Abstract
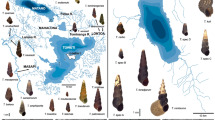
Korean freshwater snails of the genus Semisulcospira are widely distributed across East Asia. It has been a very popular nutritional food in Korea, and is an ecologically important water quality indicator because it lives only in clean water. However, no microsatellite markers have been generated to study the population genetic diversity of this genus. In the present study, we developed and characterized 18 novel microsatellite loci from Semisulcospira coreana genomic DNA. The microsatellites were isolated using 454 GS-FLX titanium sequencing and 18 markers were used for genotyping in S. coreana. In addition, we also tested the cross-species transferability of the microsatellite markers in four additional Semisulcospira spp. We identified 18 polymorphic loci and the number of alleles per loci, and their polymorphism information content values ranged from 2 to 17 and 0.203 to 0.902, respectively. The observed and expected heterozygosities of the loci ranged from 0.063 to 0.924 and 0.226 to 0.924, respectively. According to the analysis of the cross-species transferability of these markers, four species, S. forticosta, S. gottschei, S. tegulata, and S. libertina, showed a very high transferability (80%–85%). These results show that this set of nuclear markers could be useful for population genetics studies of this species and closely related species.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
All data generated and/or analyzed during this study are included in this article, or are available upon the request from the readers.
References
Barbará T, Palma-Silva C, Paggi G M, Bered F, Fay M F, Lexer C. 2007. Cross-species transfer of nuclear microsatellite markers: potential and limitations. Mol. Ecol., 16(18): 3 759–3 767.
Davis G M. 1969. A taxonomic study of some species of Semisulcospira in Japan (Mesogastropoda: Pleuroceridae). Malacologia, 7(2–3): 211–294.
Botstein D, White R L, Skolnick M, Davis R W. 1980. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am. J. Hum. Genet., 32: 314–331.
Excoffier L, Lischer H E. 2010. Arlequin suite Ver 3.5: a new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour., 10(3): 564–567.
Féral J P. 2002. How useful are the genetic markers in attempts to understand and manage marine biodiversity? J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 268(2): 121–145.
Greenley A P, Muguia-Vega A, Saenz-Arroyo A, Micheli F. 2012. New tetranucleotide microsatellite loci in pink abalone (Haliotis corrugata) isolated via 454 pyrosequencing. Conservai. Genet. Resour., 4(2): 265–268.
Gu Q H, Cheng Q Q, Li X J, Zhou C J. 2015. Novel polymorphic microsatellite markers for Bellamya and their application in population genetics of three species. Genet. Mol. Res., 14(4): 15 201–1 5212.
Gu Q H, Xiong B X, Zhu Y T, Wang Q, Shi P S. 2012. Isolation and characterization of polymorphic microsatellites loci in the freshwater snail Bellamya aeruginosa (Mollusca, Gastropoda). Conservat. Genet. Resour., 4(2): 387–390.
Kalinowski S T, Taper M L, Marshall T C. 2007. Revising how the computer program CERVUS accommodates genotyping error increases success in paternity assignment. Mol. Ecol., 16(5): 1 099–1 106.
Kim D H, Bang I C, Lee W O, Baek J M. 2012. Reproductive ecology of the freshwater Melania snail, Semisulcospira coreana (V. Martens) in Bukhan River. Korean J. Malacol., 28(2): 175–185.
Kim W J, Kim D H, Lee J S, Bang I C, Lee W O, Jung H. 2010. Systematic relationships of Korean freshwater snails of Semisulcospira, Koreanomelania, and Koreoleptoxis (Cerithiodiea; Pleuroceridae) revealed by mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase I sequences. Korean J. Malacol., 26(4): 275–283.
Knapik E W, Goodman A, Ekker M, Chevrette M, Delgado J, Neuhauss S, Shimoda N, Driever W, Fishman M C, Jacob H J. 1998. A microsatellite genetic linkage map for zebrafish (Danio rerio). Nat. Genet., 18(4): 338–343.
Lee S M, Lim T J. 2005. Effects of dietary protein and energy levels on growth and lipid composition of juvenile snail (Semisulcospira gottschei). J. Shellfish Res., 24(1): 99–102.
Lindqvist A K, Magnusson P K, Balciuniene J, Wadelius C, Lindholm E, Alarcón-Riquelme M E, Gyllensten U B. 1996. Chromosome-specific panels of triand tetranucleotide microsatellite markers for multiplex fluorescent detection and automated genotyping: evaluation of their utility in pathology and forensics. Genome Res, 6(12): 1 170–1 176.
Luikart G, England P R, Tallmon D, Jordan S, Taberlet P. 2003. The power and promise of population genomics: from genotyping to genome typing. Nat. Rev. Genet., 4(12): 981–994.
Moges A D, Admassu B, Belew D, Yesuf M, Njuguna J, Kyalo M, Ghimire S R. 2016. Development of microsatellite markers and analysis of genetic diversity and population structure of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides from Ethiopia. PLoS One, 11(3): e0151257.
Moon S K, Kim I S, Lim C W, Yoon N Y, Jeong B Y. 2015. Proximate and fatty acid compositions of commercial domestic and imported Melania snails Semisulscospira sp. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 48(6): 977–981.
Queller D C, Strassmann J E, Hughes C R. 1993. Microsatellites and kinship. Trends Ecol. Evol, 8(8): 285–288.
Rousset F. 2008. GENEPOP’007: a complete reimplementation of the GENEPOP software for Windows and Linux. Mol. Ecol. Resour, 8(1): 103–106.
Selkoe K A, Toonen R J. 2006. Microsatellites for ecologists: a practical guide to using and evaluating microsatellite markers. Ecol. Lett, 9(5): 615–629.
Tóth G, Gáspári Z, Jurka J. 2000. Microsatellites in different eukaryotic genomes: survey and analysis. Genome Res., 10(7): 967–981.
Untergasser A, Cutcutache I, Koressaar T, Ye J, Faircloth B C, Remm M, Rozen S G. 2012. Primer3—new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res., 40(15): e115.
Urabe M. 2000. Phenotypic modulation by the substratum of shell sculpture in Semisulcospira reiniana (Prosobranchia: Pleuroceridae). J. Mol. Stud., 66(1): 53–60.
Van Oosterhout C, Hutchinson W F, Wills D P M, Shipley P. 2004. MICRO-CHECKER: software for identifying and correcting genotyping errors in microsatellite data. Mol. Ecol. Notes, 4(3): 535–538.
Zeng T, Yin W, Xia R, Fu C Z, Jin B S. 2015. Complete mitochondrial genome of a freshwater snail, Semisulcospira libertina (Cerithioidea: Semisulcospiridae). Mitochondr. DNA, 26(6): 897–898.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Supported by the National Institute of Fisheries Science of Republic of Korea (Nos. R2019030, R2019033)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, Y.J., Lee, M.N., Kim, EM. et al. Development and characterization of novel polymorphic microsatellite markers for the Korean freshwater snail Semisulcospira coreana and cross-species amplification using next-generation sequencing. J. Ocean. Limnol. 38, 503–508 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-019-9058-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-019-9058-0