Abstract
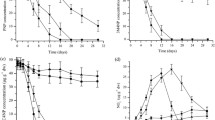
Alcaligenes faecalis strain JBW4, a strain of bacteria that is capable of degrading endosulfan, was inoculated into sterilized and natural soils spiked with endosulfan. JBW4 degraded 75.8 and 87.0 % of α-endosulfan and 58.5 and 69.5 % of β-endosulfan in sterilized and natural soils, respectively, after 77 days. Endosulfan ether and endosulfan lactone were the major metabolites that were detected by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. This result suggested that A. faecalis strain JBW4 degrades endosulfan using a non-oxidative pathway in soils. The ability of strain JBW4 to colonize endosulfan-contaminated soils was confirmed by polymerase chain reaction-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. This result suggested that strain JBW4 competed with the original inhabitants in the soil to establish a balance and successfully colonize the soils. In addition, the detoxification of endosulfan by strain JBW4 was evaluated using single-cell gel electrophoresis and by determining the soil microbial biomass carbon and enzymatic activities. The results showed that the genotoxicity and ecotoxicity of endosulfan in soil were reduced after degradation. The natural degradation of endosulfan in soil is inadequate; therefore, JBW4 shows potential for the bioremediation of industrial soils that are contaminated with endosulfan residues.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altenburger A, Ekelund F, Jacobsen CS (2010) Protozoa and their bacterial prey colonize sterile soil fast. Soil Biol Biochem 42:1636–1639
Ampe F, Omar BN, Moizan C, Wacher C, Guyot JP (1999) Polyphasic study of the spatial distribution of microorganisms in Mexican pozol, a fermented maize dough, demonstrates the need for cultivation-independent methods to investigate traditional fermentations. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(12):5464–5473
Arshad M, Hussain S, Saleem M (2008) Optimization of environmental parameters for biodegradation of alpha and beta endosulfan in soil slurry by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Appl Microbiol 104:364–370
Awasthi N, Singh AK, Jain RK, Khangarot BS, Kumar A (2003) Degradation and detoxification of endosulfan isomers by a defined co-culture of two Bacillus strains. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 62:279–283
Bajaj A, Pathak A, Mudiam MR, Mayilrajand S, Manickam N (2010) Isolation and characterization of a Pseudomonas sp. strain IITR01 capable of degrading α-endosulfan and endosulfansulfate. J Appl Microbiol 109:2135–2143
Chakrabarty S, Rajakumar A, Raghuveer K, Sridevi P, Mohanachary A, Prathibha Y, Bashyam L, Dutta-Gupta A, Senthilkumaran B (2012) Endosulfan and flutamide, alone and in combination, target ovarian growth in juvenile catfish, Clarias batrachus. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C 155:491–497
Dolci P, Zenato S, Pramotton R, Barmaz A, Alessandria V, Rantsiou K, Cocolin L (2012) Cheese surface microbiota complexity: RT-PCR-DGGE, a tool for a detailed picture? Int J Food Microbiol 162:8–12
Goswami S, Singh DK (2009) Biodegradation of α and β endosulfan in broth medium and soil microcosm by bacterial strain Bordetella sp. B9. Biodegradation 20:199–207
Goswami S, Vig K, Dileep K (2009) Biodegradation of α and β endosulfan by Aspergillus sydoni. Chemosphere 75:883–888
Gu Y, Zhang X, Tu S, Lindstro K (2009) Soil microbial biomass, crop yields, and bacterial community structure as affected by long-term fertilizer treatments under wheat-rice cropping. Eur J Soil Biol 45:239–246
Horne I, Sutherland TD, Harcourt RL, Russell R, Oakeshott JG (2002) Identification of an opd (Organophosphate Degradation) gene in an Agrobacterium isolate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 68:3371–3376
Huang H, Zhang S, Wu N, Luo L, Christie P (2009) Influence of Glomus etunicatum/Zea mays mycorrhiza on atrazine degradation, soil phosphatase and dehydrogenase activities, and soil microbial community structure. Soil Biol Biochem 41:726–734
Hussain S, Arshad M, Saleem M, Khalid A (2007) Biodegradation of α- and β-endosulfan by soil bacteria. Biodegradation 18:731–740
Kalam A, Tah J, Mukherjee AK (2004) Pesticide effects on microbial population and soil enzyme activities during vermicomposting of agricultural waste. J Environ Biol 25(2):201–208
Kataoka R, Takagi K, Sakakibara F (2011) Biodegradation of endosulfan by Mortieralla sp. strain W8 in soil: influence of different substrates on biodegradation. Chemosphere 85:548–552
Kaushik A, Sharma HR, Jain S, Dawra S, Kaushik CP (2010) Pesticide pollution of river Ghaggar in Haryana, India. Environ Monit Assess 160:61–69
Końca K, Lankoff A, Banasik A, Lisowska H, Kuszewski T, Gózdz S, Koza Z, Wojcik A (2003) A cross-platform public domain PC image-analysis program for the comet assay. Mutat Res 534:15–20
