Abstract
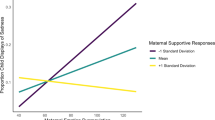
This study examined the intergenerational transmission of psychopathology symptoms with 7–12 year-old children (N = 97; 44 boys, 53 girls, M age = 9.14, SD = 1.38) and their mothers (M age = 38.46, SD = 6.86). Child emotion regulation mediated the links between maternal psychopathology and child internalizing and externalizing symptoms. In turn, the indirect effect was dependent on the level of maternal support in response to youth’s expressions of negative emotions when considering particular constellations of maternal reactions and type of psychopathology symptoms. The findings indicate that the relations between maternal and child psychopathology symptoms and child emotion regulation are complex and vary by context. Regardless of the complexity, however, for both internalizing and externalizing symptoms in youth, the results suggest that building adaptive emotion regulation skills is an important target for prevention among children who are at risk for problems due to exposure to maternal psychopathology.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cummings EM, Davies PT (1994) Maternal depression and child development. J Child Psychol Psychiatr 35:73–112
Leverton TJ (2003) Parental psychiatric illness: the implications for children. Curr Opin Psychiatry 16:395–402
Luoma I, Tamminen T, Kaukonen P, Laippala P, Puura K, Salmelin R et al (2001) Longitudinal study of maternal depressive symptoms and child well-being. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 40:1367–1374
Canino GJ, Bird HR, Rubio-Stipec M, Bravo M (1990) Children of parents with psychiatric disorder in the community. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 29:398–406
Jacobsen T, Miller LJ, Kirkwood KP (1997) Assessing parenting competency in individuals with severe mental illness: a comprehensive service. J Ment Health Adm 24:189–199
Vostanis P, Graves A, Meltzer H, Goodman R, Jenkins R, Brugha T (2006) Relationship between parental psychopathology, parenting strategies and child mental health: findings from the GB national study. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 41:509–514
Ford T, Goodman R, Meltzer H (2004) The relative importance of child, family, school and neighbourhood correlates of childhood psychiatric disorder. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 39:487–496
Ostman M, Hansson L (2002) Children in families with a severely mentally ill member. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 37:243–248
Goodman SH, Gotlib IH (1999) Risk for psychopathology in the children of depressed mothers: a developmental model for understanding mechanisms of transmission. Psychol Rev 106:458–490
Gross HE, Shaw DS, Moilanen KL (2008) Reciprocal associations between boys’ externalizing problems and mothers’ depressive symptoms. J Abnorm Child Psychol 36:693–709
Rutter M, Silberg J, O’Connor T, Simonoff E (1999) Genetics and child psychiatry: I. Advances in quantitative and molecular genetics. J Child Psychol Psychiatr 40:3–18
Rutter M, Silberg J, O’Connor T, Siminoff E (1999) Genetics and child psychiatry: II. Empirical research findings. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 40:19–55
Burt KB, Van Dulmen MHM, Carlivati J, Egeland B, Sroufe LA, Forman DR et al (2005) Mediating links between maternal depression and offspring psychopathology: the importance of independent data. J Child Psychol Psychiatr 46:490–499
Thompson RA (1994) Emotion regulation: a theme in search of definition. Mongr Soc Res Child Dev 59:25
Cicchetti D, Ackerman BP, Izard CE (1995) Emotions and emotion regulation in developmental psychopathology. Dev Psychopathol 7:1–10
Cole PM, Michel MK, O’Donnell Teti L (1994) The development of emotion regulation and dysregulation: a clinical perspective. Mongr Soc Res Child Dev 59:73
Suveg C, Southam-Gerow MA, Goodman KL, Kendall PC (2007) The role of emotion theory and research in child therapy development. Clin Psychol 14:358–371
Malatesta CZ, Haviland JM (1982) Learning display rules: the socialization of emotion expression in infancy. Child Dev 53:991–1003
