Abstract
Objects
Hepatic and pancreatic fat content become increasingly important for phenotyping of individuals with metabolic diseases. This study aimed to (1) evaluate hepatic fat fractions (HFF) and pancreatic fat fractions (PFF) using 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) and the recently introduced fast mDixon method, and to examine body fat effects on HFF and PFF, (2) investigate regional differences in HFF and PFF by mDixon.
Materials and methods
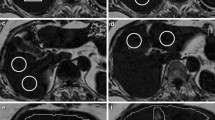
HFF and PFF were quantified by mDixon with two flexible echo times and by single voxel 1H MRS in 24 healthy subjects. The regional differences of PFF within the pancreas were assessed with mDixon. Abdominal visceral and subcutaneous fat was assessed by T1-weighted MRI at 3T.
Results
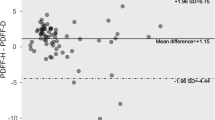
Both methods correlated well for quantification of HFF (r = 0.98, p < 0.0001) and PFF (r = 0.80, p < 0.0001). However, mDixon showed a higher low limit in HFF and PFF. PFF showed no regional differences using mDixon. In addition, both visceral and subcutaneous fat correlated with pancreatic fat, while only visceral fat correlated with liver fat, employing both 1H MRS and mDixon.
Conclusion
The novel and fast two-point mDixon exhibits a good correlation with the gold-standard 1H MRS for assessment of HFF and PFF, with limited sensitivity for assessing lower fat content.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krssak M, Petersen KF, Dresner A, DiPietro L, Vogel SM, Rothman DL, Roden M, Shulman GI (1999) Intramyocellular lipid concentrations are correlated with insulin sensitivity in humans: a 1H NMR spectroscopy study. Diabetologia 42:113–116
Hu HH, Nayak KS, Goran MI (2010) Assessment of abdominal adipose tissue and organ fat content by magnetic resonance imaging. Obesity 18:841–847
Thomsen C, Becker U, Winkler K (1994) Quantification of liver fat using magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Magn Reson Imaging 12:487–495
Sijens PE, Edens MA, Bakker SJL, Stolk RP (2010) MRI-determined fat content of human liver, pancreas and kidney. World J Gastroenterol 28(16):1993–1998
Szczepaniak LS, Nurenberg P, Leonard D, Browning JD, Reingold JS, Grundy S, Hobbs HH, Dobbins RL (2005) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy to measure hepatic triglyceride content: prevalence of hepatic steatosis in the general population. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 288:E462–E468
Dixon WT (1984) Simple proton spectroscopic imaging. Radiology 153:189–194
Ma J (2008) Dixon techniques for water and fat imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 28:543–558
Kim H, Taksali SE, Dufour S, Befroy D, Goodman TR, Petersen KF et al (2008) A Comparative MR study of hepatic fat quantification using single-voxel proton spectroscopy, two-point Dixon and three-point IDEAL. Magn Reson Med 59(3):521–527
Ma X, Holalkere NS, Kambadakone AR, Kenudson MN, Hahn PF, Sahani DV (2009) Imaging-based quantification of hepatic fat: methods and clinical applications. Radio Graphics 29:1253–1280
Xiang QS (2006) Two-point water–fat imaging with partially-opposed-phase (POP) acquisition: an asymmetric Dixon method. Magn Reson Med 56:572–584
Reeder SB, Wen Z, Yu H, Pineda AR, Gold GE, Markl M, Pelc NJ (2004) Multicoil Dixon chemical species separation with an iterative least squares estimation method. Magn Reson Med 51:35–45
Ma J (2004) Breath-hold water and fat imaging using a dual-echo two-point Dixon technique with an efficient and robust phase-correction algorithm. Magn Reson Med 52:415–419
Eggers H, Brendel B, Duijndam A, Herigault G (2011) Dual-echo Dixon imaging with flexible choice of echo times. Magn Reson Med 65:96–107
Berglund J, Ahlström H, Johansson L, Kullberg J (2011) Two-point Dixon method with flexible echo times. Magn Reson Med 65:994–1004
van Raalte DH, van der Zijl NJ, Diamant M (2010) Pancreatic steatosis in humans: cause or marker of lipotoxicity? Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 13:478–485
Heni M, Machann J, Staiger H, Schwenzer NF, Peter A, Schick F, Claussen CD, Stefan N, Häring HU, Fritsche A (2010) Pancreatic fat is negatively associated with insulin secretion in individuals with impaired fasting glucose and/or impaired glucose tolerance: a nuclear magnetic resonance study. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 26(3):200–205
