Abstract
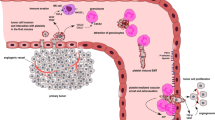
Metastatic dissemination of cancer cells is one of the hallmarks of malignancy and accounts for approximately 90 % of human cancer deaths. Within the blood vasculature, tumor cells may aggregate with platelets to form clots, adhere to and spread onto endothelial cells, and finally extravasate to form metastatic colonies. We have previously shown that sphingolipids play a central role in the interaction of tumor cells with platelets; this interaction is a prerequisite for hematogenous tumor metastasis in at least some tumor models. Here we show that the interaction between melanoma cells and platelets results in rapid and transient activation and secretion of acid sphingomyelinase (Asm) in WT but not in P-selectin-deficient platelets. Stimulation of P-selectin resulted in activation of p38 MAPK, and inhibition of p38 MAPK in platelets prevented the secretion of Asm after interaction with tumor cells. Intravenous injection of melanoma cells into WT mice resulted in multiple lung metastases, while in P-selectin-deficient mice pulmonary tumor metastasis and trapping of tumor cells in the lung was significantly reduced. Pre-incubation of tumor cells with recombinant ASM restored trapping of B16F10 melanoma cells in the lung in P-selectin-deficient mice. These findings indicate a novel pathway in tumor metastasis, i.e., tumor cell mediated activation of P-selectin in platelets, followed by activation and secretion of Asm and in turn release of ceramide and tumor metastasis. The data suggest that p38 MAPK acts downstream from P-selectin and is necessary for the secretion of Asm.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mehlen P, Puisieux A (2006) Metastasis: a question of life or death. Nat Rev Cancer 6:449–458. doi:10.1038/nrc1886
Gasic GJ, Gasic TB, Galanti N, Johnson T, Murphy S (1973) Platelet-tumor-cell interactions in mice. The role of platelets in the spread of malignant disease. Int J Cancer 11:704–718. doi:10.1002/ijc.2910110322
Gasic GJ, Gasic TB, Stewart CC (1968) Antimetastatic effects associated with platelet reduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 61:46–52. doi:10.1073/pnas.61.1.46
Honn KV, Grossi IM, Timar J, Chopra H, Taylor JD (1991) Platelets and Cancer metastasis. In: Orr WF, Buchanan MR, Weiss L (eds) Microcirculation in cancer metastasis, vol 6154. CRC, Taylor & Francis, p 328
Karpatkin S, Pearlstein E (1981) Role of platelets in tumor cell metastases. Ann Intern Med 95:636–641. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-95-5-636
Grossi IM, Fitzgerald LA, Kendall A, Taylor JD, Sloane BF, Honn KV (1987) Inhibition of human tumor cell induced platelet aggregation by antibodies to platelet glycoproteins Ib and IIb/IIIa. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 186:378–383. doi:10.3181/00379727-186-3-rc1
Karpatkin S, Pearlstein E, Ambrogio C, Coller BS (1988) Role of adhesive proteins in platelet tumor interaction in vitro and metastasis formation in vivo. J Clin Invest 81:1012–1019. doi:10.1172/JCI113411
Kimoto M, Ando K, Koike S, Matsumoto T, Jibu T, Moriya H, Kanegasaki S (1993) Significance of platelets in an antimetastatic activity of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Clin Exp Metastasis 11:285–292. doi:10.1007/bf00121171
Kim YJ, Borsig L, Varki NM, Varki A (1998) P-selectin deficiency attenuates tumor growth and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:9325–9330. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.16.9325
Stone JP, Wagner DD (1993) P-selectin mediates adhesion of platelets to neuroblastoma and small cell lung cancer. J Clin Invest 92:804–813. doi:10.1172/JCI116654
Felding-Habermann B, Habermann R, Saldivar E, Ruggeri ZM (1996) Role of beta3 integrins in melanoma cell adhesion to activated platelets under flow. J Biol Chem 271:5892–5900. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.10.5892
