Summary
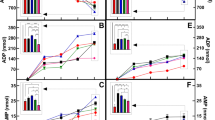
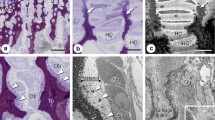
The ultrastructure of crystal formationin vitro associated with extracellular membranebound matrix vesicles (MV) isolated from rat incisor pulp was studied in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) supplemented with an organic phosphate, Na-β-glycerophosphate (BGP). Matrix vesicles were isolated from basal regions of the pulps using a collagenase digestion and ultracentrifugation method. Isolated MV contained alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity and had diameters of 30–200 nm. Membrane structures of the isolated MV were well preserved. Incubation of MV in DMEM in the presence of BGP caused the development of bilaminar electron densities associated with the vesicle membrane. These preceded crystal deposition which was observed in the culture medium after 3 days. Both heat-inactivated MV incubated with BGP, and fresh MV incubated in the absence of BGP failed to show crystal formation, even after 3 days. Staining of demineralized sections of mineralized MV with uranyl acetate and lead citrate, revealed numerous needle-like structures similar in shape to the untreated crystals. Electron diffraction patterns of the newly formed crystals revealed a pattern consistent with hydroxyapatite. The requirement of BGP for mineralization of these MV and the long lag time before crystal formation is probably due to the low calcium (Ca)×inorganic phosphate (Pi) ion product in the original medium. The requirement of ALP activity which would cause hydrolysis of BGP and a rise in Pi would favor the precipitation of biologic apatite from the culture medium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonucci E (1967) Fine structure of early cartilage calcification. J Ultrastruct Res 20:33–50
Anderson HC (1969) Vesicles associated with calcification in the matrix of epiphyseal cartilage. J Cell Biol 41:59–72
Bonucci E (1971) The locus of initial calcification in cartilage and bone. Clin Orthop 78:108–139
Bernard GW (1972) Ultrastructual observations of initial calcification in dentine and enamel. J Ultrastruct Res 41:1–17
Eisenmann DR, Glick PL (1972) Ultrastructure of initial crystal formation in dentin. J Ultrastruct Res 41:18–28
Sisca RF, Provenza DV (1972) Initial dentin formation in human deciduous teeth. An electron microscopic study. Calcif Tissue Res 9:1–16
Larsson Å, Bloom GD (1973) Studies on dentinogenesis in the rat. Fine structure of developing odontoblasts and predentin in relation to the mineralization process. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch 139:227–246
Hayashi Y (1985) Ultrastructural characterization of extracellular matrix vesicles in the mineralizing fronts of apical cementum in cats. Arch Oral Biol 30:445–449
Hayashi Y (1987) Ultrastructure of cementum formation on partially formed teeth in dogs. Acta Anat 129:279–288
Kim KK, Huang S-H (1971) Ultrastructural study of calcification on human aortic valve. Lab Invest 25:357–366
Muhlrad A, Stein H, Bab IA, Sela J (1978) Fine structure and enzymes of matrix vesicles in osteosarcoma: possible occurrence of contractile proteins. Metab Bone Dis Rel Res 1:227–233
Einhorn TA, Gordon SL, Siegel SA, Hummel CF, Avitable MJ, Carty RP (1985) Matrix vesicle enzymes in human osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res 3:160–169
Miller GJ, DeMarzo AM (1988) Ultrastructural localization of matrix vesicles and alkaline phosphatase in the rat chondrosarcoma: their role in cartilage calcification. Bone 9:235–241
Sela J, Bab IA, Muhlrad A (1978) Ultrastructural and biochemical characterization of extracellular matrix vesicles in healing alveolar bone sockets: preliminary indications for the presence of contractile proteins. Metab Bone Dis Rel Res 1:185–191
Sela J, Tamari I, Hirschfeld Z, Bab IA (1981) Transmission electron microscopy of reparative dentin in rat molar pulps. Primary mineralization via extracellular matrix vesicles. Acta Anat 109:247–251
Hayashi Y (1982) Ultrastructure of initial calcification in wound healing following pulpotomy. J Oral Pathol 11:174–180
Hirschfeld Z, Bab I, Tamari I, Sela J (1982) Primary mineralization of dentin in rats after pulp capping with calcium-hydroxide. J Oral Pathol 11:426–433