Schwenzer NF, Machann J, Martirosian P, Stefan N, Schraml C, Fritsche A, Claussen CD, Schick F (2008) Quantification of pancreatic lipomatosis and liver steatosis by MRI: comparison of in/opposed-phase and spectral–spatial excitation techniques. Invest Radiol 43:330–337
Tushuizen ME, Bunck MC, Pouwels PJ, Bontemps S, van Waesberghe JH, Schindhelm RK et al. (2007) Pancreatic fat content and β-cell function in men with and without Type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 30:2916–2921
Lingvay L, Esser V, Legendre JL, Price AL, Wertz KM, Adams-Huet B, Zhang S, Unger RH, Szczepaniak LS (2009) Noninvasive quantification of pancreatic fat in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:4070–4076
van der Zijl NJ, Goossens GH, Moors CCM, van Raalte DH, Muskiet MHA, Pouwels PJW, Blaak EE, Diamant M (2011) Ectopic fat storage in the pancreas, liver, and abdominal fat depots: impact on cell function in individuals with impaired glucose metabolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:459–467
Le KA, Ventura EE, Fischer JQ, Weigensberg MJ, Punyanitya M, Hu HH, Nayak KS, Goran MI (2011) Ethnic differences in pancreatic fat accumulation and its relationship with other fat depots and inflammatory markers. Diabetes Care 34:485–490
Kovanlikaya A, Mittelman SD, Ward A, Geffner ME, Dorey F, Gilsanz V (2005) Obesity and fat quantification in lean tissues using three-point Dixon MR imaging. Pediatr Radiol 35:601–607
Nguyen-Duy EB, Nichaman MZ, Church TS, Steven N (2003) Visceral fat and liver fat are independent predictors of metabolic risk factors in men. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 284:E1065–E1071
Hwang J-H, Stein DT, Barzilai N, Cui M-H, Tonelli J, Kishore P, Hawkins M (2007) Increased intrahepatic triglyceride is associated with peripheral insulin resistance: in vivo MR imaging and spectroscopy studies. Am J Physiol Endo Metab 293:E1663–E1669
Machann J, Thamer C, Schnoedt B, Stefan N, Häring H-U, Claussen CD, Fritsche A, Schick F (2006) Hepatic lipid accumulation in healthy subjects: a comparative study using spectral fat-selective MRI and volume-localized 1H-MR spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med 55:913–917
Gruetter R (1993) Automatic, localized in vivo adjustment of all first- and second-order shim coils. Magn Reson Med 29:804–811
Machann J, Thamer C, Stefan N, Schwenzer NF, Kantartzis K, Häring H-U, Claussen CD, Fritsche A, Schick F (2010) Follow-up whole-body assessment of adipose tissue compartments during a lifestyle intervention in a large cohort at increased risk for type 2 diabetes. Radiology 2:353–363
Hamilton G, Yokoo T, Bydder M, Cruite I, Schroeder ME, Sirlin CB, Middleton MS (2011) In vivo characterization of the liver fat 1H MR spectrum. NMR Biomed 24:784–790
Hu HH, Börnert P, Hernando D, Kellman P, Ma J, Reeder S, Sirlin C (2012) ISMRM workshop on fat–water separation: insights, applications and progress in MRI. Magn Reson Med 68(2):378–388
Yashima Y, Isayama H, Tsujino T, Nagano R, Yamamoto K, Mizuno S, Yagioka H, Kawakubo K, Sasaki T, Kogure H, Nakai Y, Hirano K, Sasahira N, Tada M, Kawabe T, Koike K, Omata M (2011) A large volume of visceral adipose tissue leads to severe acute pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol 46:1213–1218
Netter FH (1970) The CIBA collection of medical illustrations: endocrine system and selected metabolic diseases. CIBA, New York
Krssák M, Hofer H, Wrba F, Meyerspeer M, Brehm A, Lohninger A, Steindl-Munda P, Moser E, Ferenci P, Roden M (2010) Non-invasive assessment of hepatic fat accumulation in chronic hepatitis C by 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Eur J Radiol 74:e60–e66. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2009.03.062
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Ministry of Innovation, Science and Research (MIWFT) of the State of North Rhine-Westphalia for the installation of a 3-T whole body MR scanner at the German Diabetes Center (M. Roden). This work was supported in part by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) to the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD e.V.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Livingstone, R.S., Begovatz, P., Kahl, S. et al. Initial clinical application of modified Dixon with flexible echo times: hepatic and pancreatic fat assessments in comparison with 1H MRS. Magn Reson Mater Phy 27, 397–405 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-013-0421-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-013-0421-4