Abstract
Objectives
The majority of cases of unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion (RSA) remains unclear and is found to be associated with alloimmune antibodies termed as mixed lymphocyte reaction blocking factor (MLR-Bf). The decreased production of MLR-Bf may play major role in the immunologic failure of pregnancy and can lead to abortion. The present study was aimed at evaluating MLR-Bf as potential biomarker of indication and the efficacy of immunotherapy with paternal lymphocytes (LIT) in women with RSA.
Materials and methods
A total of 97 women with history of unexplained RSA were recruited for this prospective study. These women showed negative for MLR-Bf and registered for lymphocyte immunotherapy with husband cells. Women with autoimmune pathology or anti-phospholipid syndrome were excluded. All individuals gave their consent to participate in the study.
Results
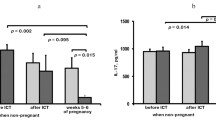
We have analyzed MLR proliferative response and MLR-Bf in nonpregnant women with history of RSA before and after LIT. Following LIT, the initially low MLR proliferative response was restored at 76.6 % of women, and MLR-Bf activity in blood serum could be detected in 74 % of women. The rate of successful pregnancy was shown to be significantly higher in women positive for MLR-Bf (50/72) as compared with the MLR-Bf negative women (7/25; χ 2 = 0.0003).
Conclusion
The data obtained demonstrate that LIT with the paternal lymphocytes in MLR-Bf negative women is accompanied by increased proliferative cell response to the paternal alloantigens and by enhanced production of soluble suppressor activity factors (MLR-Bf) that is associated with improved pregnancy outcome in women with history of RSA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dranik GN (2003) Reproduction Immunology. In: Clinical immunology and allergology, M: Russ Medical News Agency, Moscow, p 313–314
Pandey MK, Agrawal S (2004) Induction of MLR-Bf and protection of fetal loss: a current double blind randomized trial of paternal lymphocyte immunization for women with recurrent spontaneous abortion. Int Immunopharmacol 4:289–298
Khonina NA, Dzuszeva IB, Tichonova MA, Chernykh ER (2010) Immune disfunction in women with infertility. Russ J Med Imunol 12(6):511–520
Pandey MK, Saxena V, Agrawal S (2003) Characterization of mixed lymphocyte reaction blocking antibodies (MLR-Bf) in human pregnancy. Pregnancy Childbirth 3:1–7
Pandey MK, Thakur S, Agarwal S (2004) Lymphocyte immunotherapy and its probable mechanism in the maintenance of pregnancy in women with recurrent spontaneous abortion. Arch Gynecol Obstet 269:161–172
Pandey MK, Rani R, Agrawal S (2005) An update in recurrent spontaneous abortion. Arch Gynecol Obstet 272:95–108
Pandey MK, Halder A, Agarwal S, Srivastava M, Agarwal SS, Agrawal S (2006) Immunotherapy in recurrent spontaneous abortion: randomized and non-randomized trials. Internet J Gynecol Obstetrics ISSN:1528–8439
Ramhorst RE, Fainboim L (2005) New actors for immunological mechanisms involved in the materno-fetal tolerance. Curr Women’s Health Rev 1:15–20
Kling C, Schutzler A, Wilke G (2008) Two-year outcome after recurrent implantation failure: prognostic factors and additional interventions. Arch Gynecol Obstet 278:135–142
Ly KD, Aziz N, Safi J, Agarwal A (2010) Evidence-based management of infertile couples with repeated implantation failure following IVF. Current Women’s Health Rev 6:200–218
Nonako T, Takakuwa K, Ooki I, Akashi M, Yokoo T, Kikuchi A, Nanaka K (2007) Results of immunotherapy for patients with unexplained primary recurrent abortions—prospective non-randomized cohort study. Am J Reprod Immunol 58:530–536
Takeshita T (2004) Diagnosis and treatment of recurrent miscarriage associated with immunologic disorders: is paternal lymphocyte immunization a relic of the past? J Nippon Med Sch 71:308–313
The practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (2006) Effectiveness and treatment for unexplained infertility. Fertil Steril 86(5):111–114
Hayakawa S, Karasaki-Suzuki M, Itoh T, Ishii M, Kanaeda T, Nagai N, Takahashi-Yamamoto N, Tochigi M, Chishima F, Fujii TK, Oyama J, Kitanaka S, Satoh K (2000) Effects of paternal lymphocyte immunization on peripheral Th1/Th2 balance and TCR V beta and V gamma repertoire usage of patients with recurrent spontaneous abortions. Am J Reprod Immunol 43:107–115
Yokoo T, Takakuwa K, Ooki I, Kikuchi A, Tamura M, Tanaka K (2006) Alteration of TH1 and TH2 cells by intracellular cytokine detection in patients with unexplained recurrent abortion before and after immunotherapy with the husband’s mononuclear cells. Fertil Steril 85:1452–1458
Raghupathy R, Al-Mutawa E, Al-Azemi M, Makhseed M, Azizieh F, Szekeres-Bartho J (2009) Progesterone-induced blocking factor (PIBF) modulates cytokine production by lymphocytes from women with recurrent miscarriage or preterm delivery. J Reprod Immunol 80:91–99
Kling C, Magez-Zunker J, Jenisch S, Kabelitz D (2002) Experience with allogeneic leukocyte immunization for implantation failure in the in vitro fertilization program. Am J Reprod Immunol 48:147
Kling C, Steinmann J, Westphal E, Magez J, Kabelitz D (2006) Adverse effects of intradermal allogeneic lymphocyte immunotherapy: acute reactions and role of autoimmunity. Hum Reprod 21(2):429–435
Porter TF, La Coursiere Y, Scot JR (2006) Immunotherapy for recurrent miscarriage. Cochrane Database Syst Rev CD 000112
Takakuwa K, Honda K, Yokoo T, Hataya I, Tamura M, Tanaka K (2006) Molecular genetic studies on the compatibility of HLA-class II alleles in patients with unexplained recurrent miscarriage in the Japanese population. Clin Immunol 118:101–107
Shetty S, Ghosh K (2009) Anti-phospholipid antibodies and other immunological causes of recurrent foetal loss—a review of literature of various therapeutic protocols. Am J Reprod Immunol 62(1):9–24
Khonina NA, Pasman NM, Chernykh ER (2010) Russ J Human Reprod 1:57–60
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khonina, N.A., Broitman, E.V., Shevela, E.Y. et al. Mixed lymphocyte reaction blocking factors (MLR-Bf) as potential biomarker for indication and efficacy of paternal lymphocyte immunization in recurrent spontaneous abortion. Arch Gynecol Obstet 288, 933–937 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-013-2832-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-013-2832-x