Abstract
Introduction
This study aims to review the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) aspects of a large series of patients with focal cortical dysplasia type II (FCD II) and attempt to identify distinctive features in the two histopathological subtypes IIa and IIb.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the MRI scans of 118 patients with histological proven FCD IIa (n = 37) or IIb (n = 81) who were surgically treated for intractable epilepsy.
Results
MRI was abnormal in 93 patients (79 %) and unremarkable in 25 (21 %). A dysplastic lesion was identified in 90 cases (97 %) and classified as FCD II in 83 and FCD non-II in seven cases. In three cases, the MRI diagnosis was other than FCD. There was a significant association between the presence of cortical thickening (p = 0.002) and the “transmantle sign” (p < 0.001) and a correct MRI diagnosis of FCD II. MRI positivity was more frequent in the patients with FCD IIb than in those with FCD IIa (91 % vs. 51 %), and the detection rate of FCD II was also better in the patients with type IIb (88 % vs. 32 %). The transmantle sign was significantly more frequent in the IIb subgroup (p = 0.003).
Conclusions
The rates of abnormal MRI results and correct MRI diagnoses of FCD II were significantly higher in the IIb subgroup. Although other MRI stigmata may contribute to the diagnosis, the only significant correlation was between the transmantle sign and FCD IIb.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tassi L, Colombo N, Garbelli R et al (2002) Focal cortical dysplasia: neuropathological subtypes, EEG, neuroimaging and surgical outcome. Brain 125:1719–1732
Palmini A, Najm I, Avanzini G et al (2004) Terminology and classification of the cortical dysplasias. Neurology 62:S2–S8
Barkovich AJ, Kuzniecky RI, Jackson GD, Guerrini R, Dobyns WB (2005) A developmental and genetic classification for malformations of cortical development. Neurology 65:1873–1887
Blumcke I, Thom M, Aronica E et al (2011) The clinicopathologic spectrum of focal cortical dysplasias: a consensus classification proposed by an ad hoc task force of the ILAE diagnostic methods commission (1). Epilepsia 52:158–174
Berg AT, Vickrey BG, Langfitt JT et al (2003) The multicenter study of epilepsy surgery: recruitment and selection for surgery. Epilepsia 44(11):1425–1433
Bien CG, Szinay M, Wagner J, Clusmann H, Becker AJ, Urbach H (2009) Characteristics and surgical outcomes of patients with refractory magnetic resonance imaging-normal epilepsies. Arch Neurol 66(12):1491–1499
Bronen RA, Vives KP, Kim JH, Fulbright RK, Spencer SS, Spencer DD (1997) Focal cortical dysplasia of Taylor, balloon cell subtype: MR differentiation from low-grade tumors. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:1141–1151
Colombo N, Tassi L, Galli C et al (2003) Focal cortical dysplasias: MR imaging, histopathologic, and clinical correlations in surgically treated patients with epilepsy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:724–733
Colombo N, Citterio A, Galli C et al (2003) Neuroimaging of focal cortical dysplasia: neuropathological correlations. Epileptic Disord 5(Suppl 2):S67–S72
Urbach H, Scheffler B, Heinrichsmeier T et al (2002) Focal cortical dysplasia of Taylor’s balloon cell type: a clinicopathological entity with characteristic neuroimaging and histopathological features, and favorable postsurgical outcome. Epilepsia 43(1):33–40
Ruggieri PM, Najm I, Bronen R et al (2004) Neuroimaging of the cortical dysplasias. Neurology 62:S27–S29
Lawson JA, Birchansky S, Pacheco E et al (2005) Distinct clinicopathologic subtypes of cortical dysplasia of Taylor. Neurology 64:55–61
Widdess-Walsh P, Diehl B, Najm I (2006) Neuroimaging of focal cortical dysplasia. J Neuroimaging 16:185–196
Fauser S, Schulze-Bonhage A, Honegger J et al (2004) Focal cortical dysplasias: surgical outcome in 67 patients in relation to histological subtypes and dual pathology. Brain 127:2406–2418
Krsek P, Maton B, Korman B et al (2008) Different features of histopathological subtypes of pediatric focal cortical dysplasia. Ann Neurol 63:758–769
Krsek P, Pieper T, Karlmeier A et al (2009) Different presurgical characteristics and seizure outcomes in children with focal cortical dysplasia type I or II. Epilepsia 50:125–137
