Abstract
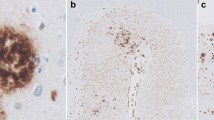
To investigate the prevalence and clinico-neuropathological characteristics of cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) in aged Chinese and its relationship to dementia and cerebrovascular lesions, we examined 362 archived brains of elderly with immunohistochemical staining for β-amyloid peptide and Congo red, Bodian and Luxol fast blue stains. We found that: (1) CAA appeared in 31.7% examined brains without sexual preponderance, and the incidence increased with age; (2) the frontal lobe was most frequently involved in CAA, followed by occipital and parietal lobe; (3) subcortical white matter and cerebellum dentate nucleus areas may also be affected by CAA; (4) CAA has a close relationship to Alzheimer's disease and multiple cerebrovascular lesions; (5) CAA alone may result in dementia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dermaut B, Kumar-Singh S, De Jonghe C, Cruts M, Lofgren A, Lubke U, Cras P, Dom R, De Deyn PP, Martin JJ, Van Broeckhoven C (2001) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy is a pathogenic lesion in Alzheimer's disease due to a novel presenilin 1 mutation. Brain 124:2383–2392
Greenberg SM (2002) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy and vessel dysfunction. Cerebrovasc Dis 13 Suppl 2:42–47
Ishihara T, Takahashi M, Yokota T, Yamashita Y, Gondo T, Uchino F, Iwamoto N (1991) The significance of cerebrovascular amyloid in the aetiology of superficial (lobar) cerebral haemorrhage and its incidence in the elderly population. J Pathol 165:229–234
Itoh Y, Yamada M, Hayakawa M, Otomo E, Miyatake T (1993) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: a significant cause of cerebellar as well as lobar cerebral hemorrhage in the elderly. J Neurol Sci 116:135–141
Jellinger KA (2002) Alzheimer disease and cerebrovascular pathology: an update. J Neural Transm 109:813–836
Mandybur TI (1975) The incidence of cerebral amyloid angiopathy in Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 25:120–126
Mandybur TI (1986) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: the vascular pathology and complications. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 45:79–90
Masuda J, Tanaka K, Ueda K, Omae T (1988) Autopsy study of incidence and distribution of cerebral amyloid angiopathy in Hisayama, Japan. Stroke 19:205–210
Mirra SS, Heyman A, McKeel D, Sumi SM, Crain BJ, Brownlee LM, Vogel FS, Hughes JP, Belle G van, Berg L (1991) The Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer's Disease (CERAD). Part II. Standardization of the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 41:479–486
Okazaki H, Reagan TJ, Campbell RJ (1979) Clinicopathologic studies of primary cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Mayo Clin Proc 54:22–31
Olichney JM, Ellis RJ, Katzman R, Sabbagh MN, Hansen L (1997) Types of cerebrovascular lesions associated with severe cerebral amyloid angiopathy in Alzheimer's disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 826:493–497
Tomonaga M (1981) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy in the elderly. J Am Geriatr Soc 29:151–157
Ulrich J, Probst A, Wuest M (1986) The brain diseases causing senile dementia. A morphological study on 54 consecutive autopsy cases. J Neurol. 233:118–122
Vinters HV, Gilbert JJ (1983) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: incidence and complications in the aging brain. II. The distribution of amyloid vascular changes. Stroke 14:924–928
Yamada M, Tsukagoshi H, Otomo E, Hayakawa M (1987) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy in the aged. J Neurol 234:371–376
Yoshimura M, Yamanouchi H, Kuzuhara S, Mori H, Sugiura S, Mizutani T, Shimada H, Tomonaga M, Toyokura Y (1992) Dementia in cerebral amyloid angiopathy: a clinicopathological study. J Neurol 239:441–450
Zarow C, Zaias B, Lyness SA, Chui H (1999) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy in Alzheimer disease is associated with apolipoprotein E4 and cortical neuron loss. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 13:1–8
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by a grant from the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Program) (No. G2000057005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, D., Yang, C. & Wang, L. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy in aged Chinese: a clinico-neuropathological study. Acta Neuropathol 106, 89–91 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-003-0706-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-003-0706-1