Abstract
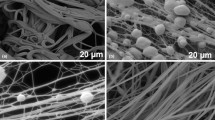
We report a novel 3-D cavity wound dressing based on a hydrogel–elastomer Interpenetrating Polymer Network (IPN) fabricated into an open-mesh architecture. IPN fibers used to form the dressing were produced by a wet spinning method and optimized in two steps. A factorial experiment was first conducted to identify key parameters that controlled fiber properties. We observed that gelatin wt% played a major role in determining fiber yield, swelling, strength and stability. Other contributing factors included coagulation solution composition, gelatin type, and pre- and post-UV irradiation time. The key factors were then further evaluated individually to achieve a condition that provided a combination of good swelling, mechanical properties and stability. The concentration of the gelatin/HydroThaneTM extrusion solution significantly affected fiber formation and properties, presumably due to the changes in solution viscosity. The effects of pre-UV irradiation were also ascribed to its impact on the solution viscosity and became negligible at higher concentrations when viscosity is mainly controlled by concentration. The composition of the coagulation bath influenced the fiber swelling and wet stress. These results, taken together with our previous studies, suggest that our biomaterial would provide a combination of mechanical and swelling properties suitable for wound dressing applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. JAYARAMAN, M. KOTAKI, Y. ZHANG, X. MO, and S. RAMAKRISHNA, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 4 (2004) 52
Z. MA, M. KOTAKI, R. INAI, and S. RAMAKRISHN, Tissue Eng. 11 (2005) 101
Y. ZHANG, C. T. LIM, S. RAMAKRISHNA, and Z. M. HUANG, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 16 (2005) 933
K. TUZLAKOGLU, C. M. ALVES, J. F. MANO, and R. L. REIS, Macromol. Biosci. 4 (2004) 811
M. LI, M. J. MONDRINOS, M. R. GANDHI, F. K. KO, A. S. WEISS, and P. I. LELKES, Biomaterials 26 (2006) 5999
S. YAMANE, N. IWASAKI, T. MAJIMA, T. FUNAKOSHI, T. MASUKO, K. HARADA, A. MINAMI, K. MONDE, and S. NISHIMURA, Biomaterials 26 (2005) 611
H. BAK, A. AFOKE, A. J. MCLEOD, R. BROWN, P. A. SHAMLOU, and P. DUNNILL, Chem. Eng. Sci. 57 (2002) 913
C.-W. NAM, Y.-H. KIM, and S.-W. KO, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 82 (2001) 1620
L. FAN, Y. DU, R. HUANG, Q. WANG, X. WANG, and L. ZHANG, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 96 (2006) 1625
H. ZHENG, Z. A. TAN, X. JIAN, and R. Z. YUAN, Key Eng. Mater. 249 (2003) 437
Y. ZHANG, H. QUYANG, C. T. LIM, S. RAMAKRISHNA, and Z.-M. HUANG, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 72B (2005) 156
J. J. STANKUS, J. GUAN, and W. R. WAGNER, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 70A (2004) 603
H. T. PENG, L. MARTINEAU, and P. N. SHEK, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 18 (2007) 975
H. T. PENG, M. MOK, L. MARTINEAU, and P. N. SHEK, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 18 (2007) 1025
H. T. PENG, L. MARTINEAU, and P. N. SHEK, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. (accepted for publication)
S. B. LEE, H. W. JEON, Y. W. LEE, Y. M. LEE, K. W. SONG, M. H. PARK, Y. S. NAM, and H. C. AHN, Biomaterials 24 (2003) 2503
S. YOUNG , M. WONG, Y. TABATA, and A. G. MIKOS, J. Control Release 109 (2005) 256
K. B. DJAGNY, Z. WANG, and S. Y. XU, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 41 (2001) 481
R. J. ZDRAHALA and I. J. ZDRAHALA, J. Biomater. Appl. 14 (1999) 67
M. NAGURA, H. YOKOTA, M. IKEURA, Y. GOTOH, and Y. OHKOSHI, Polym. J. 34 (2002) 761
K. GISSELFÄLT, B. EDBERG, and P. FLODIN, Biomacromolecules 3 (2002) 951
M.-S. KHIL, D.-I. CHA, H.-Y. KIM, I.-S. KIM, and N. BHATTARAI, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 67B (2003) 675
R. YANG, R. R. MATHER, and A. F. FOTHERINGHAM, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 96 (2005) 144
Available at http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/pri/section3/pri334.htm accessed April 22, 2005
Available at http://www.me.mtu.edu/~jwsuther/doe/notes/doe_ch10.pdf accessed April 20, 2005
E. MARSANO, M. CANETTI, G. CONIO, P. CORSINI, and G. FREDDI, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 104 (2007) 2187
L. D. BELLINCAMPI and M. G. DUNN, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 63 (1997) 1493
C.-W. NAM, Y.-H. KIM, and S.-W. KO, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 74 (1999) 2258
J. M. GARCIA, E. CHAMBERS IV, Z. MATTA, and M. CLARK, Dysphagia 20 (2005) 325
R. G. MILLER, C. Q. BOWLES, C. C. CHAPPELOW, and J. D. EICK, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 41 (1998) 237
S. H. TEOH, Z. G. TANG, and S. RAMAKRISHNA, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 10 (1999) 343
J. FEI, Z. ZHANG, L. ZHONG, and L. GU, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 85 (2002) 2423
J. S. TSAI and W. C. SU, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 10 (1991) 1253
H. BARANI and S. H. BAHRAMI, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 103 (2007) 2000
I. C. UM, C. S. KI, H. Y. KWEON, K. G. LEE, D. W. IHM, and Y. H. PARK, Intern. J. Biol. Macromol. 34 (2004) 107
S.-W. HA, A. E. TONELLI, and S. M. HUDSON, Biomacromolecules 6 (2005) 1722
http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/pri/section3/eqns/2to6m2.txt accessed November 12, 2004
Available at http://www.isixsigma.com/library/content/c020429a.asp accessed November 12, 2004
M. YUAN, V. R. JOSEPH, and Y. LIN, Technometrics, in press (available at http://www2.isye.gatech.edu/statistics/papers/05-24.pdf accessed May 28, 2007)
Y. S. OH, S. LEE, S. K. MIN, Y. J. SHIN, and B. K. KIM, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 64 (1997) 1937
I. C. UM, H. Y. KWEON, K. G. LEE, D. W. IHM, J.-H. LEE, and Y. H. PARK, Intern. J. Biol. Macromol. 34 (2004) 89
Acknowledgements
The authors are indebted to Ms. Michelle Mok and Mr. Doug Saunders for their expert technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, H.T., Martineau, L. & Hung, A. Hydrogel–elastomer composite biomaterials: 4. Experimental optimization of hydrogel–elastomer composite fibers for use as a wound dressing. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 19, 1803–1813 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-007-3324-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-007-3324-y