Abstract
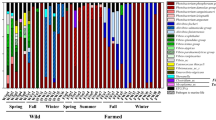
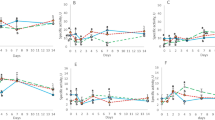
The commensal microbiota plays an important role in the well-being of the host organism, and it would be worthwhile to know the tenacious communities among them. Therefore, a study was undertaken to examine the changes in constitution of the intestinal microbiota of wild fish consequential to captivity. At first, the composition of intestinal microorganisms of Atlantic cod caught from the coastal area off Bodø, Norway, was examined. Thereafter, the changes in the bacterial community of the captive fish after offering them artificial feed or subjecting them to starvation were studied. The microbiota from the intestinal contents and wall segments were analyzed quantitatively by spread plate technique and DAPI staining and qualitatively by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. The study revealed that the counts of intestinal microbes in wild-caught Atlantic cod were not affected by captive rearing for 6 weeks, either when fed or when starved. However, the diversity of intestinal bacterial community was reduced in response to artificial feeding, whereas the change was restricted upon starvation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bairagi A, Ghosh KS, Kumar S, Sen SK, Ray AK (2002) Enzyme producing bacterial flora isolated from fish digestive tracts. Aquac Int 10:109–121
Bergh O (1995) Bacteria associated with early-life stages of halibut, Hippoglossus hippoglossus L, inhibit growth of a pathogenic Vibrio sp. J Fish Dis 18:31–40
Boon N, De Windt W, Verstraete W, Top EM (2002) Evaluation of nested PCR-DGGE (denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis) with group-specific 16S rRNA primers for the analysis of bacterial communities from different wastewater treatment plants. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 39:101–112
Brunvold L, Sandaa RA, Mikkelsen H, Welde E, Bleie H, Bergh O (2007) Characterisation of bacterial communities associated with early stages of intensively reared cod (Gadus morhua) using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE). Aquaculture 272:319–327
Caipang CMA, Brinchmann MF, Kiron V (2009) Antagonistic activity of bacterial isolates from intestinal microbiota of Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua and an investigation of their immunomodulatory capabilities. Aquac Res 41:249–256
Casamayor EO, Schafer H, Baneras L, Pedros-Alio C, Muyzer G (2000) Identification of and spatiotemporal differences between microbial assemblages from two neighboring sulfurous lakes: comparison by microscopy and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:499–508
Cebron A, Coci M, Garnier J, Laanbroek HJ (2004) Denaturing gradient gel electrophoretic analysis of ammonia oxidizing bacterial community structure in the lower Seine river: impact of Paris wastewater effluents. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6726–6737
Chang JY, Antonopoulos DA, Kalra A, Tonelli A, Khalife WT, Schmidt TM, Young VB (2008) Decreased diversity of the fecal microbiome in recurrent Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea. J Infect Dis 197:435–438
Ercolini D (2004) PCR-DGGE fingerprinting: novel strategies for detection of microbes in food. J Microbiol Methods 56:297–314
Fjellheim AJ, Playfoot KJ, Skjermo J, Vadstein O (2007) Vibrionaceae dominates the microflora antagonistic towards Listonella anguillarum in the intestine of cultured Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) larvae. Aquaculture 269:98–106
Frantzen JF, Gregersen F (2006) More money in live storage. More money in live storage, Newsletter: Fiskeriforskning Info, vol.10. http://en.fiskforsk.norut.no/nofima/publikasjoner/infobrev.
