Abstract
Objective
To review the literature concerning the management with placement of covered stent-grafts of traumatic pseudoaneurysms of the extracranial internal carotid artery (ICA) resulting from penetrating craniocervical injuries or skull base fractures.
Method
We have reviewed, from the Medline database, all the published cases in the English literature since 1990 and we have added a new case.
Results
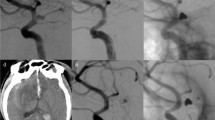
We identified 20 patients with traumatic extracranial ICA pseudoaneurysms due to penetrating craniocervical injuries or skull base fractures who had been treated with covered stent-graft implantation. Many discrepancies have been ascertained regarding the anticoagulation therapy. In 3 patients the ICA was totally occluded in the follow-up period, giving an overall occlusion rate 15%. No serious complication was reported as a result of the endovascular procedure.
Conclusion
Preliminary results suggest that placement of stent-grafts is a safe and effective method of treating ICA traumatic pseudoaneurysms resulting from penetrating craniocervical injuries or skull base fractures. The immediate results are satisfactory when the procedure takes place with appropriate anticoagulation therapy. The periprocedural morbidity and mortality and the early patency are also acceptable. A surveillance program with appropriate interventions to manage restenosis may improve the long-term patency.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cogbill TH, Moore EE, Meissner M, et al. (1994) The spectrum of blunt injury to the carotid artery: A multicenter perspective. J Trauma 37:473–479
Pearce WH, Whitehill TA (1988) Carotid and vertebral arterial injuries. Surg Clin North Am 68:705–723
Klein GE, Szolar DH, Raith J, et al. (1997) Posttraumatic extracranial aneurysm of the internal carotid artery: Combined endovascular treatment with coils and stents. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 18:1261–1264
Redekop G, Marotta T, Weill A (2001) Treatment of traumatic aneurysms and arteriovenous fistulas of the skull base by using endovascular stents. J Neurosurg 95:412–419
Marotta TR, Buller C, Taylor D, et al. (1998) Autologous vein-covered stent repair of a cervical internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm: Technical case report. Neurosurgery 42:408–412; discussion 412–413
Parodi JC, Schonholz C, Ferreira LM, et al. (1999) Endovascular stent-graft treatment of traumatic arterial lesions. Ann Vasc Surg 13:121–129
Szopinski P, Iwanowski J, Kielar M, et al. (2000) Posttraumatic pseudoaneurysm of stenotic internal carotid artery repair by stent graft: A case report. Vasc Surg 34:81–85
ul Haq T, Yaqoob J, Munir K, et al. (2004) Endovascular-covered stent treatment of posttraumatic cervical carotid artery pseudoaneurysms. Australas Radiol 48:220–223
Layton KF, Kim YW, Hise JH. (2004) Use of covered stent grafts in the extracranial carotid artery: Report of three patients with follow-up between 8 and 42 months. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1760–1763
McNeil JD, Chiou AC, Gunlock MG, et al. (2002) Successful endovascular therapy of a penetrating zone III internal carotid injury. J Vasc Surg 36:187–190
Fusonie GE, Edwards JD, Reed AB (2004) Covered stent exclusion of blunt traumatic carotid artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature. Ann Vasc Surg 18:376–379
Scavee V, De Wispelaere JF, Mormont E, et al. (2001) Pseudoaneurysm of the internal carotid artery: Treatment with a covered stent. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 24:283–285
Kubaska SM 3rd, Greenberg RK, Clair D, et al. (2003) Internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysms: Treatment with the Wallgraft endoprosthesis. J Endovasc Ther 10:182–189