Colombo N, Salamon N, Raybaud C, Ozkara C, Barkovich AJ (2009) Imaging of malformations of cortical development. Epileptic Disord 11:194–205
Besson P, Andermann F, Dubeau F, Bernasconi A (2008) Small focal cortical dysplasia lesions are located at the bottom of a deep sulcus. Brain 131(Pt 12):3246–3255
Taylor DC, Falconer MA, Bruton CJ, Corsellis JA (1971) Focal dysplasia of the cerebral cortex in epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 34:369–387
Wagner J, Weber B, Urbach H, Elger CE, Huppertz HJ (2011) Morphometric MRI analysis improves detection of focal cortical dysplasia type II. Brain 134(Pt 10):2844–2854
Muhlebner A, Coras R, Kobov K et al (2012) Neuropathologic measurements in focal cortical dysplasia: validation of the ILAE 2011 classification system and diagnostic implications for MRI. Acta Neuropathol 123:259–272
Han X, Jovicich J, Salat D et al (2006) Reliability of MRI-derived measurements of human cerebral cortical thickness: the effects of field strength, scanner upgrade and manufacturer. NeuroImage 32:180–194
Kassubek J, Huppertz HJ, Spreer J, Schulze-Bonhage A (2002) Detection and localization of focal cortical dysplasia by voxel-based 3-D MRI analysis. Epilepsia 43(6):596–602
Colliot O, Antel SB, Naessens VB, Bernasconi N, Bernasconi A (2006) In vivo profiling of focal cortical dysplasia on high-resolution MRI with computational models. Epilepsia 47(1):134–142
Haidar H, Soul JS (2006) Measurement of cortical thickness in 3D brain MRI data: validation of the Laplacian method. J Neuroimaging 16(2):146–153
Bastos AC, Comeau RM, Andermann F et al (1999) Diagnosis of subtle focal dysplastic lesions: curvilinear reformatting from three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 46(1):88–94
Bernasconi A, Bernasconi N, Bernhardt BC, Schrader D (2011) Advances in MRI for ‘cryptogenic’ epilepsies. Nat Rev Neurol 7(2):99–108
Kim SK, Na DG, Byun HS et al (2000) Focal cortical dysplasia: comparison of MRI and FDG-PET. J Comput Assist Tomogr 24:296–302
Salamon N, Kung J, Shaw SJ et al (2008) FDG-PET/MRI coregistration improves detection of cortical dysplasia in patients with epilepsy. Neurology 71:1594–1601
Chassoux F, Rodrigo S, Semah F et al (2010) FDG-PET improves surgical outcome in negative MRI Taylor-type focal cortical dysplasias. Neurology 75(24):2168–2175
Acknowledgment
We thank Dr Alessio Moscato, Medical Physics Department, Ospedale Niguarda—Milano, for his assistance in imaging editing.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Key learning points
1 — Focal cortical dysplasia type II (FCD II) are highly epileptogenic lesions that are frequently associated with early-onset drug-resistant partial epilepsy (DRPE).
2 — According to the original description and to the most recent classification systems two histological subgroups of FCD II are recognized: IIa characterized by the presence of abnormal cortical dyslamination and dysmorphic neurons and IIb with additional BCs.
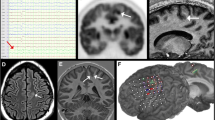
3 — The most frequent MRI features for FCD II include: increased cortical thickness, blurred gray/white matter junction on T1WI, blurred or sharp gray/white matter junction on T2WI, increased signal on T2WI and decreased signal on T1WI of the subcortical white matter and gyration anomalies. The most peculiar feature is the tapering of the WM signal alteration towards the ventricle, the so called “transmantle sign”.
4 — According to the present results, a differential MRI diagnosis between the two histopathological subgroups can be attempted. Abnormal MRI results as well as the peculiar “funnel-shaped” transmantle sign are significantly more frequent in FCD IIb.
5 — The differential MRI diagnosis has a prognostic value owing to a more favourable surgical outcome in FCD IIb.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colombo, N., Tassi, L., Deleo, F. et al. Focal cortical dysplasia type IIa and IIb: MRI aspects in 118 cases proven by histopathology. Neuroradiology 54, 1065–1077 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-012-1049-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-012-1049-1