Abstract
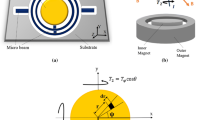
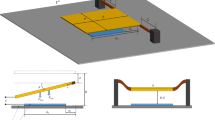
For the case of micro/nano-scale structures, it is well-known that the physico-mechanical behavior of such devices is size-dependent. However, the classical continuum theory cannot correctly predict the size-dependency. In this paper, the modified couple stress theory is employed to examine the instability characteristics of scanner-type nano-mirrors with circular geometry. The governing equation of the scanner is derived incorporating the effects of electrostatic Coulomb and corrected Casimir forces with the consideration of the finite conductivity of interacting surfaces. In addition, to investigate the influence of air damping, a modified nonlinear expression for the squeeze film model is proposed. The influences of vacuum fluctuation, applied voltage, nonlinear damping and length scale parameter on the dynamic instability of equilibrium points are studied by plotting the phase portrait and bifurcation diagrams. It is concluded from the obtained results that the Casimir attraction reduces the instability threshold of the nano-systems. The small-scale parameter and the nonlinear squeeze film damping enhance the torsional stability. In the presence of the applied voltage, the phase portrait shows the saddle-node bifurcation while for free-standing scanner a subcritical pitchfork bifurcation is observed.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdi J, Koochi A, Kazemi AS, Abadyan M (2011) Modeling the effects of size dependence and dispersion forces on the pull-in instability of electrostatic cantilever NEMS using modified couple stress theory. Smart Mater Struct 20:055011
Batra RC, Porfiri M, Spinello D (2007) Effects of Casimir force on pull-in instability in micromembranes. Europhys Lett 77(2):20010
Batra RC, Porfiri M, Spinello D (2008) Reduced-order models for microelectromechanical rectangular and circular plates incorporating the Casimir force. Int J Solids Struct 45(11–12):3558–3583
Bezerra VB, Klimchitskaya GL, Romero C (1997) Casimir force between a flat plate and a spherical lens: application to the results of a new experiment. Mod Phys Lett A 12(34):2613–2622
Bukes E, Roukes ML (2001) Stiction, adhesion energy, and the Casimir effect in micromechanical systems. Phys Rev B 63:033402
Capasso F, Munday JN, Lannuzzi D, Chan HB (2007) Casimir forces and quantum electrodynamical torques: physics and nanomechanics. IEEE J Select Top Quantum Electron 13:400–414
Chang KM, Lee SC, Li SH (2002) Squeeze film damping effect on a MEMS torsion mirror. J Micromech Microeng 12:556–561
Daqaq MF, Abdel-Rahman EM, Nayfeh AH (2008) Towards a stable low-voltage torsional microscanner. Microsyst Technol 14:725–737
Degani O, Nemirovsky Y (2002) Design considerations of rectangular electrostatic torsion actuators based on new analytical pull-in expressions. J Microelectromech Syst 11:20–26
Duan JS, Rach R (2013) A pull-in parameter analysis for the cantilever NEMS actuator model including surface energy, fringing field and Casimir effects. Int J Solids Struct 50(22–23):3511–3518
Eringen AC (1983) On differential equations of nonlocal elasticity and solutions of screw dislocation and surface waves. J Appl Phys 54:4703–4710
Fathalilou M, Sadeghi M, Rezazadeh G (2014) Gap dependent bifurcation behavior of a nano-beam subjected to a nonlinear electrostatic pressure. Lat Am J Solids Struct 11(13):2426–2443
Ford JE, Aksyuk VA, Bishop DJ, Walker JA (1999) Wavelength add-drop switching using tilting micromirrors. J Lightwave Technol 17:904–911
Ghadiri M, Shafiei N (2016) Vibration analysis of rotating functionally graded Timoshenko microbeam based on modified couple stress theory under different temperature distributions. Acta Astronautica 121:221–240
Guo JG, Zhao YP (2004) Influence of van der Waals and Casimir forces on electrostatic torsional actuators. J Microelectromech Syst 13(6):1027–1035
Guo JG, Zhao YP (2006) Dynamic stability of electrostatic torsional actuators with van der Waals effect. Int J Solids Struct 43:675–685
