Abstract:
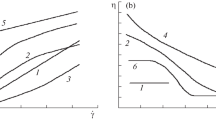
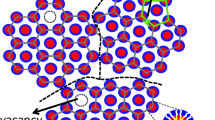
We investigate the rheological properties of a cubic fcc phase of micelles obtained by aggregation of a triblock copolymer (PEO)127(PPO)48(PEO)127 in water as selective solvent. The resulting soft solid is submitted to a range of stresses varying from 20 to 800Pa in Couette geometry. Creep and flow behaviour can be distinguished and interpreted in terms of structural changes previously observed by SAXS under flow. Contrasting with other systems, no discontinuity in the flow behaviour is associated with the structural changes. The strong shear thinning is interpreted from the scattering data, as resulting from the nucleation of a new structure of hexagonal compact planes parallel to the Couette walls. This creates a lubricating domain in the gap, whose size grows with the applied shear rate. We argue moreover that the very existence of flow (as a steady state opposed to creep) is associated with this so-called layer-sliding structure in a fraction, however small, of the sample.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received on 4 June 1999 and Received in final form 6 September 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eiser, E., Molino, F. & Porte, G. Correlation between the viscoelastic properties of a soft crystal and its microstructure. Eur. Phys. J. E 2, 39–46 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s101890050038
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s101890050038