Abstract:
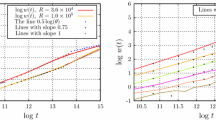
Two types of mechanisms are proposed for mound coarsening during unstable epitaxial growth: stochastic, due to deposition noise, and deterministic, due to mass currents driven by surface energy differences. Both yield the relation H=(RWL)2 between the typical mound height W, mound size L, and the film thickness H. An analysis of simulations and experimental data shows that the parameter R saturates to a value which discriminates sharply between stochastic (\(R \simeq 1\)) and deterministic (\(R \ll 1\)) coarsening. We derive a scaling relation between the coarsening exponent 1/z and the mound-height exponent \(\beta \) which, for a saturated mound slope, yields \(\beta = 1/z = 1/4\).
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 11 November 1997 / Revised in final form: 28 November 1997 / Accepted: 28 November 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, LH., Smilauer, P. & Vvedensky, D. Noise-assisted mound coarsening in epitaxial growth. Eur. Phys. J. B 2, 409–412 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100510050264
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100510050264