Bradley S (2000) Affect regulation and the development of psychopathology. The Guilford Press, New York, NY
Knappe S, Beesdo K, Fehm L, Hofler M, Lieb R, Wittchen HU (2009) Do parental psychopathology and unfavorable family environment predict the persistence of social phobia? J Anxiety Disord 23:986–994
Jenkins JM, Oatley K (1998) The development of emotion schemas in children. In: Flack WF, Laird JD (eds) Emotions in psychopathology: theory and research. Oxford University Press, New York, NY, pp 45–56
Suveg C, Zeman J, Flannery-Schroeder E, Cassano M (2005) Emotion socialization in families of children with an anxiety disorder. J Abnorm Child Psychol 33:145–155
Hoffman C, Crnic KA, Baker JK (2006) Maternal depression and parenting: implications for children’s emergent emotion regulation and behavioral functioning. Parent Sci Pract 6:271–295
Suveg C, Zeman J (2004) Emotion regulation in children with anxiety disorders. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol 33:750–759
Southam-Gerow MA, Kendall PC (2002) Emotion regulation and understanding: implications for child psychopathology and therapy. Clin Psychol Rev 22:189–222
Maughan A, Cicchetti D, Toth SL, Rogosch FA (2007) Early-occurring maternal depression and maternal negativity in prediction young children’s emotion regulation and socioemotional difficulties. J Abnorm Child Psychol 35:685–703
Burt KB, Obradovic J, Long JD, Masten AS (2008) The interplay of social competence and psychopathology over 20 years: testing transactional and cascade models. Child Dev 79:359–374
Strauss CC, Lahey BB, Frick P, Frame CL, Hynd GW (1988) Peer social status of children with anxiety disorders. J Consult Clin Psychol 56:137–141
Kraemer HC, Stice E, Kazdin A, Offord D, Kupfer D (2001) How do risk factors work together? Mediators, moderators, and independent, overlapping, and proxy risk factors. Am J Psychiatry 158(6):848–856
Dallaire DH, Pineda AQ, Cole DA, Ciesla JA, Jacquez F, LaGrange B et al (2006) Relation of positive and negative parenting to children’s depressive symptoms. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychology 35:313–322
Masten AS, Shaffer A (2006) How families matter in child development: reflections from research on risk and resilience. In: Clarke-Stewart A, Dunn J (eds) Families count: effects on child and adolescent development. Cambridge University Press, New York, NY, pp 5–25
Cunningham JN, Kliewer W, Garner PW (2009) Emotion socialization, child emotion understanding and regulation, and adjustment in urban African American families: differential associations across child gender. Dev Psychopathol 21(1):261–283
Eisenberg N, Fabes RA, Murphy BC (1996) Parents’ reactions to children’s negative emotions: relations to children’s social competence and comforting behavior. Child Dev 67(5):2227–2247
Garner PW, Jones DC, Miner JL (1994) Social competence among low-income preschoolers: emotion socialization practices and social cognitive correlates. Child Dev 65(2):622–637
Gottman JM, Katz LF, Hooven C (1996) Parental meta-emotion structure and the emotional life of families: theoretical models and preliminary analyses. J Fam Psyhol 19:243–268
Brennan PA, Le Brocque R, Hammen C (2003) Maternal depression, parent–child relationships, and resilient outcomes in adolescence. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 42:1469–1477
Biederman J, Petty C, Hirshfeld-Becker DR, Henin A, Faraone SV, Dang D et al (2006) A controlled longitudinal 5-year follow-up study of children at high and low risk for panic disorder and major depression. Psychol Med 36(8):1141–1152
Burstein M, Ginsburg GS, Tein JU (2010) Parental anxiety and child symptomatology: an examinzation of additive and interactive effects of parent psychopathology. J Abnorm Child Psychol 38:897–909
Burstein M, Stanger C, Kamon J, Dumenci L (2006) Parent psychopathology, parenting, and child internalizing problems in substance-abusing families. Psychol Addict Behav 20:97–106
Marmorstein NR, Malone SM, Iacono WG (2004) Psychiatric disorders among offspring of depressed mothers: associations with paternal psychopathology. Am J Psychiatry 161:1588–1594
