Abstract
Aims and Background
The aim of this study was to evaluate the potential contribution of Tc-99m-MIBI scintigraphy to the follow-up of patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma, who had elevated Tg levels and negative I-131 whole-body scan results.
Materials and Methods
In this retrospective study, we evaluated 28 patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma, who had total or near total thyroidectomy followed by an ablative dose of I-131 at various time intervals (15 women, 13 men; mean age 43 ± 17 years). All patients were treated with T4 suppression. After a mean follow-up period of 6.1 years (range 3–15) all patients were determined to have a high serum Tg concentrations (>2 ng/ml) and previous negative I-131 WBS results. All patients were examined for metastatic sites using Tc-99m-MIBI scan. Scans were visually evaluated for detecting lymph node metastases and/or local recurrence, lung metastases and skeletal metastases.
Results
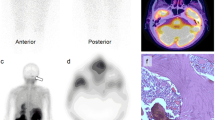
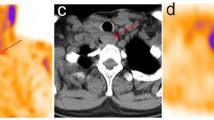
Tc-99m-MIBI scan demonstrated lesions in 23 patients (83.3%). In five patients with negative Tc-99m-MIBI scan findings (FN results): * Chest CT showed small-sized mediastinal LN metastases in 2 patients and lung metastases in another 2 patients (<1 cm). * Neck CT showed small-sized cervical LN involvement in 1 patient. The sensitivity of detection for neck was 94.4%, for lung 63.6%, and for bone lesions 100%. For all scan sites taken together, the sensitivity of disease detection was 83.3%, the specificity was 50%, positive predictive value (PPV) was 96.2%, and finally negative predictive value (NPV) was 16.7%.
Conclusion
We concluded that Tc-99m-MIBI scan should be considered as a supplementary scintigraphic method for the follow-up of patients with high serum Tg levels and negative I-131 WBS results, and it can help clinicians in making the decision to treat these patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeGroot LJ, Kaplan EL, McCormik M, et al. Natural history, treatment, and course of papillary thyroid carcinoma.J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997; 71: 414–424.
Gilliland FD, Hunt WC, Morris DM, et al. Prognostic factors for thyroid carcinoma.Cancer 1997; 79: 564–573.
Mazzaferri EL. Papillary thyroid carcinoma: factors influencing prognosis and current therapy.Sem Oncol 1987; 14: 315–332.
Saaman NA, Maheshwari YK, Narder Sİ, et al. Impact of therapy for differentiated carcinoma of the thyroid: an analysis of 706 cases.J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1983; 56: 1131–1138.
Thoresen SO, Akslen LA, Glattre E, et al. Survival and prognostic factors in differentiated thyroid cancer, a multi-variate analysis of 1055 cases.Br J Cancer 1989; 59: 231–235.
Ronga G, Fiorentino A, Paserio E, et al. Can iodine-131 whole body scan be replaced by thyroglobulin measurement in the post-surgical follow-up of differentiated thyroid carcinoma?J Nucl Med 1990; 31: 1766–1771.
Lubin E, Mechlis-Frisch S, Zatz S, et al. Serum thyroglobulin and iodine-131 whole body scan in the diagnosis and assessment of treatment for metastatic differentiated thyroid carcinoma.J Nucl Med 1994; 35: 257–262.
Roelants V, De Nayer P, Bouckaert A, et al. The predictive value of serum thyroglobulin in the follow-up of differentiated thyroid cancer.Eur J Nucl Med 1997; 24: 722–727.
Filesi M, Signore A, Ventroni O, et al.Role of initial iodine-131 whole body scan and serum thyroglobulin in the follow-up of differentiated thyroid carcinoma metastases.J Nucl Med 1998; 39: 1542–1546.
Galloway RJ, Smallridge RC. Imaging in thyroid cancer.Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 1996; 25: 93–113.
Saaman NA, Schultz PN, Haynie TP, et al. Pulmonary metastasis of differentiated thyroid carcinoma: treatment results in 101 patients.J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1985; 60: 376–380.