Trikha M, Zhou Z, Timar J, Raso E, Kennel M, Emmell E, Nakada MT (2002) Multiple roles for platelet GPIIb/IIIa and alphavbeta3 integrins in tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Cancer Res 62:2824–2833
Amirkhosravi A, Mousa SA, Amaya M, Blaydes S, Desai H, Meyer T, Francis JL (2003) Inhibition of tumor cell-induced platelet aggregation and lung metastasis by the oral GpIIb/IIIa antagonist XV454. Thromb Haemost 90:549–554. doi:10.1267/THRO03030549
Nierodzik ML, Klepfish A, Karpatkin S (1995) Role of platelets, thrombin, integrin IIb–IIIa, fibronectin and von Willebrand factor on tumor adhesion in vitro and metastasis in vivo. Thromb Haemost 74:282–290
Tang DG, Onoda JM, Steinert BW, Grossi IM, Nelson KK, Umbarger L, Diglio CA, Taylor JD, Honn KV (1993) Phenotypic properties of cultured tumor cells: integrin alpha IIb beta 3 expression, tumor-cell-induced platelet aggregation, and tumor-cell adhesion to endothelium as important parameters of experimental metastasis. Int J Cancer 54:338–347. doi:10.1002/ijc.2910540229
Carpinteiro A, Becker KA, Japtok L, Hessler G, Keitsch S, Pozgajova M, Schmid KW, Adams C, Muller S, Kleuser B, Edwards MJ, Grassme H, Helfrich I, Gulbins E (2015) Regulation of hematogenous tumor metastasis by acid sphingomyelinase. EMBO Mol Med 7:714–734. doi:10.15252/emmm.201404571
Carpinteiro A, Beckmann N, Seitz A, Hessler G, Wilker B, Soddemann M, Helfrich I, Edelmann B, Gulbins E, Becker KA (2016) Role of acid sphingomyelinase-induced signaling in melanoma cells for hematogenous tumor metastasis. Cell Physiol Biochem 38:1–14. doi:10.1159/000438604
Schissel SL, Keesler GA, Schuchman EH, Williams KJ, Tabas I (1998) The cellular trafficking and zinc dependence of secretory and lysosomal sphingomyelinase, two products of the acid sphingomyelinase gene. J Biol Chem 273:18250–18259
Theoret JF, Yacoub D, Hachem A, Gillis MA, Merhi Y (2011) P-selectin ligation induces platelet activation and enhances microaggregate and thrombus formation. Thromb Res 128:243–250. doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2011.04.018
Begonja AJ, Geiger J, Rukoyatkina N, Rauchfuss S, Gambaryan S, Walter U (2007) Thrombin stimulation of p38 MAP kinase in human platelets is mediated by ADP and thromboxane A2 and inhibited by cGMP/cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Blood 109:616–618. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-07-038158
Dangelmaier C, Jin J, Daniel JL, Smith JB, Kunapuli SP (2000) The P2Y1 receptor mediates ADP-induced p38 kinase-activating factor generation in human platelets. Eur J Biochem 267:2283–2289. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01235.x
Elstad MR, La Pine TR, Cowley FS, McEver RP, McIntyre TM, Prescott SM, Zimmerman GA (1995) P-selectin regulates platelet-activating factor synthesis and phagocytosis by monocytes. J Immunol 155:2109–2122
Ostrovsky L, King AJ, Bond S, Mitchell D, Lorant DE, Zimmerman GA, Larsen R, Niu XF, Kubes P (1998) A juxtacrine mechanism for neutrophil adhesion on platelets involves platelet-activating factor and a selectin-dependent activation process. Blood 91:3028–3036
Rasheed H, Saeed SA (2004) Involvement of thromboxane A2 and tyrosine kinase in the synergistic interaction of platelet activating factor and calcium ionophore A23187 in human platelet aggregation. Exp Mol Med 36:220–225. doi:10.1038/emm.2004.30
Massberg S, Vogt F, Dickfeld T, Brand K, Page S, Gawaz M (2003) Activated platelets trigger an inflammatory response and enhance migration of aortic smooth muscle cells. Thromb Res 110:187–194. doi:10.1016/s0049-3848(03)00342-6
Muylle L, Joos M, Wouters E, De Bock R, Peetermans ME (1993) Increased tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha), interleukin 1, and interleukin 6 (IL-6) levels in the plasma of stored platelet concentrates: relationship between TNF alpha and IL-6 levels and febrile transfusion reactions. Transfusion 33:195–199. doi:10.1046/j.1537-2995.1993.33393174443.x