Derogatis LR (1994) Symptom Checklist-90-R (SCL-90-R): administration, scoring, and procedures manual. National Computer Systems, Inc, Minneapolis
Shields A, Cicchetti D (1997) Emotion regulation among school-age children: the development and validation of a new criterion Q-sort scale. Dev Psychol 33(6):906–916
Zeman J, Shipman K, Penza-Clyve S (2001) Development and initial validation of the children’s sadness management scale. J Nonverbal Behav 25(3):187–205
Zeman JL, Cassano M, Suveg C, Shipman K (2010) Initial validation of the worry management scale. J Child Fam Stud 19:381–392
Achenbach TM (1991) Manual for the child behavior checklist/4–18 and 1991 profile. Department of Psychiatry, University of Vermont, Burlington
Achenbach TM, Rescorla LA (2001) Manual for the ASEBA school-age forms & profiles. Research Center for Children, Youth and Families, University of Vermont, Burlington
Fabes RA, Eisenberg N, Bernzweig J (1990) The coping with children’s negative emotions scale: description and scoring. Unpublished scale, Department of Family Resources and Human Development, Arizona State University
Eisenberg N, Fabes RA (1994) The relations of emotionality and regulation to children’s anger-related reactions. Child Dev 65(1):109–128
Eisenberg N, Fabes RA, Shepard SA, Guthrie IK, Murphy BC, Reiser M (1999) Parental reactions to children’s negative emotions: longitudinal relations to quality of children’s social functioning. Child Dev 70:513–534
Fabes RA, Leonard SA, Kupanoff K, Martin CL (2001) Parental coping with children’s negative emotions: relations with children’s emotional and social responding. Child Dev 72(3):907
Fabes RA, Poulin RE, Eisenberg N, Madden-Derdich DA (2002) The coping with children’s negative emotions scale (CCNES): psychometric properties and relations with children’s emotional competence. Marriage Fam Rev 34(3–4):285–310
DeBoard-Lucas RL, Fosco GM, Raynor SR, Grych JH (2010) Interparental conflict in context: exploring relations between parenting processes and children’s conflict appraisals. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol 39:163–175
Nelson JA, O’Brien M, Blankson N, Calkins SD, Keane SP (2009) Family stress and parental responses to children’s negative emotions: tests of the spillover, crossover, and compensatory hypotheses. J Fam Psychol 5:671–679
Preacher KJ, Hayes AF (2004) SPSS and SAS procedures for estimating indirect effect in simple mediation models. Behav Res Methods Instrum Comput 36:717–731
Preacher KJ, Rucker DD, Hayes AF (2007) Addressing moderated mediation hypotheses: theory, methods, and prescriptions. Multivar Behav Res 42:185–227
Eisenberg N, Cumberland A, Spinrad TL (1998) Parental socialization of emotion. Psychol Inq 94:241–273
Dodge K, Prince J, Newman J (1990) Hostile attribution biases in severely aggressive adolescents. Abnorm Child Psych 99:385–392
Lansford JE, Deater-Deckard K, Dodge KA, Bates JE, Pettit GS (2004) Ethnic differences in the link between physical discipline and later adolescent externalizing behaviors. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 45:801–812
Laird RD, Jordan KY, Dodge KA, Petitt GS, Bates JE (2001) Peer rejection in childhood, involvement with antisocial peers in early adolescence, and the development of externalizing behavior problems. Dev Psychopathol 13:337–354
Shortt J, Stoolmiller M, Smith-Shine JN, Eddy MJ, Sheeber L (2010) Maternal emotion coaching, adolescent anger regulation, and siblings externalizing symptoms. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 51:799–808
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the University of Georgia Research Foundation and William A. and Barbara R. Owens Institute for Behavioral Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suveg, C., Shaffer, A., Morelen, D. et al. Links Between Maternal and Child Psychopathology Symptoms: Mediation Through Child Emotion Regulation and Moderation Through Maternal Behavior. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 42, 507–520 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-011-0223-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-011-0223-8