Abstract
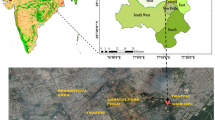
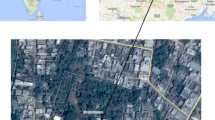
Observations of carbonaceous species [organic carbon (OC), elemental carbon (EC), water soluble organic carbon (WSOC), carbonaceous aerosols (CAs) and secondary organic carbon (SOC) ] and trace elements (As, Cr, Ni, Zn, Na, Mg, Al, P, K, Ca, Ti, Fe, and Mn) in PM10 are made over a high altitude site (ARIES, Nainital, 29.4° N, 79.5° E, ~1958 m amsl) in the central Himalayan region during October 2018−February 2019 to explore their possible sources. The average concentrations of PM10, OC, EC, WSOC, CA and SOC were recorded as 44±13 µg m-3, 3.66±1.26 µg m-3, 1.29±0.61 µg m-3, 2.28±0.76 µg m-3, 7.15±1.96 µg m-3 and 1.45±0.73 µg m-3, respectively during the study period. The concentrations of PM10, OC, EC, WSOC, CAs and SOC were significantly varied during autumn (October-November) and winter (December-February) seasons. During both the seasons, significant positive linear trend between OC & EC and OC & WSOC have been observed which is indicative of their common sources of carbonaceous aerosols at the study site. WSOC/OC ratio was estimated as 0.56 and 0.67 during autumn and winter, respectively suggested that the biomass burning could be one of the major sources of carbonaceous aerosols at Nainital. The significant positive correlation of PM10 with crustal elements (Al, Fe, Ca, Mg and Ti) as well as correlation of Al with other crustal elements (Fe, Ca, Mg and Ti) indicates the abundance of mineral dust at the sampling site. The observed Fe/Al ratio (1.07) also indicates mineral dust as a source at the sampling site, similarly, Ca/Al ratio (1.36) indicates that aerosols over this region is rich in Ca mineral as compared to average continental crust. Principal component analysis (PCA) identified the contribution of crustal/soil dust, biomass burning and industrial emissions to the PM10 over the central Himalayan region of India. Five days back trajectory analysis indicates that the air mass impacting the sampling site is from local surrounding area in Uttrakhand as well from Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Ingo Gangetic Plain (IGP) region, Pakistan, Afghanistan region and Thar Desert.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balachandran, S., Meena, B.R., Khillare, P.S.: Particle size distribution and its elemental composition in the ambient air of Delhi. Environ. Internat. 26, 49–54 (2000)
Begum, B.A., Hossain, A., Saroar, G., Biswas, S.K., Nasiruddin, M., Nahar, N., Chowdury, Z., Hopke, P.K.: Sources of carbonaceous materials in the airborne particulate matter of Dhaka. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 5(4), 237–246 (2011a)
Begum, B.A., Biswas, S.K., Hopke, P.K.: Key issues in controlling air pollutants in Dhaka. Bangladesh. Atmos. Environ. 45, 7705–7713 (2011b)
Belis, C., Karagulian, F., Larsen, B., Hopke, P.: Critical review and meta-analysis of ambient particulate matter source apportionment using receptor models in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 69, 94–108 (2013)
Bernd, R.T., Simoneit, B.R.T., Kobayashi, M., Mochida, M., Kawamura, K., Huebert, B.J.: Aerosol particles collected on aircraft flights over the northwestern Pacific region during the ACE‐Asia campaign: Composition and major sources of the organic compounds. J. Geophy. Res. Atmos. 109, D19S09 (2004)
Bond, T.C., Doherty, S.J., Fahey, D.W., et al.: Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: a scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 118, 5380–5552 (2013)