Shames ML, Davis JW, Evans AJ (1999) Endoluminal stent placement for the treatment of traumatic carotid artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature. J Trauma 46:724–726
Duane TM, Parker F, Stokes GK, et al. (2002) Endovascular carotid stenting after trauma. J Trauma 52:149–153
Reiter BP, Marin ML, Teodorescu VJ, et al. (1998) Endoluminal repair of an internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm. J Vasc Interv Radiol 9:245–248
Ahn JY, Chung YS, Lee BH, et al. (2004) Stent-graft placement in a traumatic internal carotid-internal jugular fistula and pseudoaneurysm. J Clin Neurosci 11:636–639
Biffl WL, Moore EE, Offner PJ, et al. (1999) Blunt carotid arterial injuries: Implications of a new grading scale. J Trauma 47:845–853
Mokri B (1990) Traumatic and spontaneous extracranial internal carotid artery dissections. J Neurol 237:356–361
Costantino PD, Russell E, Reisch D, et al. (1991) Ruptured petrous carotid aneurysm presenting with otorrhagia and epistaxis. Am J Otol 12:378–383
Willinsky R, Lasjaunias P, Berenstein A (1987) Intracavernous branches of the internal carotid artery (ICA): Comprehensive review of their variations. Surg Radiol Anat 9:201–215
Chen D, Concus AP, Halbach VV, et al. (1998) Epistaxis originating from traumatic pseudoaneurysm of the internal carotid artery: Diagnosis and endovascular therapy. Laryngoscope 108:326–331
Han MH, Sung MW, Chang KH, et al. (1994) Traumatic pseudoaneurysm of the intracavernous ICA presenting with massive epistaxis: Imaging diagnosis and endovascular treatment. Laryngoscope 104:370–377
Tachibana E, Suzuki Y, Harada T, et al. (2000) Bypass surgery using a radial artery graft for bilateral extracranial carotid arteries occlusion. Neurosurg Rev 23:52–55
Cothren CC, Moore EE, Ray CE Jr, et al. (2005) Carotid artery stents for blunt cerebrovascular injury: Risks exceed benefits. Arch Surg 140:480–485; discussion 485–486
Krupski WC (2005) Uncommon disorders affecting the carotid arteries. In: Rutherford’s vascular surgery, 6th edn. Pennsylvania: Elsevier Saunders
Diaz-Daza O, Arraiza FJ, Barkley JM, et al. (2003) Endovascular therapy of traumatic vascular lesions of the head and neck. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 26:213–221
Gomez CR, May AK, Terry JB, et al. (1999) Endovascular therapy of traumatic injuries of the extracranial cerebral arteries. Crit Care Clin 15:789–809
Ramadan F, Rutledge R, Oller D, et al. (1995) Carotid artery trauma: A review of contemporary trauma center experiences. J Vasc Surg 21:46–55; discussion 55–56
D’Alise MD, Vardiman AB, Kopitnik TA Jr, et al. (1996) External carotid-to-middle cerebral bypass in the treatment of complex internal carotid injury. J Trauma 40:452–455
Rostomily RC, Newell DW, Grady MS, et al. (1997) Gunshot wounds of the internal carotid artery at the skull base: Management with vein bypass grafts and a review of the literature. J Trauma 42:123–132
Perez-Cruet MJ, Patwardhan RV, Mawad ME, et al. (1997) Treatment of dissecting pseudoaneurysm of the cervical internal carotid artery using a wall stent and detachable coils: Case report. Neurosurgery 40:622–625; discussion 625–626
Matsuura JH, Rosenthal D, Jerius H, et al. (1997) Traumatic carotid artery dissection and pseudoaneurysm treated with endovascular coils and stent. J Endovasc Surg 4:339–343
Mericle RA, Lanzino G, Wakhloo AK, et al. (1998) Stenting and secondary coiling of intracranial internal carotid artery aneurysm: Technical case report. Neurosurgery 43:1229–1234
Singh RR, Barry MC, Ireland A, et al. (2004) Current diagnosis and management of blunt internal carotid artery injury. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 27:577–584
Zetterling M, Carlstrom C, Konrad P (2000) Internal carotid artery dissection. Acta Neurol Scand 101:1–7