Guo JG, Zhou LJ, Zhao YP (2009) Instability analysis of torsional MEMS/NEMS actuators under capillary force. J Colloid Interface Sci 331:458–462
Hamid Zeighampour Y, Tadi Beni Y (2014) Cylindrical thin-shell model based on modified strain gradient theory. Int J Eng Sci 78:27–47
Hargreaves CM (1965) Corrections to the related dispersion force between metal bodies. In: Proceedings of the Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie van Wetenschappen, 68231
Huang JM, Liu AQ, Deng ZL, Zhang QX, Ahn J, Asundi A (2004) An approach to the coupling effect between torsion and bending for electrostatic torsional micromirrors. Sens Actuators A 115:159–167
Jazar RN (2012) Nonlinear modeling of squeeze-film phenomena in microbeam MEMS. Nonlinear Approaches Eng Appl 41–68
Khatami F, Rezazadeh G (2009) Dynamic response of a torsional micromirror to electrostatic force and mechanical shock. Microsyst Technol 15:535–545
Kong S, Zhou S, Nie Z, Wang K (2009) Static and dynamic analysis of micro beams based on strain gradient elasticity theory. Int J Eng Sci 47:487–498
Lam DCC, Yang F, Chong ACM, Wang J, Tong P (2003) Experiments and theory in strain gradient elasticity. J Mech Phys Solids 51(8):1477–1508
Lambrecht A, Jaekel MT, Reynaud S (1997) The Casimir force for passive mirrors. Phys Lett A 225:164–188
Lamoreaux SK (1999) Calculation of the Casimir force between imperfectly conducting plates. Phys Rev A 59(5):3149–3153
Lamoreaux SK (2005) The Casimir force: background, experiments, and applications. Rep Prog Phys 68:201–236
Lin WH, Zhao YP (2003) Dynamics behavior of nanoscale electrostatic actuators. Chin Phys Lett 20:2070–2073
Lin WH, Zhao YP (2005a) Casimir effect on the pull-in parameters of nanometer switches. Microsyst Technol 11:80–85
Lin WH, Zhao YP (2005b) Nonlinear behavior for nanoscale electrostatic actuators with Casimir force. Chaos Solitons Fractals 23:1777–1785
Lin WH, Zhao YP (2007a) Stability and bifurcation behaviour of electrostatic torsional NEMS varactor influenced by dispersion forces. J Phys D Appl Phys 40:1649
Lin WH, Zhao YP (2007b) Influence of damping on the dynamical behavior of the electrostatic parallel-plate and torsional actuators with intermolecular forces. Sensors 7:3012–3026
Lyshevski SE (2003) Nano- and microelectromechanical systems, fundamentals of nano- and microengineering. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Ma HM, Gao XL, Reddy JN (2008) A microstructure-dependent Timoshenko beam model based on a modified couple stress theory. J Mech Phys Solids 56(12):3379–3391
Milanovis V, Castelino K (2004) sub-100 ms setting time and low voltage operation foe gimbal-less two axis scanners. IEEE/LEOS optical MEMS 2004, Takamatsu, Japan
Mobki H, Rezazadeh G, Sadeghi M, Vakili-Tahami F, Seyyed-Fakhrabadi M (2013) A comprehensive study of stability in an electro-statically actuated micro-beam. Int J Non-Linear Mech 48:78–85
Mobki H, Sadeghi MH, Rezazadeh G, Fathalilou M, Keyvani-Janbahan A (2014) Nonlinear behavior of a nano-scale beam considering length scale-parameter. Appl Math Model 38(5–6):1881–1895
Noruzifar E, Emig T, Zandi R (2011) Universality versus material dependence of fluctuation forces between metallic wires. Phys Rev A 84:042501
Ouakad HM, Younis MI (2010) Nonlinear dynamics of electrically actuated carbon nanotube resonators. J Comput Nonlinear Dyn 5:011009
Ouakad HM, Younis MI (2011) Natural frequencies and mode shapes of initially curved carbon nanotube resonators under electric excitation. J Sound Vib 330:3182–3195
Park SK, Gao XL (2006) Bernoulli–Euler beam model based on a modified couple stress theory. J Micromech Microeng 16:2355–2359
Rezazadeh G, Khatami F, Tahmasebi A (2007) Investigation of the torsion and bending effects on static stability of electrostatic torsional micromirrors. Microsyst Technol 13:715–722
Rodriguez AW, Capasso F, Johnson SG (2011) The casimir effect in microstructured geometries. Nat Photon 5:211–221
Sattler R, Plotz F, Fattinger G, Wachutka G (2002) Modeling of electrostatic torsional actuator: demonstrated with an RF MEMS switch. Sens Actuators A 97–98:337–346
