Summary
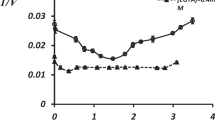
In order to determine if there is a relationship between Na+, K+-ATPase inhibition and cardiac glycoside-induced arrhythmia, the time course of the onset and offset of the arrhythmia induced by the semi-synthetic glycoside, actodigin, and the enzyme activity during arrhythmia and following reversion to normal sinus rhythm was studied in the intact, anesthetized dog. An infusion of actodigin (AY 22,241) at the rate of 0.1 μmol/kg/min for 30 min induced a severe and persistent arrhythmia within 13.1±1.2 min in 9 dogs. Upon termination of the actodigin infusion, the arrhythmia spontaneously converted to sinus rhythm within 17.5±2.3 min. Left ventricular tissue was taken from dogs sacrificed at the peak of the actodigin-induced arrhythmic periods or from the dogs that were allowed to recover from the actodigin-induced arrhythmia. These samples were homogenized and the membrane-containing fraction was passed through a Millipore filter. The membrane fraction trapped in the filter was the assayed for Na++K+ stimulate, Mg2+ dependent ATPase activity. The results showed that, in comparison to the time matched control dogs, the cardiac microsomes prepared from the arrhythmic dogs had a markedly reduced Na+, K+-ATPase activity. On the other hand, actodigin-treated dogs that were allowed to recover from the arrhythmic episode had Na+, K+-ATPase activity that was not significantly different from the control values.
The amount of 3H-actodigin bound by the cardiac muscle microsomal fraction was also investigated. The microsomes from left ventricle were isolated with a slight modification of the method of Dutta et al. (1968). The microsomal binding of 3H-actodigin was maximum at 30 min (26.6 pmol/mg protein) when the sample was prepared from the dogs at the peak of the arrhythmic effect. However, the binding was significantly reduced (11.5 pmol/mg protein) in the microsomal fraction from hearts that had returned to sinus rhythm. These data provide direct evidence that inhibition of Na+, K+-ATPase and cardiac glycosideinduced arrhythmia may have some cause and effect relationship.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akera, T., Larsen, F. S., Brody, T. M.: The effect of ouabain on sodium and potassium activated adenosine triphosphatase from the hearts of several mammalian species. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 170, 17–26 (1969)
Akera, T., Baskin, S. I., Tobin, T., Brody, T. M.: Ouabain: temporal relationship between the inotropic effect and the in vitro binding to, and dissociation from (Na++K+)-activated ATPase. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 277, 151–162 (1973)
Allen, J. C., Entman, M. L., Schwartz, A.: The nature of the transport adenosine triphosphatase-digitalis complex. VIII. The relationship between in vivo-formed (3H-ouabain-Na+, K+-adenosine triphosphatase) complex and ouabain-induced positive inotropism. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 192, 105–112 (1975)
Besch, H. R., Allen, J. C., Glick, G., Schwartz, A.: Correlation between the inotropic action of ouabain and its effects on subcellular enzyme systems from canine myocardium. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 171, 1–12 (1970)
Bray, G. A.: A simple efficient liquid scintillator for counting aqueous solutions in a liquid scintillation counter. Analyt. Biochem. 1, 279–285 (1960)
Deghenghi, R.: Synthetic cardenolides and related products. Pure appl. Chem. 21, 153–165 (1970)
Dutta, S., Goswami, S., Datta, D. K., Lindower, J. O., Marks, B. H.: The uptake and binding of six radiolabelled cardiac glycosides by guinea pig hearts and by isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 164, 10–21 (1968)
Dutta, S., Zavecz, J. H., Marks, B. H., Rhee, H. M., Brar, S., Richards, S. R., Bhat, H. B.: Dog heart sodium plus potassium activated ATPase activity during and after arrhythmic response to AY-22,241. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 242, 671–682 (1974)
Goldstein, R. E., Penzotti, S. C., Kuehl, K. S., Prindle, K. H., Jr., Hall, C. A., Titus, E. O., Epstein, S. E.: Correlation of antiarrhythmic effects of diphenylhydantoin with digoxin-induced changes in myocardial contractility, sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase activity, and potassium efflux. Circulat. Res. 33, 175–182 (1973)
Klaus, W., Kuschinsky, C., Lullmann, H.: The influence of therapeutic and toxic concentrations of digitoxigenin on the K flux and the ion concentrations in isolated guinea pig auricles. In: Proceeding of the first international Pharmacological meeting, Vol. 3, New Aspects of Cardiac Glycosides (W. Wilbrandt, ed.), pp. 211–218. New York: Pergamon Press 1963