Cao, J.J., Chow, J.C., Lee, S.C., Li, Y., Chen, S.W., An, Z.S., Fung, K., Watson, J.G., Zhu, C.S., Liu, S.X.: Characterization and source apportionment of atmospheric organic and elemental carbon during fall and winter of 2003 in Xi’an. China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 5, 3561–3593 (2005)
Castro, L.M., Pio, C.A., Harrison, R.M., Smith, D.J.T.: Carbonaceous aerosol in urban and rural European atmospheres: estimation of secondary organic carbon concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 33, 2771–2781 (1999)
Chelani, A.B., Gajghate, D.G., Devotta, S.: Source apportionment of PM10 in Mumbai, India using CMB model. Bull. Environ. Contamin. Toxicol. 81, 190–195 (2008)
Chow, J.C., Watson, J.G., Chen, L.W.A., Arnott, W.P., Moosmuller, H.: Equivalence of elemental carbon by thermal/optical reflectance and transmittance with different temperature protocols. Environ.l Sci. Technol. 38, 4414–4422 (2004)
Draxler, R.R., Rolph, G.D.: HYSPLIT (HYbrid Single-particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory) Model. Access via NOAA ARL READY website. NOAA Air Resources Laboratory, Silver Spring. http://www.arl.noaa.gov/ready/hysplit4.html (2003)
Gadi, R., Shivani, Sharma, S.K., Mandal, T.K.: Source apportionment and health risk assessment of organic constituents in fine ambient aerosols (PM2.5): a complete year study over National Capital Region of India. Chemosphere 221, 583–596 (2019)
Gajananda, K., Kuniyal, J.C., Momin, G.A., Rao, P.S.P., Safai, P.D., Tiwari, S., Ali, K.: Trend of atmospheric aerosols over the north northwestern Himalayan region, India. Atmos. Environ. 39, 4817–4825 (2005)
Hegde, P., Kawamura, K., Joshi, H., Naja, M.: Organic and inorganic components of aerosols over the central Himalayas: winter and summer variations in stable carbon and nitrogen isotopic composition. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 23, 6102–6118 (2016)
Ho, K.F., Cao, J.J., Lee, S.C., Kawamura, K., Zhang, R.J.: Dicarboxylic acids, ketocarboxylic acids and dicarbonyls in urban atmosphere of China. J. Geophy. Res. 112, D22S27 (2007)
Jain, S., Sharma, S.K., Mandal, T.K., Saxena, M.: Source apportionment of PM10 in Delhi, India using PCA/APCS, UNMIX and PMF. Particuology 37, 107–118 (2018)
Jain, S., Sharma, S.K., Srivastava, M.K., Chaterjee, A., Singh, R.K., Saxena, M., Mandal, T.K.: Source apportionment of PM10 using receptor models in Indo-Gangetic plain (IGP) of India. Archives Environ. Contamin. Toxicol. 76, 114–128 (2019)
Kaushal, D., Kumar, A., Yadav, S., Tandon, A., Attri, A.K.: Wintertime carbonaceous aerosols over Dhauladhar region of North-Western Himalayas. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 25, 8044–8056 (2018)
Khare, P., Baruah, B.P.: Elemental characterization and source identification of PM2.5 using multivariate analysis at the suburban site of north-East India. Atmos. Res. 98, 148–162 (2010)
Khillare, P.K., Balachandran, S., Meena, B.R.: Spatial and temporal variation of heavy metals in atmospheric aerosol in India. Environ. Monit. Asses. 90, 1–21 (2004)
Kumar, A., Attri, A.K.: Biomass combustion a dominant source of carbonaceous aerosols in the ambient environment of western Himalayas. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 16(3), 519–529 (2016)
Kumar, A., Sarin, M.M.: Mineral aerosols from western India: temporal variability of course and fine atmospheric dust and elemental characteristics. Atmos. Environ. 43, 4005–4013 (2009)
Kumar, A., Ram, K., Ojha, N.: Variations in carbonaceous species at a high-altitude site in Western India: role of synoptic scale transport. Atmos. Environ. 125, 371–382 (2016)
Lighty, J.S., Veranth, J.M., Sarofim, A.F.: Combustion aerosols: factors governing their size and composition implications to human health. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 50(9), 1565–1618 (2000)