Goggel R, Winoto-Morbach S, Vielhaber G, Imai Y, Lindner K, Brade L, Brade H, Ehlers S, Slutsky AS, Schutze S, Gulbins E, Uhlig S (2004) PAF-mediated pulmonary edema: a new role for acid sphingomyelinase and ceramide. Nat Med 10:155–160. doi:10.1038/nm977
Mathias S, Younes A, Kan CC, Orlow I, Joseph C, Kolesnick RN (1993) Activation of the sphingomyelin signaling pathway in intact EL4 cells and in a cell-free system by IL-1 beta. Science 259:519–522. doi:10.1126/science.8424175
Beaulieu LM, Lin E, Mick E, Koupenova M, Weinberg EO, Kramer CD, Genco CA, Tanriverdi K, Larson MG, Benjamin EJ, Freedman JE (2014) Interleukin 1 receptor 1 and interleukin 1beta regulate megakaryocyte maturation, platelet activation, and transcript profile during inflammation in mice and humans. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 34:552–564. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302700
Brooks AC, Menzies-Gow NJ, Wheeler-Jones CP, Bailey SR, Elliott J, Cunningham FM (2009) Regulation of platelet activating factor-induced equine platelet activation by intracellular kinases. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 32:189–196. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2885.2008.01020.x
Hwang SB, Lee CS, Cheah MJ, Shen TY (1983) Specific receptor sites for 1-O-alkyl-2-O-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (platelet activating factor) on rabbit platelet and guinea pig smooth muscle membranes. Biochemistry 22:4756–4763. doi:10.1021/bi00289a022
Schaufelberger HD, Uhr MR, McGuckin C, Logan RP, Misiewicz JJ, Gordon-Smith EC, Beglinger C (1994) Platelets in ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease express functional interleukin-1 and interleukin-8 receptors. Eur J Clin Invest 24:656–663. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2362.1994.tb01057.x
Romiti E, Vasta V, Meacci E, Farnararo M, Linke T, Ferlinz K, Sandhoff K, Bruni P (2000) Characterization of sphingomyelinase activity released by thrombin-stimulated platelets. Mol Cell Biochem 205:75–81
Simon CG Jr, Chatterjee S, Gear AR (1998) Sphingomyelinase activity in human platelets. Thromb Res 90:155–161. doi:10.1016/S0049-3848(98)00033-4
Hannun YA, Newcomb B (2015) A new twist to the emerging functions of ceramides in cancer: novel role for platelet acid sphingomyelinase in cancer metastasis. EMBO Mol Med 7:692–694. doi:10.15252/emmm.201505161
Bianco F, Perrotta C, Novellino L, Francolini M, Riganti L, Menna E, Saglietti L, Schuchman EH, Furlan R, Clementi E, Matteoli M, Verderio C (2009) Acid sphingomyelinase activity triggers microparticle release from glial cells. EMBO J 28:1043–1054. doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.45
Matsuo Y, Amano S, Furuya M, Namiki K, Sakurai K, Nishiyama M, Sudo T, Tatsumi K, Kuriyama T, Kimura S, Kasuya Y (2006) Involvement of p38alpha mitogen-activated protein kinase in lung metastasis of tumor cells. J Biol Chem 281:36767–36775. doi:10.1074/jbc.M604371200
Acknowledgments
We thank F. Witte, S. Moyrer and S. Harde for excellent help with the manuscript, artwork and animal experiments. This study was supported by DFG Grant Gu 335/24-1 to Erich Gulbins.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Research involving animal and human rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Katrin Anne Becker and Nadine Beckmann have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Becker, K.A., Beckmann, N., Adams, C. et al. Melanoma cell metastasis via P-selectin-mediated activation of acid sphingomyelinase in platelets. Clin Exp Metastasis 34, 25–35 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-016-9826-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-016-9826-6