Elser H, Henze M, Hermann C, et al. Tc-99m-MIBI for recurrent and metastatic differentiated thyroid carcinoma.Nuklearmedizin 1997; 36: 7–12.
Miyamoto S, Kasagi K, Misaki T, et al. Evaluation of technetium-99m-MIBI scintigraphy in metastatic differentiated thyroid carcinoma.J Nucl Med 1997; 38: 352–356.
Ugur O, Kostakoglu L, Caner B, et al. Comparison of Tl-201, Tc-99m-MIBI and I-131 imaging in the follow-up of patients with well-differentiated thyroid carcinoma.Nucl Med Commun 1996; 17: 373–377.
Piwnica-Worms D, Holman LB. Noncardiac application of hexakis(alkyl-isonitrile) technetium-99m complexes (Editorial).J Nucl Med 1990; 31: 1166–1167.
Chiu ML, Kronauge JF, Piwnica Worms D. Effect of mitochondrial and plasma membrane potentials on accumulation of hexakis(2-methoxyisobutyl-isonitrile) technetium in cultured mouse fibroblast.J Nucl Med 1990; 31: 1646–1653.
Grunwald F, Menzel C, Bender H, et al. Comparison of18FDG-PET with131iodine and99mTc-sestamibi scintigraphy in differentiated thyroid cancer.Thyroid 1997; 7: 327–335.
Fridrich L, Messa C, Landoni C, et al. Whole-body scintigraphy with99mTc-sestamibi,18F-FDG and131I in patient with metastatic thyroid carcinoma.Nucl Med Commun 1997; 18: 3–9.
Dadparvar S, Chevres A, Tulchinsky M, et al. Clinical utility of technetium-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile imaging in differentiated thyroid carcinoma: comparison with thallium-201 and iodine-131 scintigraphy, and serum thyroglobulin quantitation.Eur J Nucl Med 1995; 22: 1330–1338.
Casara D, Rubello D, Saladini G, et al. Different features of pulmonary metastases in differentiated thyroid cancer: natural history and multivariate statistical analysis of prognostic variables.J Nucl Med 1993; 34: 1626–1631.
Marcocci C, Pacini F, Elisei R, et al. Clinical and biologic behaviour of bone metastases from differentiated thyroid carcinoma.Surgery 1989; 106: 960–966.
Schlumberger M, Tubiana M, De Vathaire F, et al. Long-term results of treatment of 283 patients with lung and bone metastases from differentiated thyroid carcinoma.J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1986; 63: 960–970.
Girelli ME, Busnardo B, Amerio R, et al. Serum thyroglobulin levels in patients with well differentiated thyroid cancer during suppressive therapy: study on 429 patients.Eur J Nucl Med 1985; 10: 252–256.
Pacini F, Lippi F, Formica N, et al. Therapeutic doses of iodine-131 reveal undiagnosed metastases in thyroid cancer with detectable serum thyroglobulin levels.J Nucl Med 1987; 28: 1888–1891.
Briele B, Hotze A, Kopp J, et al. Comparison of201Tl and99mTc-MIBI in the follow-up of differentiated thyroid carcinomas.Nuclearmedizin 1991; 30: 115–124.
Yen TC, Lin HD, Lee CH, et al. The role of technetium-99m sestamibi whole-body scans in diagnosing metastatic Hürthle cell carcinoma of the thyroid gland after total thyroidectomy: comparison with iodine-131 and thallium-201 whole body scans.Eur J Nucl Med 1994; 21: 980–983.
Nemec J, Nyvltova O, Blazek T, Vlcek P, Racek P, Novak Z, et al. Positive thyroid cancer scintigraphy using technetium-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile.Eur J Nucl Med 1996; 23: 69–71.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KüÇük, N.Ö., Kulak, H.A. & Aras, G. Clinical importance of technetium-99m-methoxyisobutylisonitrile (MIBI) scintigraphy in differentiated thyroid carcinoma patients with elevated thyroglobulin levels and negative I-131 scanning results. Ann Nucl Med 20, 393–397 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03027374
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03027374