McLennan, S.: Relationship between the trace element composition of sedimentary rocks and upper continental crust. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2, 1021 (2001)
Menon, S., Hansen, J., Nazarenko, L., Luo, Y.: Climate effects of black carbon aerosols in China and India. Science 297, 2250–2253 (2002)
Naja, M., Akimoto, H., Staehelin, J.: Ozone in background and photochemically aged air over central Europe: Analysis of long-term ozonesonde data from Hohenpeissenberg and Payerne. J. Geophys. Res., 108, (D22), https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JD002477 (2003)
Naja, M., Bhardwaj, P., Singh, N., Kumar, P., Kumar, R., Ojha, N., Sagar, R., Satheesh, S.K., Krishna Moorthy, K., Kotamarthi, V.R.: High-frequency vertical profiling of meteorological parameters using AMF1 facility during RAWEX–GVAX at ARIES, Nainital. Curr. Sci. 111, 1 (2016)
Pant, P., Harrison, R.M.: Critical review of receptor modeling for particulate matter: a case study of India. Atmos. Environ. 49, 1–12 (2012)
Pope, C.A., Ezzati, M., Dockery, D.W.: Fine-particulate air pollution and life expectancy in the United States. New England Journal of Medicine. 360(4), 376–386 (2009)
Rai, A., Mukherjee, S., Chatterjee, A., Choudhary, N., Kotnala, G., Mandal, T.K., Sharma, S.K.: Seasonal variation of OC, EC and WSOC of PM10 and their CWT analysis over the eastern Himalayas. Aerosol Sci. Engin. 4, 26–40 (2020)
Ram, K., Sarin, M.M.: Day–night variability of EC, OC, WSOC and inorganic ions in urban environment of Indo-Gangetic Plain: Implications to secondary aerosol formation. Atmos. Environ. 45, 460–468 (2011)
Ram, K., Sarin, M., Hegde, P.: Atmospheric abundances of primary and secondary carbonaceous species at two high altitude sites in India: Sources and temporal variability. Atmos. Environ. 42(28), 6785–6796 (2008)
Ramana, M.V., Ramanathan, V., Feng, Y., Yoon, S.C., Kim, S.W., Carmichael, G.R., Schauer, J.J.: Warming influenced by the ratio of black carbon to sulphate and the black-carbon source. Nat Geosci 3, 542–545 (2010)
Ramgolam, K., Favez, O., Cachier, H., Gaudichet, A., Marano, F., Martinon, L., et al.: Size-partitioning of an urban aerosol to identify particle determinants involved in the proinflammatory response induced in airway epithelial cells. Particle and Fibre Toxicology. 6(1), (2009). https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-8977-6-10
Rengarajan, R., Sarin, M.M., Sudheer, A.K.: Carbonaceous and inorganic species in atmospheric aerosols during wintertime over urban and high-altitude sites in North India. J. Geophy. Res. 112, D21307 (2007)
Sarangi, T., Naja, M., Ojha, N., Kumar, R., Lal, S., Venkataramani, S., Kumar, A., Sagarand, R., Chandola, H.C.: First simultaneous measurements of ozone, CO and NOy at a high altitude regional representative site in the central Himalayas, J. Geophys. Res., 119, https://doi.org/10.1002/2013JD020631 (2014)
Sarin, M.M., Borole, D.V., Krishnaswami, S.: Geochemistry and geochronology of sediments from the Bay of Bengal and the equitorial Indian Ocean. Proc. Indian Academy of Science 88, 131–154 (1979)
Sen, A., Karapurkar, S.G., Saxena, M., Shenoy, D.M., Chaterjee, A., Choudhuri, A.K., Das, T., Khan, A.H., Kuniyal, J.C., Pal, S., Singh, D.P., Sharma, S.K., Kotnala, R.K., Mandal, T.K.: Stable isotopic composition (C & N) of PM10 over Indo-Gangetic Plains (IGP), adjoining regions and Indo-Himalayan Range during a winter, 2014 campaign. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 25(26), 26279–26296 (2018)
