Abstract
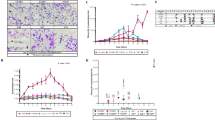
Recent studies on chromosomes have shown the presence of diploid and triploid types of Paragonimus westermani. To determine any possible biological differences between them, the migration route and development of the diploid type in the final hosts were compared with those of the triploid type. In the cat, the definitive host, larvae of the diploid type migrated to the abdominal wall, remained there for two weeks, and then migrated to the lung. In the rat, the abnormal host, some orally administered metacercariae of the diploid type made cysts in the lung and laid eggs, but the triploid type did not lay any eggs. Neither type of P. westermani migrated to the liver of the rat, in contrast to the previously reported fact that P. miyazakii and P. ohirai migrate to the liver and develop there. From these results, it seems likely that the two types of P. westermani are closely related.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agatsuma T, Habe S (1985) Electrophoretic studies on enzymes of diploid and triploid Paragonismus westermani. Parasitology 91:489–497
Habe S (1978) Experimental studies on the mode of human infection with the lung fluke, Paragonismus westermani (Kerbert 1878). Japan J Parasitol 27:261–292
Habe S (1983) A newly recognized paratenic host of Paragonimus spp. Japan J Trop Med Hyg 11:1–6
Hashiguchi Y, Takei T (1971) Experimental transplantation of Paragonimus miyazakii metacercariae into the pleural cavity of albino rats. Japan J Parasitol 20:67–71
Hashiguchi Y, Takei T, Miyazaki I (1968) Experimental infection of Paragonimus miyazakii Kamo, Nishida, Hatsushika et Tomimura, 1961 to Norway rat (Rattus norvegicus norvegicus) and albino rat. Japan J Parasitol 17:115–120
Miyazaki I (1977) A newly introduced question on Paragonimus westermani (Kerbert 1878). Nihon Iji Shinpou 2788:43–46 (in Japanese)
Miyazaki I (1978) Two types of the lung fluke which has been called Paragonimus westermani (Kerbert 1878). Med Bull Fukuoka University 5:251–261
Miyazaki I (1979) On the newly proposed lung fluke Paragonimus pulmonalis (Baelz 1880). Med Bull Fukuoka University 6:267–276
Okura T (1963a) Studies on the development of Paragonimus ohirai Miyazaki, 1939 in the final hosts. I. The route of the migration of the larvae of P. ohirai in rats. Japan J Parasitol 12:57–67
Okura T (1963b) Studies on the development of Paragonimus ohirai Miyazaki, 1939 in the final hosts. II. The development of P. Ohirai in rats. Japan J Parasitol 12:99–118
Oshima T, Yoshida Y, Kihata M (1958) Excystation of the metacercariae of Paragonimus westermani. 1. Especially on the effect of bile salts. Bull Institute of Public Health 7:256–269
Sakaguchi Y, Tada I (1976) Chromsomes of a lung fluke Paragonimus westermani. Chrom Inf Service 20:23–24
Shibahara T (1983) Studies on the lung fluke, Paragonimus westermani — diploid type — in northern part of Hyogo prefecture, Japan. II. Experimental oral infection with metacercariae to dogs and cats, with reference to morphological characteristics of adult worms. Japan J Parasitol 32:293–304
Shibahara T (1984) Studies on the lung fluke, Paragonismus westermani — diploid type — in the northern part of Hyogo prefecture, Japan. III. Experimental oral infection with metacercariae of rats with reference to juvenile worms removed from the muscles. Japan J Parasitol 33:119–132
Sugiyama H, Kikuchi T, Matsumoto M, Tomimura T (1985) The albino rat as an experimental paratenic host for Paragonimus westermani (Kerbert 1878) (II). Japan J Parasitol 34 (suppl):10
Tada I (1969) Comparative studies on Paragonismus miyazakii and P. ohirai infection in albino rats. Japan J Parasitol 18:34–51
Terasaki K (1977) Studies on chromosomes of the lung fluke in Japan. Japan J Parasitol 26:222–229
Tsuda M (1959) Biological studies on Paragonismus westermani (1) On a new technique for collection of the metacercariae of Paragonismus westermani from the second intermediate host and on the distribution of the metacercariae in Eriocheir japonicus by this technique. Japan J Parasitol 8:805–811
Yokogawa M (1965) Paragonimus and paragonimiasis. In: Ben Dawes (ed), Advances in Parasitology, vol. 3, Academic Press, London and New York, pp 375–387
Yokogawa M (1982) Newly introduced questions concerning Paragonimus westermani. J Formosan Med Assoc 81:774–780
Yokogawa M, Yoshimura H, Sano M, Okura T, Tsuji M (1962) The route of migration of the larvae of Paragonimus westermani in the final hosts. J Parasitol 48:525–531
Yokogawa M, Tsuji M, Araki K, Nomoto T (1964) Studies on the route of the migration of the larvae of Paragonimus miyazakii in rats with Evans-blue technique. Japan J Parasitol 13 (suppl):323
Yokogawa S (1915) Studies on the route of migration of Paragonimus westermani in the definitive host. Taiwan Igakukai Zashi 152:685–701 (in Japanese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanazawa, T., Hata, H., Kojima, S. et al. Paragonimus westermani: A comparative study on the migration route of the diploid and triploid types in the final hosts. Parasitol Res 73, 140–145 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00536470
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00536470