Gomez GD, Balcazar JL (2008) A review on the interactions between gut microbiota and innate immunity of fish. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 52:145–154
Griffiths S, Melville K, Cook M, Vincent S, St Pierre M, Lanteigne C (2001) Profiling of bacterial species associated with haddock larviculture by PCR amplification of 16S rDNA and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. J Aquat Anim Health 13:355–363
Hansen GH, Strom E, Olafsen JA (1992) Effect of different holding regimens on the intestinal microflora of herring (Clupea harengus) larvae. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:461–470
Holben WE, Williams P, Saarinen M, Sarkilahti LK, Apajalahti JHA (2002) Phylogenetic analysis of intestinal microflora indicates a novel Mycoplasma phylotype in farmed and wild salmon. Microb Ecol 44:175–185
Hovda MB, Lunestad BT, Fontanillas R, Rosnes JT (2007) Molecular characterisation of the intestinal microbiota of farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 272:581–588
Huber I, Spanggaard B, Appel KF, Rossen L, Nielsen T, Gram L (2004) Phylogenetic analysis and in situ identification of the intestinal microbial community of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum). J Appl Microbiol 96:117–132
Kepner RL, Pratt JR (1994) Use of fluorochromes for direct enumeration of total bacteria in environmental samples - past and present. Microbiol Rev 58:603–615
Kostanjšek R, Štrus J, Avguštin G (2007) “Candidatus Bacilloplasma”, a novel lineage of Mollicutes associated with the hindgut wall of the terrestrial isopod Porcellio scaber (Crustacea: Isopoda). Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5566–5573
Lazado CC, Caipang CMA, Gallage S, Brinchmann MF, Kiron V (2009) Expression profiles of genes associated with immune response and oxidative stress in Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua head kidney leukocytes modulated by live and heat-inactivated intestinal bacteria. Comp Biochem Physiol B 155:249–255
Ley RE, Hamady M, Lozupone C, Turnbaugh PJ, Ramey RR, Bircher JS, Schlegel ML, Tucker TA, Schrenzel MD, Knight R, Gordon JI (2008) Evolution of mammals and their gut microbes. Science 320:1647–1651
Lindsay GJH, Gooday GW (1985) Chitinolytic enzymes and the bacterial microflora in the digestive tract of cod, Gadus morhua. J Fish Biol 26:255–265
Muyzer G, Dewaal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction amplified genes coding for 16S ribosomal RNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Muyzer G, Smalla K (1998) Application of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) and temperature gradient gel electrophoresis (TGGE) in microbial ecology. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 73:127–141
Muyzer G, Teske A, Wirsen CO, Jannasch HW (1995) Phylogenetic relationships of Thiomicrospira species and their identification in deep sea hydrothermal vent samples by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis of 16S rDNA fragments. Arch Microbiol 164:165–172
Olafsen JA, Hansen GH (1992) Intact antigen uptake in intestinal epithelial cells of marine fish larvae. J Fish Biol 40:141–156
Ramirez RF, Dixon BA (2003) Enzyme production by obligate intestinal anaerobic bacteria isolated from oscars (Astronotus ocellatus), angelfish (Pterophyllum scalare) and southern flounder (Paralichthys lethostigma). Aquaculture 227:417–426
Ringø E, Bendiksen HR, Wesmajervi MS, Olsen RE, Jansen PA, Mikkelsen H (2000) Lactic acid bacteria associated with the digestive tract of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). J Appl Microbiol 89:317–322
Ringø E, Olsen RE (1999) The effect of diet on aerobic bacterial flora associated with intestine of Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus L.). J Appl Microbiol 86:22–28
Ringø E, Olsen RE, Mayhew TM, Myklebust R (2003) Electron microscopy of the intestinal microflora of fish. Aquaculture 227:395–415
Ringø E, Sinclair PD, Birkbeck H, Barbour A (1992) Production of eicosapentaenoic acid (20-5 n-3) by Vibrio pelagius isolated from turbot (Scophthalmus maximus (L)) larvae. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:3777–3778
Ringø E, Sperstad S, Myklebust R, Refstie S, Krogdahl A (2006) Characterisation of the microbiota associated with intestine of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) - The effect of fish meal, standard soybean meal and a bioprocessed soybean meal. Aquaculture 261:829–841
Romero J, Navarrete P (2006) 16S rDNA-based analysis of dominant bacterial populations associated with early life stages of coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Microb Ecol 51:422–430
Rosenlund G, Skretting M (2006) Worldwide status and perspective on gadoid culture. ICES J Mar Sci 63:194–197
