Abstract
Purpose
We aimed to investigate the relationship between right atrial pressure (RAP) and liver stiffness (LS) determined by liver elastography (LE) during cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) in patients with heart failure (HF) and conventional pacemaker (PM) implantation in patients without HF.
Methods
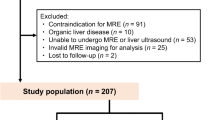
60 patients with HF who underwent CRT and 60 patients without HF who underwent PM were enrolled. Routine echocardiography and laboratory examinations were performed. Systolic, diastolic, and mean RAP measurements were performed inversely during PM implantation and LS measurement with ElastPQ technique.
Results
Systolic, diastolic, and mean RAP, left ventricular (LV) systolic-diastolic, right ventricular (RV) diastolic and left atrial diameters, tricuspid regurgitation pressure gradient, and RV-myocardial performance index (MPI) values were significantly higher in patients with HF (p < 0.05 each-one). LV ejection fraction and tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion values were significantly lower in patients with HF group (p < 0.05 each-one). LS values and inspiratory (Ins) and expiratory inferior vena cava (IVC) diameters were significantly higher in the patients with HF (p < 0.05 each-one). Mean RAP was found to be closely related to LS value, Ins-IVC diameter, RV-MPI, and NT-proBNP levels. LS value and Ins-IVC diameter were found to determine patients with mean RAP > 5 mmHg and > 10 mmHg. When the cut-off value of LS was taken as 7 kPa, it was found that the mean RAP > 10 mmHg with 89.6% sensitivity and 87.5% specificity.
Conclusions
The non-invasive LS value determined by LE independently determines the mean RAP in patients with and without HF. According to our study results, > 7 kPa value for LS determined in liver US may be predictive for increased mean RAP.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, et al. (2016). 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 37:2129-2200.
Icen YK, Demirtas AO, Koc AS, et al. (2018) Liver stiffness value obtained with ElastPQ ultrasound increases with NYHA class in chronic heart failure patients and reduced ejection fraction. Turk Kardiyol Dern Ars. https://doi.org/10.5543/tkda.2018.62282.
Myers RP, Cerini R, Sayegh R, et al. (2003) Cardiac hepatopathy: clinical, hemodynamic, and histologic characteristics and correlations. Hepatology 37:393-400.
Sahn DJ, DeMaria A, Kisslo J, et al. (1978) Recommendations regarding quantitation in M-mode echocardiography: results of a survey of echocardiographic measurements. Circulation 58: 1072-1083.
Lang RM, Bierig M, Devereux RB, et al. (2005) Recommendations for chamber quantification: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography’s Guidelines and Standards Committee and the Chamber Quantification Writing Group, developed in conjunction with the European Association of Echocardiography, branch of the European Society of Cardiology. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 18: 1440-1463.
Eidem BW, O'Leary PW, Tei C, et al. (2000) Usefulness of the myocardial performance index for assessing right ventricular function in congenital heart disease. Am J Cardiol 86:654-658.
Castéra L, Foucher J, Bernard PH, et al. (2010) Pitfalls of liver stiffness measurement: a 5-year prospective study of 13,369 examinations. Hepatology 51:828-835.
Corpechot C, Gaouar F, El Naggar A, et al. (2014) Baseline values and changes in liver stiffness measured by transient elastography are associated with severity of fibrosis and outcomes of patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gastroenterology 146:970-979.
Saito Y, Kato M, Nagashima K, et al. (2018) Prognostic Relevance of Liver Stiffness Assessed by Transient Elastography in Patients With Acute Decompensated Heart Failure. Circ J 82:1822-1829.
Taniguchi T, Sakata Y, Ohtani T, et al. (2014) Usefulness of transient elastography for noninvasive and reliable estimation of right-sided filling pressure in heart failure. Am J Cardiol 113:552-558.
Taniguchi T, Ohtani T, Kioka H, et al. (2018) Liver Stiffness Reflecting Right-Sided Filling Pressure Can Predict Adverse Outcomes in Patients With Heart Failure. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmg.2017.10.022.
Seo Y, Nakatsukasa T, Sai S, et al. (2018) Clinical implications of organ congestion in heart failure patients as assessed by ultrasonography. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther 8:57-69.
Jalal Z, Iriart X, de Lédinghen V, et al. (2017) Impact of Surgery and Valvuloplasty on Liver Stiffness in a Patient With Pericarditis and Pulmonary Valvulopathy. World J Pediatr Congenit Heart Surg 8:103-105.
DiPaola FW, Schumacher KR, Goldberg CS, et al. (2017) Effect of Fontan operation on liver stiffness in children with single ventricle physiology. Eur Radiol 27:2434-2442.
Hopper I, Kemp W, Porapakkham P, et al. (2012) Impact of heart failure and changes to volume status on liver stiffness: non-invasive assessment using transient elastography. Eur J Heart Fail 14:621-627.
Colli A, Pozzoni P, Berzuini A, et al. (2010) Decompensated chronic heart failure: increased liver stiffness measured by means of transient elastography. Radiology 257:872-878.
Sporea I, Bota S, Grădinaru-Taşcău O, et al. (2014) Comparative study between two point Shear Wave Elastographic techniques: Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) elastography and ElastPQ. Med Ultrason 16:309-314.
Bota S, Sporea I, Sirli R, et al. (2014) Factors associated with the impossibility to obtain reliable liver stiffness measurements by means of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) elastography--analysis of a cohort of 1,031 subjects. Eur J Radiol 83:268-272.
Bonow RO, Mann DL, Zipes DP, Libby P, Braunwald E. Braunwald’s Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 9th edition: page 394.
Yoshitani T, Asakawa N, Sakakibara M, et al. (2016) Value of Virtual Touch Quantification Elastography for Assessing Liver Congestion in Patients With Heart Failure. Circ J 80:1187-1195.
Chon YE, Choi EH, Song KJ, et al. (2012) Performance of transient elastography for the staging of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B: a meta-analysis. PLoS One 7:e44930.
Potthoff A, Schettler A, Attia D, et al. (2015) Liver stiffness measurements and short-term survival after left ventricular assist device implantation: A pilot study. J Heart Lung Transplant 34:1586-1594.
Dietrich CF, Bamber J, Berzigotti A, et al. (2017) EFSUMB Guidelines and Recommendations on the Clinical Use of Liver Ultrasound Elastography, Update 2017 (Long Version). Ultraschall Med. 38:e16-e47.
Jaffer OS, Lung PF, Bosanac D, et al. (2012) Acoustic radiation force impulse quantification: repeatability of measurements in selected liver segments and influence of age, body mass index and liver capsule-to-box distance. Br J Radiol. 85:e858-863.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demirtas, A.O., Koc, A.S., Sumbul, H.E. et al. Liver stiffness obtained by ElastPQ ultrasound shear wave elastography independently determines mean right atrial pressure. Abdom Radiol 44, 3030–3039 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-02083-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-02083-3