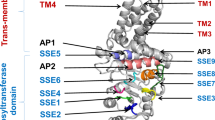
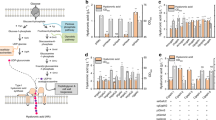
Abstract
The molecular weight (Mw) of hyaluronic acid (HA) determines its suitability for medical and cosmetic applications. Here, we characterize in vitro and in vivo HA synthesis of streptococcal HA synthases (HASs) with a special focus on HA Mw. To date, four streptococcal HA producers are described (Streptococcus equi subsp. equi, S. equi subsp. zooepidemicus, S. pyogenes, and S. uberis). We identified two more potential HA producers in this study: S. iniae and S. parauberis. Indeed, the HA Mw produced by the different streptococcal HASs differs in vitro. To exploit these different HA Mw synthesis capacities, Lactococcus lactis strains expressing the streptococcal HASs were constructed. HA of different Mw was also produced in vivo by these engineered strains, strongly suggesting that the protein sequences of the HASs influence HA Mw. Since the HA Mw in vivo is also influenced by metabolic factors like specific growth rate and HA precursor availability, these were also determined. In summary, the maximal Mw of HA synthesized is specific for the individual synthase, while any decrease from the maximal HA Mw is influenced by physiological and metabolic factors. The results open new avenues for Mw-tailored HA synthesis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong DC, Johns MR (1997) Culture conditions affect the molecular weight properties of hyaluronic acid produced by Streptococcus zooepidemicus. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(7):2759–2764
Badle SS, Jayaraman G, Ramachandran KB (2014) Ratio of intracellular precursors concentration and their flux influences hyaluronic acid molecular weight in Streptococcus zooepidemicus and recombinant Lactococcus lactis. Bioresour Technol 163:222–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.04.027
Baggenstoss BA, Harris EN, Washburn JL, Medina AP, Nguyen L, Weigel PH (2017) Hyaluronan synthase control of synthesis rate and hyaluronan product size are independent functions differentially affected by mutations in a conserved tandem B-X7-B motif. Glycobiology 27(2):154–164. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cww089
Blank LM, McLaughlin RL, Nielsen LK (2005) Stable production of hyaluronic acid in Streptococcus zooepidemicus chemostats operated at high dilution rate. Biotechnol Bioeng 90(6):685–693. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.20466
Blank LM, Hugenholtz P, Nielsen LK (2008) Evolution of the hyaluronic acid synthesis (has) operon in Streptococcus zooepidemicus and other pathogenic streptococci. J Mol Evol 67(1):13–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-008-9117-1
Chauhan AS, Badle SS, Ramachandran KB, Jayaraman G (2014) The P170 expression system enhances hyaluronan molecular weight and production in metabolically-engineered Lactococcus lactis. Biochem Eng J 90:73–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2014.05.012
Chen WY, Marcellin E, Hung J, Nielsen LK (2009) Hyaluronan molecular weight is controlled by UDP-N-acetylglucosamine concentration in Streptococcus zooepidemicus. J Biol Chem 284(27):18007–18014. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.011999
Chen WY, Marcellin E, Steen JA, Nielsen LK (2014) The role of hyaluronic acid precursor concentrations in molecular weight control in Streptococcus zooepidemicus. Mol Biotechnol 56(2):147–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-013-9690-4
Chong B, Nielsen LK (2003a) Aerobic cultivation of Streptococcus zooepidemicus and the role of NADH oxidase. Biochem Eng J 16:153–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-703X(03)00031-7
Chong BF, Nielsen LK (2003b) Amplifying the cellular reduction potential of Streptococcus zooepidemicus. J Biotechnol 100(1):33–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1656(02)00239-0
Chong BF, Blank LM, McLaughlin R, Nielsen LK (2005) Microbial hyaluronic acid production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66(4):341–351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1774-4
de Oliveira J, Carvalho L, Gomes A, Queiroz L, Magalhães B, Parachin N (2016) Genetic basis for hyper production of hyaluronic acid in natural and engineered microorganisms. Microb Cell Factories 15(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-016-0517-4
DeAngelis PL (1997) Hyaluronan synthase of Chlorella virus PBCV-1. Science 278:1800–1803. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.278.5344.1800
DeAngelis PL, Papaconstantinou J, Weigel PH (1993) Molecular cloning, identification, and sequence of the hyaluronan synthase gene from group A Streptococcus pyogenes. J Biol Chem 268(26):19181–19184
Doss SS, Bhatt NP, Jayaraman G (2017) Improving the accuracy of hyaluronic acid molecular weight estimation by conventional size exclusion chromatography. J Chromatogr B 1060:255–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.06.006
