Abstract
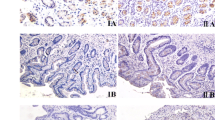
Evidence suggests that the carcinogenic process guided by Helicobacter pylori is related to the expression of cell cycle and apoptosis proteins as BCL-2, BAX, and MYC. However, the literature is conflicting regarding the expression frequency in the histological subtypes and did not consider cagA gene presence. To investigate the expression of these proteins considering the histological subtypes of gastric cancer associated with H. pylori (cagA), a total of 89 cases were used. H. pylori infection and cagA status were determined by PCR. Immunodetection was performed for MYC, BCL-2, and BAX proteins. H. pylori was found in 95.5% of the patients, among them, 65.8% were cagA(+). Nuclear MYC was detected in 36.4%, BAX in 55.7%, while BCl-2 in just 5%. Nuclear MYC staining was significantly lower in the intestinal than diffuse subtype (p = 0.008) and was related with the presence of H. pylori cagA(+). Additionally, most of the few cases cytoplasmic MYC positive were in the intestinal subtype. In diffuse tumors, although most nuclear MYC positive cases were cagA(+), it was not significant. No difference was observed between BCL-2 or BAX expression considering the presence of cagA gene in the histological subtypes. It seems that MYC could be relevant for the diffuse tumorigenic pathway associated with H. pylori and possibly influenced by the presence of cagA gene, while in intestinal tumors, the tumorigenic pathway does not occur through the MYC expression.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Costa-Raiol L, Figueira-Silva E, Mendes-da-Fonseca D, Leal M, Guimarães A, Calcagno D, Khayat A, Assumpção P, Smith M, Burbano R (2008) Interrelationship between MYC gene numerical aberrations and protein expression in individuals from northern Brazil with early gastric adenocarcinoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 181:31–35
Hatakeyama M (2009) Helicobacter pylori and gastric carcinogenesis. J Gastroenterol 44:239–248
Lauren P (1965) The two histological main types of gastric carcinoma: diffuse and so-called intestinal-type carcinoma. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand 64:31–49
Kountouras J, Zavos C, Chatzopoulos D, Katsinelos P (2008) New aspects of Helicobacter pylori infection involvement in gastric oncogenesis. J Surg Res 146:149–158
Calcagno D, Leal M, Assumpcao P, Smith M, Burbano R (2008) MYC and gastric adenocarcinoma carcinogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 14:5962–5968
Alves M, Lima V, André A, Ferreira M, Barros M, Rabenhorst S (2010) p27(KIP1) expression in gastric cancer: differential pathways in the histological subtypes associated with Helicobacter pylori infection. Scand J Gastroenterol 45:409–420
Bir F, Calli-Dermikan N, Tufan-Akbulut A, Satiroglu-Tufan N (2007) Apoptotic cell death and its relationship to gastric carcinogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 13:3183–3188
Wang C, Yuan Y, Hunt R (2007) The association between Helicobacter pylori infection and early gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol 102:1789–1798
Wen S, Moss S (2009) Helicobacter pylori virulence factors in gastric carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett 282:1–8
Atherton J, Cao P, Peek R, Tummuru M, Blaser M, Cover T (1995) Mosaicism in vacuolating cytotoxin alleles of Helicobacter pylori. Association of specific vacA types with cytotoxin production and peptic ulceration. J Biol Chem 270:17771–17777
Ashktorab H, Frank S, Khaled R, Durum S, Kifle B, Smoot D (2004) Bax translocation and mitochondrial fragmentation induced by Helicobacter pylori. Gut 53:805–813
van der Woude C, Kleibeuker J, Tiebosch A, Homan M, Beuving A, Jansen P, Moshage M (2003) Diffuse and intestinal type gastric carcinomas differ in their espression of apoptosis related proteins. J Clin Pathol 56:699–702
Lee H, Lee H, Yang H, Kim W, Lee K, Choe K, Kim J (2003) Prognostic significance of Bcl-2 and p53 expression in gastric cancer. Int J Coloretal Dis 18:518–525
Xu A, Li S, Liu J, Gan A (2001) Function of apoptosis and expression of the proteins Bcl-2, p53 and C-myc in the development of gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 7:403–406
Liu H, Liu W, Fang D, Men R (1998) Expression of bcl-2 protein in gastric carcinoma and its significance. World J Gastroenterol 4:228–230
Pelengaris S, Khan M, Evan G (2002) c-MYC: more than just a matter of life and death. Nat Rev Cancer 2:764–776
Calcagno D, Leal M, Seabra A, Khayat A, Chen E, Demachki S, Assumpção P, Faria M, Rabenhorst S, Ferreira M, Smith M, Burbano R (2006) Interrelationship between chromosome 8 aneuploidy, C-MYC amplification and increased espression in individuals from northern Brazil with gastric adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 12:6207–6211
Pelengaris S, Khan M (2003) The many faces of c-MYC. Arch Biochem Biophys 416:129–136