Sela J, Amir D, Schwartz Z, Weinberg H (1987) Changes in the distribution of extracellular matrix vesicles during healing of rat tibial bone (computerized morphometry and electron microscopy). Bone 8:245–250
Schwartz Z, Amir D, Weinberg H, Sela J (1987) Extracellular matrix vesicle distribution in primary mineralization two week after injury to rat tibia bone (ultrastructural tissue morphometry). Eur J Cell Biol 45:97–101
Amir D, Schwartz Z, Sela J, Weinberg H (1988) The relationship between extracellular matrix vesicles and the calcifying front on the 21st day after injury to rat tibial bone. Clin Orthop 230:289–295
Ali SY, Sajdera SW, Anderson HC (1970) Isolation and characterization of calcifying matrix vesicles from epiphyseal cartilage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 67:1513–1520
Ali SY, Evans L (1973) The uptake of [45Ca] calcium ions by matrix vesicles from calcifying cartilage. Biochem J 134:647–650
Ali SY (1976) Analysis of matrix vesicles and their role in the calcification of epiphyseal cartilage. Fed Proc 35:135–142
Hsu HHT, Anderson HC (1977) A simple and defined method to study calcification by isolated matrix vesicles. Effect of ATP and vesicle phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta 500:162–172
Hsu HHT, Anderson HC (1978) Calcification of isolated matrix vesicles and resonstituted vesicles from fetal bovine cartilage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:3805–3808
Wuthier RE, Linder RE, Warner GP, Gore ST, Borg TK (1978) Non-enzymatic isolation of matrix vesicles: characterization and initial studies on45Ca and32P-orthophosphate metabolism. Metab Bone Dis Rel Res 1:125–136
Hsu HHT, Cecil RNA, Anderson HC (1978) Role of adenosine triphosphatase, phospholipids, and vesicular structure in the calcification of isolated and reconstituted matrix vesicles. Metab Bone Dis Rel Res 1:169–172
Murphree S, Hsu HHT, Anderson HC (1982) In vitro formation of crystalline apatite by matrix vesicles isolated from rachitic rat epiphyseal cartilage. Calcif Tissue Int. 34:S62-S68
Warner GP, Hubbard HL, Lloyd GC, Wuthier RE (1983) Pi-Ca-metabolism by matrix vesicle-enriched microsomes prepared from chicken epiphyseal cartilage by isosmotic percoll density-gradient fraction. Calcif Tissue Int 35:327–338
Ali SY, Evans L, Griffiths S (1984) Mechanism of physiological calcification. In: Cohn DV, Potts JT, Fujita T (eds) Endocrine control of bone and calcium metabolism. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 406–409
Hsu HHT, Anderson HC (1986) The deposition of calcium pyrophosphate by NTP pyrophosphohydrolase of matrix vesicles from fetal bovine epiphyseal cartilage. Int J Biochem 18:1141–1146
McLean FM, Keller PJ, Genge BR, Walters SA, Wuthier RE (1987) Deposition of preformed mineral in matrix vesicles. J Biol Chem 262:10481–10488
Sudo H, Kodama H, Amagai Y, Itakura Y, Yamamoto S (1986) Mineralized tissue formation by MC3T3-E1 osteogenic cells embedded in three-dimensional gell matrix. In: Ali SY (ed) Cell mediated calcification and matrix vesicles. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 291–296
Nefussi J-R, Boy-Lefevre ML, Boulekbache H, Forest N (1985) Mineralization in vitro of matrix formed by osteoblasts isolated by collagenase digestion. Differentiation 29:160–168
Peterson GL (1977) A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem 83:346–356
Bonucci E, Reurink J (1978) The fine structure of decalcified cartilage and bone: A comparison between decalcification procedures performed before and after embedding. Calcif Tissue Res 25:179–190
Tenenbaum HC (1981) Role of organic phosphate in mineralization of bone in vitro. J Dent Res 60(C):1586–1589
Tenenbaum HC, Heersche JNM (1982) Differentiation of osteoblasts and formation of mineralized bone in vitro. Calcif Tissue Int 34:76–79
Ecarot-Charrier B, Glorieux FH, van der Rest M, Pereira G (1983) Osteoblasts isolated from mouse calvaria initiate matrix mineralization in culture. J Cell Biol 96:639–643
Kodama H, Amagai Y, Sudo H, Ohno T, Iigima K (1986) Culture conditions affecting differentiation and calcification in the MC3T3-E1 osteogenic cell line. In: Ali SY (ed) Cell mediated calcification and matrix vesicles. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 297–302
Ecarot-Charrier B, Shepard N, Charette G, Grynpas M, Glorieux FH (1988) Mineralization in osteoblast cultures: A light and electron microscopic study. Bone 9:147–154