Kong LF, Zhu SY, Zhu LS, Xie H, Su KC, Yan TX, Wang J, Wang JH, Wang FH, Sun FX (2013) Biodegradation of the organochlorine pesticide endosulfan by the bacterial strain Alcaligenes faecalis JBW4. J Environ Sci. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(12)60288-5
Kumar K, Saravana S, Krishnamurthi K, Kanade GS, Chakrabarti T (2007) Enrichment and isolation of endosulfan degrading and detoxifying bacteria. Chemosphere 68:317–322
Kumar M, Lakshmi VC, Khanna S (2008) Biodegradation and bioremediation of endosulfan contaminated soil. Bioresource Technol 99:3116–3122
Kumar A, Nayak AK, Shukla AK, Panda BB, Raja R, Shahid M, Tripathi R, Mohanty S, Rath PC (2012) Microbial biomass and carbon mineralization in agricultural soils as affected by pesticide addition. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 88:538–542
Kwon GS, Kim JE, Kim TK, Sohn HY, Koh SC, Shin KS, Kim DG (2002) Klebsiella pneumoniae KE-1 degrades endosulfan without formation of the toxic metabolite, endosulfan sulfate. FEMS Microbiol Lett 215:255–259
Kwon GS, Sohn HY, Shin KS, Kim E, Seo BI (2005) Biodegradation of the organochlorine insecticide, endosulfan, and the toxic metabolite, endosulfan sulfate, by Klebsiellaoxytoca KE-8. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:845–850
Lecomte J, Arnaud M, Hijri M (2011) Isolation and identification of soil bacteria growing at the expense of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. FEMS Microbiol Lett 317:43–51
Li W, Dai Y, Xue BB, Li YY, Peng X, Zhangg JS, Yan YC (2009) Biodegradation and detoxification of endosulfan in aqueous medium and soil by Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain CS5. J Hazard Mater 167:209–216
Lubick N (2010) Endosulfan’s exit: US EPA pesticide review leads to a ban. Science 328:1466
OECD (1996) Guideline for testing of chemicals. OECD, Paris, pp 62–76
Omar SA, Abdel-Sater MA (2001) Microbial populations and enzyme activities in soil treated with pesticides. Water Air Soil Poll 127:49–63
Rao D, Skovhus T, Tujula N, Holmstro C, Dahllo I, Webb JS, Kjelleberg S (2010) Ability of Pseudoalteromonas tunicata to colonize natural biofilms and its effect on microbial community structure. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 73:450–457
Sannino F, Gianfreda L (2001) Pesticide influence on soil enzymatic activities. Chemosphere 45:417–425
Sheu C, Wu CY, Chen SC, Lo CC (2008) Extraction of DNA from soil for analysis of bacterial diversity in transgenic and nontransgenic papaya sites. J Agric Food Chem 56:11969–11975
Shivaramaiah HM, Kennedy IR (2006) Biodegradation of endosulfan by a soil bacterium. J Environ Sci Health B 41:895–905
Shivaramaiah HM, Sanchez-Bayo F, Al-Rifai J, Kennedy IR (2005) The fate of endosulfan in water. J Environ Sci Health B 40:711–720
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191
Song Y, Zhu LS, Wang J, Wang JH, Liu W, Xie H (2009) DNA damage and effects on antioxidative enzymes in earthworm (Eisenia foetida) induced by atrazine. Soil Biol Biochem 41:905–909
Sparling GP (1992) Ratio of microbial biomass carbon to soil organic carbon as a sensitive indicator of changes in soil organic matter. Aust J Soil Res 30(2):195–207
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987) An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 19:703–707
Verma A, Ali D, Farooq M, Pant AB, Hans RK (2011) Expression and inducibility of endosulfan metabolizing gene in Rhodococcus strain isolated from earthworm gut microflora for its application in bioremediation. Bioresource Technol 102:2979–2984
Weber J, Halsall C, Muir D, Teixeira C, Small J, Solomon K, Hermanson M, Hung H, Bidleman T (2010) Endosulfan, a global pesticide: a review of its fate in the environment and occurrence in the Arctic. Sci Total Environ 408:2966–2984
Weir KM, Sutherland TD, Horne I, Russell R, Oakeshott JG (2006) A single monooxygenase, ese, is involved in the metabolism of the organochlorides endosulfan and endosulfate in an Arthrobacter sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:3524–3530
Wu J, Joergensen RG, Pommerening B, Chaussod R, Brookes PC (1990) Measurement of soil microbial biomass C by fumigation–extraction—an automated procedure. Soil Bio Biochem 22:1167–1169
Yang C, Sun T, He W, Zhou Q, Chen S (2007) Single and joint effects of pesticides and mercury on soil urease. J Environ Sci 19:210–216
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41071164, 21277083, 40801203, and 41001152) and the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20113702110007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, L., Zhu, S., Zhu, L. et al. Colonization of Alcaligenes faecalis strain JBW4 in natural soils and its detoxification of endosulfan. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 1407–1416 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5033-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5033-4