Faria M, Patrocínio R, Moraes-Filho M, Rabenhorst S (2006) Expressão das proteínas BCL-2 e BAX em tumores astrocíticos humanos. Jornal Brasileiro de Patologia e Medicina Laboratorial 4:271–278
Zhang G, Gu Y, Zhao Z, Xu S, Zhang H, Wang H, Hao B (2004) Coordinate increase of telomerase activity and c-Myc expression in Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric diseases. World J Gastroenterol 10:1759–1762
Foster G, Twell D (eds) (1996) Plant gene isolation: principles and practice. Wiley, New York
Lage A, Godfroid E, Fauconnier A, Burette A, Butzler J, Bollen A, Glupczynski Y (1995) Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection by PCR: comparison with other invasive techniques and detection of cagA gene in gastric biopsy specimens. J Clin Microbiol 33:2752–2756
Domingo D, Alarcon T, Prieto N, Sanchez I, Lopez-Brea M (1999) cagA and vacA status of Spanish Helicobacter pylori clinical isolates. J Clin Microbiol 37:2113–2114
Lima V, Lima M, André A, Ferreira M, Barros M, Rabenhorst S (2008) H pylori (Cag A) and Epstein-Barr vírus infection in gastric carcinomas: correlation with p53 mutation and c-Myc, Bcl-2 and Bax expression. World J Gastroenterol 14:884–891
Thomazini C, Pinheiro N, Pardini M, Naresse L, Rodrigues M (2006) Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: distribution of cagA and vacA genotypes in patients with gastric carcinoma. J Bras Patol Med Lab 42:25–30
Saribasak H, Salih B, Yamaoka Y, Sander E (2004) Analysis of Helicobacter pylori genotypes and correlation with clinical outcome in Turkey. J Clin Microbiol 42:1648–1651
Nomura A, Stemmermann G, Chyou P, Kato I, Perez-Perez G, Blaser M (1991) Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric carcinoma among Japanese Americans in Hawaii. N Engl J Med 325:1132–1136
Yu J, Leung W, Ng E, To K, EbertM Go M, Chan W, Chan F, Chung S, Malfertheiner P, Sung J (2001) Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on expression of cyclin D2 and p27 in gastric intestinal metaplasia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 15:1505–1511
Eguchi H, Herschenhous N, Kuzushita N, Moss S (2003) Helicobacter pylori increases proteasome-mediated degradation of p27kip1 in gastric epithelial cells. Cancer Res 63:4739–4746
Kim S, Meitner P, Konkin T, Cho Y, Resnick M, Moss S (2006) Altered expression of Skp2, c-Myc and p27 proteins but not mRNA after H. pylori eradication in chronic gastritis. Mod Pathol 19:49–58
André A, Ferreira M, Mota R, Ferrasi A, Pardini M, Rabenhorst S (2010) Gastric adenocarcinoma and Helicobacter pylori: correlation with p53 mutation and p27 immunoexpression. Cancer Epidemiol 34:618–625
Konturek P, Pierzchalski P, Konturek S, Meixner H, Faller G, Kirchner T, Hahn E (1999) Helicobacter pylori induces apoptosis in gastric mucosa through an upregulation of Bax expression in humans. Scand J Gastroenterol 34:375–383
Konturek P, Konturek S, Sulekova Z, Meixner H, Bielanski W, Starzynska T, Karczewska E, Marlicz K, Stachura J, Hahn E (2001) Expression of hepatocyte growth factor, transforming growth factor alpha, apoptosis related proteins Bax and Bcl-2, and gastrin in human gastric cancer. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 15:989–999
Yang Y, Deng C, Peng J, Wong B, Lam S, Xia H (2003) Effect of Helicobacter pylori on apoptosis and apoptosis related genes in gastric cancer cells. Mol Pathol 56:19–24
Cabral M, Mendes C, Castro L, Cartelle C, Guerra J, Queiroz D, Nogueira A (2006) Apoptosis in Helicobacter pylori gastritis is related to cagA status. Helicobacter 11:469–476
Zhu Y, Wang C, Huang J, Ge Z, Dong Q, Zhong X, Su Y, Zheng S (2007) The Helicobacter pylori virulence factor CagA promotes Erk1/2-mediated Bad phosphorylation in lymphocytes: a mechanism of CagA-inhibited lymphocyte apoptosis. Cell Microbiol 9:952–961
Ding S, O’Hara A, Denning T, Dirden-Kramer B, Mifflin R, Reyes V, Ryan K, Elliott S, Izumi T, Boldogh I, Mitra S, Ernst P, Crowe S (2004) Helicobacter pylori and H2O2 increase AP endonuclease-1/redox factor-1 in human gastric epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 127:845–858
Kim HK, Choi IJ, Kim CG, Kim HS, Oshima A, Yamada Y, Arao T, Nishio K, Michalowski A, Green JE (2010) Three-gene predictor of clinical outcome for gastric cancer patients treated with chemotherapy. Pharmacogenomics J. doi:10.1038/tpj.2010.87
Bach S, Makristathis A, Rotter M, Hirschl A (2002) Gene expression profiling in AGS cells stimulated with Helicobacter pylori isogenic strains (cagA positive or cagA negative). Infect Immun 70:988–992
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva-Fernandes, I.J.L., Alves, M.K.S., Lima, V.P. et al. Differential expression of MYC in H. pylori-related intestinal and diffuse gastric tumors. Virchows Arch 458, 725–731 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-011-1085-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-011-1085-y