Bhargava U, Bar-Lev M, Bellows CG, Aubin JE (1988) Ultrastructural analysis of bone nodules formed in vitro by isolated fetal rat calvaria cells. Bone 9:155–163
Sauer GR, Wuthier RE (1988) Fourier transform infrared characterization of mineral phases formed during induction of mineralization by collagenase-released matrix vesicles in vitro. J Biol Chem 263:13718–13724
Anderson HC, Cecil R, Sajdera SW (1975) Calcification of rachitic rat cartilage in vitro by extracellular matrix vesicles. Am J Pathol 79:237–254
Matsuzawa T, Anderson HC (1971) Phosphatases of epiphyseal cartilage studied by electron microscopic cytochemical methods. J Histochem Cytochem 19:801–808
Morris DC, Väänänen HK, Munoz P, Anderson HC (1986) Light and electron microscopic immunolocalization of alkaline phosphatase in bovine growth plate cartilage. In: Ali SY (ed) Cell mediated calcification and matrix vesicles. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 21–26
de Bernard B, Bianco P, Bonucci E, Constantini M, Lunazzi GC, Martinuzzi P, Modricky C, Moro L, Panfili E, Pollesello P, Stagni N, Vittur F (1986) Biochemical and immunohistochemical evidence that in cartilage an alkaline phosphatase is a Ca2+-binding glycoprotein. J Cell Biol 103:1615–1623
Majeska RJ, Wuthier RE (1975) Studies on matrix vesicles isolated from chick epiphyseal cartilage. Association of pyrophosphatase and ATPase activities with alkaline phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta 391:51–60
Wuthier RE (1975) Lipid composition of isolated epiphyseal cartilage cells, membranes and matrix vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta 409:128–143
Fortuna R, Anderson HC, Carty RP, Sajdera SW (1980) Enzymatic characterization of the matrix vesicle alkaline phosphatase isolated from bovine fetal epiphyseal cartilage. Calcif Tissue Int 30:217–225
Wuthier RE, Chin JE, Hale JE, Register TC, Hale LV, Ishikawa Y (1985) Isolation and characterization of calcium-accumulating matrix vesicles from chondrocytes of chicken epiphyseal growth plate cartilage in primary culture. J Biol Chem 260:15972–15979
Fleisch H, Straumann F, Schenk R, Bisaz S, Algower M (1966) Effect of condensed phosphates on calcification of chick embryo femurs in tissue culture. Am J Physiol 211:821–825
Anderson HC, Reynolds JJ (1973) Pyrophosphate stimulation of calcium uptake into cultured embryonic bones. Fine structure of matrix vesicles and their role in calcification. Dev Biol 34:211–227
Register TC, Wuthier RE (1985) Effect of pyrophosphate and two diphosphonates on45Ca and32Pi uptake and mineralization by matrix vesicle-enriched fractions and by hydroxyapatite. Bone 6:307–312
Bett F, Blumenthal NC, Posner AS, Becker GL, Lehninger AL (1975) Atomic structure of intracellular amorphous calcium phosphate deposits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:2088–2090
Register TC, Warner GP, Wuthier RE (1984) Effect of L- and D-tetramisole on32Pi and45Ca uptake and mineralization by matrix vesicle-enriched fractions from chicken epiphyseal cartilage. J Biol Chem 25:922–928
Bishop MA, Warshawsky H (1982) Electron microscopic studies on the potential loss of crystallites from routinely processed sections on young enamel in the rat incisor. Anat Rec 202:177–186
Nanci A, Bai P, Warshawsky H (1983) The effect of osmium postfixation and uranyl and lead staining on the ultrastructure of young enamel in the rat incisor. Anat Rec 207:1–16
Hayashi Y, Bianco P, Shimokawa H, Termine JD, Bonucci E (1986) Organic-inorganic relationships, and immunohistochemical localization of amelogenins and enamelins in developing enamel. Basic Appl Histochem 30:291–299
Goldberg M, Molon-Noblot M, Septier D (1980) Effets de deux méthodes de déminéralisation sur la préservation des glycoprotéines et des protéoglycanes dans les dentines intercanaliculaires et péricanaliculaires chez le cheval. J Biol Buccale 8:315–330
Hayashi Y (1988) Ultrastructural demonstration of the carbohydrate in developing mantle dentine with soybean agglutinin-gold complexes. J Electron Microsc 37:150–154
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayashi, Y., Nagasawa, H. Matrix vesicles isolated from apical pulp of rat incisors: Crystal formation in low Ca×Pi ion-product medium containing β-glycerophosphate. Calcif Tissue Int 47, 365–372 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02555888
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02555888