Sharma, S.K., Mandal, T.K., Sharma, C., Kuniyal, J.C., Joshi, R., Dhyani, P.P., Rohtash, Ghayas, H., Gupta, N.C., Sharma, P., Saxena, M., Sharma, A., Arya, B.C., Kumar, A.: Measurements of particulate (PM2.5), BC and trace gases over the Northwestern Himalayan region of India. Mapan 29(4), 243–253 (2014)
Sharma, S.K., Mandal, T.K., Dey, A.K., Deb, N., Jain, S., Saxena, M., Pal, S., Choudhuri, A.K., Yadav, S.: Carbonaceous and inorganic species in PM10 during wintertime over Giridih, Jharkhand (India). J. Atmos. Chem. 75, 219–233 (2018a)
Sharma, S.K., Mandal, T.K., Sharma, A., Saraswati, Jain, S.: Seasonal and annual trends of carbonaceous species of PM10 over a megacity Delhi, India during 2010–2017. J. Atmos. Chem. 75, 305–318 (2018b)
Sharma, S.K., Singh, A.K., Saud, T., Mandal, T.K., Saxena, M., Singh, S., Ghosh, S., Raha, S.: Study on water soluble ionic composition of PM10 and trace gases over Bay of Bengal during W_ICARB campaign. Meteo Atmos Phy. 118, 37–51 (2012)
Shivani, Gadi, R., Kumar, R., Sharma, M., Sharma, S.K., Mandal, T.K., Kumar, S., Kumar, S.: Levels and Sources of organic compounds in Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) over Delhi and National Capital Region of India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 25(31), 31071–31090 (2018)
Shivani, Gadi, R., Saxena, M., Sharma, S.K., Mandal, T.K.: Short Term Degradation of Air Quality during Major Firework Events in Delhi, India. Meteoro. Atmos. Phys. 131(4), 753–764 (2019a)
Shivani, Gadi, R., Sharma, S.K., Mandal, T.K.: Seasonal variation, source apportionment and source attributed health risk of carbonaceous aerosols in fine particulate matter over National Capital Region, India. Chemosphere 237, 124500 (2019b)
Srivastava, A.K., Ram, K., Pant, P., Hegde, P., Hema, J.: Black carbon aerosols over Manora Peak in the Indian Himalayan foothills: implications for climate forcing. Environ. Res. Lett. 7(1), 014002 (2012)
Venkataraman, C., Habib, G., Eiguren-Fernandez, A., Miguel, A.H., Friedlander, S.K.: Residential biofuel in South Asia: Carbonaceous aerosol emissions and climate impacts. Science 307(5714), 1454–1456 (2005)
Viana, M., Kuhlbusch, T.A.J., Querol, X., Alastuey, A., Harrison, R.M., Hopke, P.K., Winiwarter, W., Vallius, M., et al.: Source apportionment of particulate matter in Europe: a review of methods and results. J. Aerosol Sci. 39, 827–849 (2008)
Zhang, Q., Worsnop, D.R., Canangaratna, M.R., Jimenez, J.L.: Hydocarbon-like and ogygenated organic aerosols in Pittsburgh: Insights into sources and processes of organic aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 5, 3289–3311 (2005)
Acknowledgement
The authors are thankful to Director, CSIR-NPL, New Delhi; Director, ARIES, Nainital and Head, Environmental Sciences and Biomedical Metrology Division, CSIR-NPL, New Delhi for their encouragement and support. The authors also acknowledge the Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi for providing financial support for this study (DST/CCP/Aerosol/88/2017). Authors thankfully acknowledge the NOAA Air Resources Laboratory for download the air mass trajectories (http://www.arl.noaa.gov/ready/hysplit4.html). The authors are thankful to the anonymous reviewers and Editor-in-Chief for their constructive suggestions to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Fig. S1
(DOCX 405 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, S.K., Choudhary, N., Srivastava, P. et al. Variation of carbonaceous species and trace elements in PM10 at a mountain site in the central Himalayan region of India. J Atmos Chem 77, 49–62 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-020-09402-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-020-09402-9