Duan XJ, Niu HX, Tan WS, Zhang X (2009) Mechanism analysis of effect of oxygen on molecular weight of hyaluronic acid produced by Streptococcus zooepidemicus. J Microbiol Biotechnol 19(3):299–306. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.0801.073
Eisele A, Zaun H, Kuballa J, Elling L (2018) In vitro one-pot enzymatic synthesis of hyaluronic acid from sucrose and N-acetylglucosamine: optimization of the enzyme module system and nucleotide sugar regeneration. ChemCatChem 10(14):2969–2981. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201800370
Fallacara A, Baldini E, Manfredini S, Vertuani S (2018) Hyaluronic acid in the third millennium. Polymers 10(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070701
Forsee WT, Cartee RT, Yother J (2000) Biosynthesis of type 3 capsular polysaccharide in Streptococcus pneumoniae - enzymatic chain release by an abortive translocation process. J Biol Chem 275(34):25972–25978. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M002613200
Guan F, Jin J, Zhao H, Hong L, Shen Z, Zhu Y (2016) Hyaluronic acid production by Streptococcus iniae and its application in rabbit skin’s regeneration. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao 32(8):1104–1114. https://doi.org/10.13345/j.cjb.150517
Häusler H (2015) Efficacy of a hyaluronic acid gel to improve the skin properties. SOFW Journal 141(9):16–18
Hmar R, Prasad S, Jayaraman G, Ramachandran KB (2014) Chromosomal integration of hyaluronic acid synthesis (has) genes enhances the molecular weight of hyaluronan produced in Lactococcus lactis. Biotechnol J 9(12):1554–1564. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201400215
Hoffmann J, Altenbuchner J (2014) Hyaluronic acid production with Corynebacterium glutamicum: effect of media composition on yield and molecular weight. J Appl Microbiol 117(3):663–678. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.12553
Holo H, Nes IF (1989) High-frequency transformation, by electroporation, of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris grown with glycine in osmotically stabilized media. Appl Environ Microbiol 55(12):3119–3123
Hubbard C, McNamara JT, Azumaya C, Patel MS, Zimmer J (2012) The hyaluronan synthase catalyzes the synthesis and membrane translocation of hyaluronan. J Mol Biol 418(1–2):21–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2012.01.053
Itano N, Sawai T, Yoshida M, Lenas P, Yamada Y, Imagawa M, Shinomura T, Hamaguchi M, Yoshida Y, Ohnuki Y, Miyauchi S, Spicer AP, McDonald JA, Kimata K (1999) Three isoforms of mammalian hyaluronan synthases have distinct enzymatic properties. J Biol Chem 274(35):25085–25092. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.35.25085
Jagannath S, Ramachandran KB (2010) Influence of competing metabolic processes on the molecular weight of hyaluronic acid synthesized by Streptococcus zooepidemicus. Biochem Eng J 48(2):148–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2009.09.003
Jeeva P, Doss SS, Sundaram V, Jayaraman G (2019) Production of controlled molecular weight hyaluronic acid by glucostat strategy using recombinant Lactococcus lactis cultures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103(11):4363–4375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09769-0
Jones P, Binns D, Chang HY, Fraser M, Li WZ, McAnulla C, McWilliam H, Maslen J, Mitchell A, Nuka G, Pesseat S, Quinn AF, Sangrador-Vegas A, Scheremetjew M, Yong SY, Lopez R, Hunter S (2014) InterProScan 5: genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 30(9):1236–1240. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu031
Karbownik MS, Nowak JZ (2013) Hyaluronan: towards novel anti-cancer therapeutics. Pharmacol Rep 65(5):1056–1074. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1734-1140(13)71465-8
Kaur M, Jayaraman G (2016) Hyaluronan production and molecular weight is enhanced in pathway-engineered strains of lactate dehydrogenase-deficient Lactococcus lactis. Metab Eng Commun 3:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meteno.2016.01.003
Kim JH, Yoo SJ, Oh DK, Kweon YG, Park DW, Lee CH, Gil GH (1996) Selection of a Streptococcus equi mutant and optimization of culture conditions for the production of high molecular weight hyaluronic acid. Enzym Microb Technol 19(6):440–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(96)00019-1
Kitchen JR, Cysyk RL (1995) Synthesis and release of hyaluronic acid by Swiss 3t3 fibroblasts. Biochem J 309:649–656. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj3090649
Kogan G, Soltés L, Stern R, Gemeiner P (2007) Hyaluronic acid: a natural biopolymer with a broad range of biomedical and industrial applications. Biotechnol Lett 29(1):17–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-006-9219-z