Sedighi HM, Shirazi KH (2015) Dynamic pull-in instability of double-sided actuated nano-torsional switches. Acta Mech Solida Sin 28(1):91–101
Shabani R, Tariverdilo S, Rezazadeh G, Agdam AP (2011) Nonlinear vibrations and chaos in electrostatic torsional actuators. Nonlinear Anal: Real World Appl 12:3572–3584
Starr J (1990) Squeeze-film damping in solid-state accelerometers. Proc Solid-State Sens Actuators Workshop 44–47
Tadi Beni Y, Koochi A, Abadyan M (2011) Theoretical study of the effect of Casimir force, elastic boundary conditions and size dependency on the pull-in instability of beam-type NEMS. Physica E 43:979–988
Tadi Beni Y, Koochi A, Kazemi AS, Abadyan M (2012) Modeling the influence of surface effect and molecular force on pull-in voltage of rotational nano–micro mirror using 2-DOF model. Can J Phys 90(10):963–974
Tadi Beni Y, Mehralian F, Razavi H (2015) Free vibration analysis of size-dependent shear deformable functionally graded cylindrical shell on the basis of modified couple stress theory. Compos Struct 120:65–78
Taghizadeh M, Mobki H (2014) Bifurcation analysis of torsional micromirror actuated by electrostatic forces. Archives Mech 66(2):95–111
Tang TL, Fang W (2011) Magnetostatic torsional actuator with embedded nickel structures for the improvement of driving force and wobble motion. J Micromech Microeng 21:095007
Tsiatas GC, Katsikadelis JT (2011a) A new microstructure-dependent SainteVenant torsion model based on a modified couple stress theory. Eur J Mech A Solids 30:741–747
Tsiatas GC, Katsikadelis JT (2011b) A new microstructure-depen dent SainteVenant torsion model based on a modified couple stress theory. Eur J Mech. A-Solid 30(5):741–747
Venkatesh C, Bhat N (2008) Reliability analysis of torsional MEMS varactor. IEEE Trans Device Mater Reliab 8(1):129–134
Venkatesh C, Pati S, Bhat N, Pratap R (2005) A torsional MEMS varactor with wide dynamic range and low actuation voltage. Sens Actuators A: Phys 121(2):480–487
Venkatesh C, Bhat N, Vinoy KJ, Grandhi S (2012) Microelectromechanical torsional varactors with low parasitic capacitances and high dynamic range. J Micro/Nanolithography MEMS MOEMS 11(1):013006
White A (2002) Review of some current research in microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) with defence applications, DSTO Aeronautical and Maritime Research Laboratory, Fishermans Bend Vic, Australia, 10
Xiang W, Lee C (2010) Nanoelectromechanical torsion switch of low operation voltage for nonvolatile memory application. Appl Phys Lett 96:193113
Xiao ZX, Wu XT, Peng WY, Farmer KR (2001) An angle-based design approach for rectangular electrostatic torsion actuators. J Microelectromech Syst 10:561–568
Yan D, Lal A (2006) The squeeze film damping effect of perforated microscanners: modeling and characterization. Smart Mater Struct 15:480–484
Yang F, Chong ACM, Lam DCC, Tong P (2011) Couple stress based strain gradient theory for elasticity. Int J Solids Struct 39(10):2731–2743
Younis JM (1993) Mirrors on a chip. IEEE Spectr 30(11):27–31
Younis MI, Alsaleem F, Jordy D (2007) The response of clamped–clamped microbeams under mechanical shock. Int J Non-Linear Mech 42(4):643–657
Zeighampour H, Tadi Beni Y (2015) Free vibration analysis of axially functionally graded nanobeam with radius varies along the length based on strain gradient theory. Appl Math Model 39(18):5354–5369
Zhang XM, Chau FS, Quan C, Lam YL, Liu AQ (2001) A study of the static characteristics of a torsional micromirror. Sens Actuators A 90:73–81
Zhang C, Xu G, Jiang Q (2004) Characterization of the squeeze-film damping effect on the quality factor of a microbeam resonator. J Micromech Microeng 14:1302–1306
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sedighi, H.M., Moory-Shirbani, M., Koochi, A. et al. A modified model for circular scanner-type nano-mirrors with size-dependency, squeeze film damping and Casimir effects by considering finite conductivity. Microsyst Technol 23, 875–888 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-2852-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-2852-0