Fabian TC, Patton JH Jr, Croce MA, et al. (1996) Blunt carotid injury: Importance of early diagnosis and anticoagulant therapy. Ann Surg 223:513–522; discussion 522–525
Wahl WL, Brandt MM, Thompson BG, et al. (2002) Antiplatelet therapy: An alternative to heparin for blunt carotid injury. J Trauma 52:896–901
Parikh AA, Luchette FA, Valente JF, et al. (1997) Blunt carotid artery injuries. J Am Coll Surg 185:80–86
Ahuja A, Guterman LR, Hopkins LN (1992) Carotid cavernous fistula and false aneurysm of the cavernous carotid artery: Complications of transsphenoidal surgery. Neurosurgery 31:774–778; discussion 778–779
Schievink WI, Piepgras DG, McCaffrey TV, et al. (1994) Surgical treatment of extracranial internal carotid artery dissecting aneurysms. Neurosurgery 35:809–815; 815–816 discussion
Bush RL, Lin PH, Dodson TF, et al. (2001) Endoluminal stent placement and coil embolization for the management of carotid artery pseudoaneurysms. J Endovasc Ther 8:53–61
Patel JV, Rossbach MM, Cleveland TJ, et al. (2002) Endovascular stent-graft repair of traumatic carotid artery pseudoaneurysm. Clin Radiol 57:308–311
McCready RA, Divelbiss JL, Bryant MA, et al. (2004) Endoluminal repair of carotid artery pseudoaneurysms: A word of caution. J Vasc Surg 40:1020–1023
Bhatt DL, Kapadia SR, Bajzer CT, et al. (2001) Dual antiplatelet therapy with clopidogrel and aspirin after carotid artery stenting. J Invas Cardiol 13:767–771
McKevitt FM, Randall MS, Cleveland TJ, et al. (2005) The benefits of combined anti-platelet treatment in carotid artery stenting. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 29:522–527
Schuhlen H, Kastrati A, Dirschinger J et al. (1998) Intracoronary stenting and risk for major adverse cardiac events during the first month. Circulation 98:104–111
Elsner M, Auch-Schwelk W, Britten M, et al. (1999) Coronary stent grafts covered by a polytetrafluoroethylene membrane. Am J Cardiol 84:335–338, A8
von Birgelen C, Haude M, Herrmann J, et al. (1999) Early clinical experience with the implantation of a novel synthetic coronary stent graft. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 47:496–503
Duke BJ, Ryu RK, Coldwell DM, et al. (1997) Treatment of blunt injury to the carotid artery by using endovascular stents: An early experience. J Neurosurg 87:825–829
May J, White GH, Waugh R, Brennan J (1997) Endoluminal repair of internal carotid artery aneurysm: A feasible but hazardous procedure. J Vasc Surg 26:1055–1060
Willfort-Ehringer A, Ahmadi R, Gschwandtner ME, et al. (2002) Single-center experience with carotid stent restenosis. J Endovasc Ther 9:299–307
Setacci C, Pula G, Baldi I, de Donato G, et al. (2003) Determinants of in-stent restenosis after carotid angioplasty: A case-control study. J Endovasc Ther 10:1031–1038
Gercken U, Lansky AJ, Buellesfeld L et al. (2002) Results of the Jostent coronary stent graft implantation in various clinical settings: Procedural and follow-up results. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 56:353–360
Fujiwara NH, Lin HB, Zabat D, et al. (2002) Patency rates of Type 1 collagen stent-grafts versus PTFE stent-grafts for aneurysm therapy. Presented at the Fifth Annual Joint Meeting of the American Association of Neurological Surgeons/Congress of Neurological Surgeons and the American Society of Interventional and Therapeutic Neuroradiology, Big Island, Hawaii, February 9–12, 2001. Cited in: Alexander MJ, Smith TP, Tucci DL. Treatment of an iatrogenic petrous carotid artery pseudoaneurysm with a Symbiot covered stent: Technical case report. Neurosurgery 50:658–662
Horowitz MB, Miller G 3rd, Meyer Y, et al. (1996) Use of intravascular stents in the treatment of internal carotid and extracranial vertebral artery pseudoaneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 17:693–696