Kumari K, Weigel PH (1997) Molecular cloning, expression, and characterization of the authentic hyaluronan synthase from group C Streptococcus equisimilis. J Biol Chem 272(51):32539–32546. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.51.32539
Kumari K, Baggenstoss BA, Parker AL, Weigel PH (2006) Mutation of two intramembrane polar residues conserved within the hyaluronan synthase family alters hyaluronan product size. J Biol Chem 281(17):11755–11760. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M600727200
Lai ZW, Rahim RA, Ariff A, Mohamad R (2011) Medium formulation and impeller design on the biosynthesis of high molecular weight hyaluronic acid by Streptococcus zooepidemicus ATCC 39920. Afr J Microbiol Res 5(15):2114–2123. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR11.305
Liu L, Liu YF, Li JH, Du GC, Chen J (2011) Microbial production of hyaluronic acid: current state, challenges, and perspectives. Microb Cell Factories 10 https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-10-99, 99
Mandawe J, Infanzon B, Eisele A, Zaun H, Kuballa J, Davari MD, Jakob F, Elling L, Schwaneberg U (2018) Directed evolution of hyaluronic acid synthase from Pasteurella multocida towards high-molecular weight hyaluronic acid. ChemBioChem 19(13):1414–1423. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201800093
Marcellin E, Steen JA, Nielsen LK (2014) Insight into hyaluronic acid molecular weight control. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(16):6947–6956. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5853-x
Nakajima K, Kitazume S, Angata T, Fujinawa R, Ohtsubo K, Miyoshi E, Taniguchi N (2010) Simultaneous determination of nucleotide sugars with ion-pair reversed-phase HPLC. Glycobiology 20(7):865–871. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwq044
Neuman MG, Nanau RM, Oruna-Sanchez L, Coto G (2015) Hyaluronic acid and wound healing. J Pharm Pharm Sci 18(1):53–60. https://doi.org/10.18433/J3k89d
Nho SW, Hikima J, Cha IS, Park SB, Jang HB, del Castillo CS, Kondo H, Hirono I, Aoki T, Jung TS (2011) Complete genome sequence and immunoproteomic analyses of the bacterial fish pathogen Streptococcus parauberis. J Bacteriol 193(13):3356–3366. https://doi.org/10.1128/Jb.00182-11
Notredame C, Higgins DG, Heringa J (2000) T-Coffee: a novel method for fast and accurate multiple sequence alignment. J Mol Biol 302(1):205–217. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2000.4042
Oueslati N, Leblanc P, Harscoat-Schiavo C, Rondags E, Meunier S, Kapel R, Marc I (2014) CTAB turbidimetric method for assaying hyaluronic acid in complex environments and under cross-linked form. Carbohydr Polym 112:102–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.05.039
Prasad SB, Jayaraman G, Ramachandran KB (2010) Hyaluronic acid production is enhanced by the additional co-expression of UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase in Lactococcus lactis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86(1):273–283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2293-0
Pummill PE, DeAngelis PL (2003) Alteration of polysaccharide size distribution of a vertebrate hyaluronan synthase by mutation. J Biol Chem 278(22):19808–19814. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M301097200
Puvendran K, Jayaraman G (2019) Enhancement of acetyl-CoA by acetate co-utilization in recombinant Lactococcus lactis cultures enables the production of high molecular weight hyaluronic acid. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09987-6
Ramos A, Boels IC, de Vos WM, Santos H (2001) Relationship between glycolysis and exopolysaccharide biosynthesis in Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(1):33–41. https://doi.org/10.1128/Aem.67.1.33-41.2001
Rivas M, Aragona P, Simmons P, Wang H, Wang T, Vehige J (2017) Physical properties of hyaluronic acid-based eye drops predict viscosity and potential clinical performance. Paper presented at the The 8th World Congress on Controversies in Ophthalmology (COPHy), Madrid, Spain,
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4(4):406-425
Schiraldi C, Gatta LA, Rosa DM (2010) Biotechnological production and application of hyaluronan. Biopolymers. Magdy Elnashar, IntechOpen, pp 387–412, https://doi.org/10.5772/10271
Shah MV, Badle SS, Ramachandran KB (2013) Hyaluronic acid production and molecular weight improvement by redirection of carbon flux towards its biosynthesis pathway. Biochem Eng J 80:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2013.09.013
Sheng JZ, Ling PX, Zhu XQ, Guo XP, Zhang TM, He YL, Wang FS (2009) Use of induction promoters to regulate hyaluronan synthase and UDP-glucose-6-dehydrogenase of Streptococcus zooepidemicus expression in Lactococcus lactis: a case study of the regulation mechanism of hyaluronic acid polymer. J Appl Microbiol 107(1):136–144. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04185.x
