. Vadakkumbatt, E. Joseph, A. Pal, A. Ghosh, Studying electrons on curved surfaces by trapping and manipulating multielectron bubbles in liquid helium. Nat. Commun. 5, 4571 (2014)
E.M. Joseph, V. Vadakkumbatt, A. Pal, A. Ghosh, Stable trapping of multielectron helium bubbles in a paul trap. J. Low Temp. Phys. 187, 580–587 (2017)
A. Pal et al., Collapse of vapor-filled bubbles in liquid helium. J. Low Temp. Phys. 188, 101–111 (2017)
F. Pobell, Matter and Methods at Low Temperatures (Springer, Berlin, 2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-46360-3_1
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by MHRD, Government of India under Grant No. SPARC-1236. We thank DST for supporting the research and INSPIRE for providing financial support to one of the authors. We thank MHRD, MeitY, and DST for supporting the facilities at CeNSE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rath, P.K., Huang, Y. & Ghosh, A. Collapse of Vapor-Filled Multielectron Bubbles Held Against a Surface. J Low Temp Phys 201, 106–113 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-020-02345-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-020-02345-1