Bergeron P, Roux M, Khanoyan P, et al. (2005) Long-term results of carotid stenting are competitive with surgery. J Vasc Surg 41:213–221; discussion 221–222
O’Donnell TF Jr, Rodriguez AA, Fortunato JE, et al. (1996) Management of recurrent carotid stenosis: Should asymptomatic lesions be treated surgically? J Vasc Surg 24:207–212
Lal BK, Hobson RW 2nd, Goldstein J, et al. (2003) In-stent recurrent stenosis after carotid artery stenting: Life table analysis and clinical relevance. J Vasc Surg. 38:1162–1168; discussion 1169
Fleming SE, Bluth EI, Milburn J (2005) Role of sonography in the evaluation of carotid artery stents. J Clin Ultrasound 33:321–328
Letourneau-Guillon L, Soulez G, Beaudoin G, et al. (2004) CT and MR imaging of nitinol stents with radiopaque distal markers. J Vasc Interv Radiol 15:615–624
Borisch I, Hamer OW, Zorger N, et al. (2005) In vivo evaluation of the carotid Wallstent on three-dimensional contrast material-enhanced MR angiography: Influence of artifacts on the visibility of stent lumina. J Vasc Interv Radiol 16:669–677
Corti R, Ferrari C, Roberti M, et al. (1998) Spiral computed tomography: A novel diagnostic approach for investigation of the extracranial cerebral arteries and its complementary role in duplex ultrasonography. Circulation 98:984–989
Goldman CK, Morshedi-Meibodi A, White CJ, et al. (2006) Surveillance imaging for carotid in-stent restenosis. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 67:302–308
Coldwell DM, Novak Z, Ryu RK, et al. (2000) Treatment of posttraumatic internal carotid arterial pseudoaneurysms with endovascular stents. J Trauma 48:470–472
Baril DT, Ellozy SH, Carroccio A, et al. (2004) Endovascular repair of an infected carotid artery pseudoaneurysm. J Vasc Surg 40:1024–1027
Simionato F, Righi C, Melissano G, et al. (2000) Stent-graft treatment of a common carotid artery pseudoaneurysm. J Endovasc Ther 7:136–140
Auyeung KM, Lui WM, Chow LC, et al. (2003) Massive epistaxis related to petrous carotid artery pseudoaneurysm after radiation therapy: Emergency treatment with covered stent in two cases. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1449–1452
Eckert B, Thie A, Carvajal M, et al. (1998) Predicting hemodynamic ischemia by transcranial Doppler monitoring during therapeutic balloon occlusion of the internal carotid artery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:577–582
Larson JJ, Tew JM Jr, Tomsick TA, et al. (1995) Treatment of aneurysms of the internal carotid artery by intravascular balloon occlusion: Long-term follow-up of 58 patients. Neurosurgery 36:26–30
Lee CY, Yim MB, Kim IM, et al. (2004) Traumatic aneurysm of the supraclinoid internal carotid artery and an associated carotid-cavernous fistula: Vascular reconstruction performed using intravascular implantation of stents and coils. Case report. J Neurosurg 100:115–119
Celil G, Engin D, Orhan G, et al. (2004) Intractable epistaxis related to cavernous carotid artery pseudoaneurysm: Treatment of a case with covered stent. Auris Nasus Larynx 31:275–278
Felber S, Henkes H, Weber W, et al. (2004) Treatment of extracranial and intracranial aneurysms and arteriovenous fistulae using stent grafts. Neurosurgery 55:631–638; discussion 638–639
Lutsep HL, Barnwell SL, Mawad M, et al. (2003) Stenting of Symptomatic Atherosclerotic Lesions in the Vertebral or Intracranial Arteries (SSYLVIA): Study results. Stroke 34:253
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maras, D., Lioupis, C., Magoufis, G. et al. Covered Stent-Graft Treatment of Traumatic Internal Carotid Artery Pseudoaneurysms: A Review. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 29, 958–968 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-005-0367-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-005-0367-7