Sun JF, Wang MM, Chen YR, Shang F, Ye H, Tan TW (2012) Understanding the influence of phosphatidylcholine on the molecular weight of hyaluronic acid synthesized by Streptococcus zooepidemicus. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 168(1):47–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9320-1
Sze JH, Brownlie JC, Love CA (2016) Biotechnological production of hyaluronic acid: a mini review. 3 Biotech 6:67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-016-0379-9
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30(12):2725–2729. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197
Tlapak-Simmons VL, Kempner ES, Baggenstoss BA, Weigel PH (1998) The active streptococcal hyaluronan synthases (HASs) contain a single HAS monomer and multiple cardiolipin molecules. J Biol Chem 273(40):26100–26109. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.40.26100
Tlapak-Simmons VL, Baggenstoss BA, Clyne T, Weigel PH (1999a) Purification and lipid dependence of the recombinant hyaluronan synthases from Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus equisimilis. J Biol Chem 274(7):4239–4245. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.7.4239
Tlapak-Simmons VL, Baggenstoss BA, Kumari K, Heldermon C, Weigel PH (1999b) Kinetic characterization of the recombinant hyaluronan synthases from Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus equisimilis. J Biol Chem 274(7):4246–4253. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.7.4246
Tognana E, Padera RF, Chen F, Vunjak-Novakovic G, Freed LE (2005) Development and remodeling of engineered cartilage-explant composites in vitro and in vivo. Osteoarthr Cartil 13(10):896–905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2005.05.003
Ward PN, Field TR, Ditcham WG, Maguin E, Leigh JA (2001) Identification and disruption of two discrete loci encoding hyaluronic acid capsule biosynthesis genes hasA, hasB, and hasC in Streptococcus uberis. Infect Immun 69(1):392–399. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.69.1.392-399.2001
Waterhouse AM, Procter JB, Martin DMA, Clamp M, Barton GJ (2009) Jalview Version 2 - a multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 25(9):1189–1191. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp033
Weigel PH, Baggenstoss BA (2012) Hyaluronan synthase polymerizing activity and control of product size are discrete enzyme functions that can be uncoupled by mutagenesis of conserved cysteines. Glycobiology 22(10):1302–1310. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cws102
Westbrook AW, Ren X, Moo-Young M, Chou CP (2018) Engineering of cell membrane to enhance heterologous production of hyaluronic acid in Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol Bioeng 115(1):216–231. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26459
Widner B, Behr R, Von Dollen S, Tang M, Heu T, Sloma A, Sternberg D, DeAngelis PL, Weigel PH, Brown S (2005) Hyaluronic acid production in Bacillus subtilis. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(7):3747–3752. https://doi.org/10.1128/Aem.71.7.3747-3752.2005
Yoshida M, Itano N, Yamada Y, Kimata K (2000) In vitro synthesis of hyaluronan by a single protein derived from mouse HAS1 gene and characterization of amino acid residues essential for the activity. J Biol Chem 275(1):497–506. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.275.1.497
Yu H, Stephanopoulos G (2008) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid. Metab Eng 10(1):24–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2007.09.001
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Prof. Lars K. Nielsen from the University of Queensland for providing strain S. zooepidemicus ATCC 35246 and Dr. Mark van der Linden from the National Reference Laboratory (NRZ) on streptococcal diseases for providing genomic DNA of four streptococci. Moreover, the authors kindly thank John Mandawe from the Institute of Biotechnology, RWTH Aachen University, for helpful discussions about in vitro HA synthesis assays.
Funding
This study was partly funded by the German Federal Environmental Foundation (grant number AZ 30812-32) and by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (grant number 031B0104A). Moreover, the study was financially supported by the Strategic Partnership RWTH Aachen and IIT Madras through a travel grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 247 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schulte, S., Doss, S.S., Jeeva, P. et al. Exploiting the diversity of streptococcal hyaluronan synthases for the production of molecular weight–tailored hyaluronan. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103, 7567–7581 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10023-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10023-w