Sakata T, Okabayashi J, Kakimoto D (1980) Microflora in the alimentary tract of tilapia.1. Variations in the intestinal microflora of tilapia reared in fresh and sea water. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 46:313–317
Sakata T, Sugita H, Mitsuoka T, Kakimoto D, Kadota H (1980) Microflora in the gastrointestinal tracts of fresh water fish.1. Isolation and distribution of obligate anaerobic bacteria from the intestines of fresh water fish. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 46:1249–1255
Samuelsen OB, Nerland AH, Jorgensen T, Schroder MB, Swasand T, Bergh O (2006) Viral and bacterial diseases of Atlantic cod Gadus morhua, their prophylaxis and treatment: a review. Dis Aquat Organ 71:239–254
Sandaa RA, Brunvold L, Magnesen T, Bergh O (2008) Monitoring the opportunistic bacteria Pseudoalteromonas sp LT-13 in a great scallop, Pecten maximus hatchery. Aquaculture 276:14–21
Sandaa RA, Magnesen T, Torkildsen L, Bergh O (2003) Characterisation of the bacterial community associated with early stages of great scallop (Pecten maximus), using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE). Syst Appl Microbiol 26:302–311
Seeto GS, Veivers PC, Clements KD, Slaytor M (1996) Carbohydrate utilisation by microbial symbionts in the marine herbivorous fishes Odax cyanomelas and Crinodus lophodon. J Comp Physiol (B) 165:571–579
Simpson JM, McCracken VJ, White BA, Gaskins HR, Mackie RI (1999) Application of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis for the analysis of the porcine gastrointestinal microbiota. J Microbiol Methods 36:167–179
Smith CJ, Danilowicz BS, Meijer WG (2007) Characterization of the bacterial community associated with the surface and mucus layer of whiting (Merlangius merlangus). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 62:90–97
Spanggaard B, Huber I, Nielsen J, Nielsen T, Appel KF, Gram L (2000) The microflora of rainbow trout intestine: a comparison of traditional and molecular identification. Aquaculture 182:1–15
Sugita H, Kawasaki J, Deguchi Y (1997) Production of amylase by the intestinal microflora in cultured freshwater fish. Lett Appl Microbiol 24:105–108
Sugita H, Miyajima C, Deguchi Y (1991) The vitamin B12 producing ability of the intestinal microflora of fresh water fish. Aquaculture 92:267–276
Sugita H, Shibuya K, Hanada H, Deguchi Y (1997) Antibacterial abilities of intestinal microflora of the river fish. Fish Sci 63:378–383
Svasand T, Ottera H, Taranger GL (2004) Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). In: Moksness E, Kjorsvik E, Olsen Y (eds) Culture of cold-water marine fish. Fishing news books, Blackwell Science Ltd, Oxford, pp 433–444
Uchii K, Matsui K, Yonekura R, Tani K, Kenzaka T, Nasu M, Kawabata Z (2006) Genetic and physiological characterization of the intestinal bacterial microbiota of bluegill (Lepomis macrochirus) with three different feeding habits. Microb Ecol 51:277–284
Verner-Jeffreys DW, Shields RJ, Bricknell IR, Birkbeck TH (2003) Changes in the gut-associated microflora during the development of Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus L.) larvae in three British hatcheries. Aquaculture 219:21–42
Westerdahl A, Olsson JC, Kjelleberg S, Conway PL (1991) Isolation and characterization of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) associated bacteria with inhibitory effects against Vibrio anguillarum. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:2223–2228
Willems A, Moore WEC, Weiss N, Collins MD (1997) Phenotypic and phylogenetic characterization of some Eubacterium-like isolates containing a novel type B wall murein from human feces: description of Holdemania filiformis gen. nov., sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:1201–1204
Acknowledgments
This research is part of the master’s thesis of the first author, funded in parts by Bodø University College and by Research Council of Norway (Project176528/V10). The authors would like to thank Morten Krogstad, Engineer, Mørkvedbukta Research Station, for procuring the experimental animals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Fig. S1
The lanes and bands identified in the Gel W using Quantity One® program. The gel has DGGE profiles generated from intestinal bacteria of wild Atlantic cod obtained from posterior wall samples. Lanes 1 and 17: markers (M); lanes 2–6: fish soon after capture (I1–I5); lanes 7–11: kept unfed in captivity (U1–U5); lanes 12–16: reared in captivity with artificial feed (F1–F5). (PPT 200 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhanasiri, A.K.S., Brunvold, L., Brinchmann, M.F. et al. Changes in the Intestinal Microbiota of Wild Atlantic cod Gadus morhua L. Upon Captive Rearing. Microb Ecol 61, 20–30 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-010-9673-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-010-9673-y