Ku, D. D., Akera, T., Tobin, T., Brody, T. M.: Comparative species studies on the effect of monovalent cations and ouabain on cardiac Na+, K+-adenosine triphosphatase and contractile force. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 197, 458–469 (1976)
Lowry, O. H., Rosenbrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J.: Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951)
Mason, D. T., Zelis, R., Lee, G., Hughes, J. L., Spann, J. F., Amsterdam, E. A.: Current concepts and treatment of digitalis toxicity. Amer. J. Cardiol. 27, 546–559 (1971)
Mendez, R., Pastelin, G., Kabela, E.: The influence of the position of attachment of the lactone ring to the steroid nucleus on the action of the cardiac glycosides. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 188, 189–197 (1974)
Murthy, R. V., Kidwai, A. M., Daniel, E. E.: Dissociation of contractile effect and binding and inhibition of Na+, K+-adenosine triphosphatase by cardiac glycosides in rabbit myometrium. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 188, 575–581 (1974)
Okita, G. T., Richardson, F., Roth-Schechter, B. F.: Dissociation of the positive inotropic action of digitalis from inhibition of sodium and potassium activated adenosine triphosphatase. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 185, 1–11 (1973)
Pastelin, G., Mendez, R.: Singular effects of a new short acting cardiac glycoside in Purkinje cells. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 19, 291–293 (1972)
Polimeni, P. I., Vassalle, M.: Potassium fluxes in Purkinje and ventricular muscle fibers during rest and activity. Amer. J. Physiol. 218, 1381–1388 (1970)
Repke, K.: Metabolism of cardiac glycosides. In: Proceedings of the first international pharmacological meeting, Vol. 3, New Aspects of Cardiac Glycosides (W. Wilbrandt, ed.), pp. 47–73. New York: Pergamon Press 1963
Repke, K.: Effect of digitalis on membrane adenosine triphosphatase of cardiac muscle. In: Proceedings of the second international pharmacological meeting, Vol. 4, Drugs and Enzymes (B. B. Brodie and J. R. Gillette, eds.), pp. 65–88. New York: Pergamon Press 1965
Rhee, H. M., Dutta, S., Marks, B. H.: Cardiac NaK ATPase activity during positive inotropic and toxic actions of ouabain. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 37, 141–153 (1976)
Ross, C. R., Pessah, N. I.: Reversible inhibition of (Na++K+)-ATPase with a cardiac glycoside. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 33, 223–226 (1975)
Schwartz, A.: Active transport in mammalian myocardium. In: The mammalian myocardium (G. A. Langer and A. J. Brady, eds.), pp. 81–104. New York: John Wiley and Sons, Inc. 1974
Schwartz, A.: Is the cell membrane Na+, K+-ATPase enzyme system the pharmacological receptor for digitalis? Circulat. Res. 39, 2–7 (1976)
Schwartz, A., Allen, J. C., Van Winkle, B., Munson, R.: Further studies on the correlation between the ionotropic action of ouabain and its interaction with the Na+, K+-adenosine triphosphatase: isolated perfused rabbit and cat hearts. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 191, 119–127 (1974)
Schwartz, A., Lindenmayer, G. E., Allen, J. C.: The sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase: pharmacological, physiological and biochemical aspects. Pharmacol. Rev. 27, 3–134 (1975)
Spain, R. C., Chidsey, C. A.: Myocardial Na/K adenosine triphosphatase activity during reversal of ouabain toxicity with diphenylhydantoin. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 179, 594–598 (1971)
Ten-Eick, R. E., Basset, A. L., Okita, G. T.: Dissociation of electrophysiological and inotropic actions of strophanthidin-3-bromoacetate: possible role of adenosine triphosphatase in the maintenance of the myocardial transmembrane Na+ and K+ gradients. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 185, 12–23 (1973)
Vick, R. L., Hazelwood, C. F., Nichols, B. L.: Distribution of potassium, sodium and chloride in canine Purkinje and ventricular tissues. Circulat. Res. 27, 159–169 (1970)
Wester, P. O.: Trace elements in the conductive tissue of the beef heart determined by neutron activation analysis. Acta med. scand. 178, 789–799 (1965)
Yoda, A., Hokin, L. E.: On the reversibility of binding of cardiotonic steroids to a partially purified (Na++K+)-activated adenosine triphosphatase from beef brain. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 40, 880–886 (1970)
Zavecz, J. H.: The relationship between Na++K+-ATPase inhibition and actodigin-induced cardiac arrhythmia. Ph. D. Thesis, The Ohio State University Columbus, Ohio, 1974
Zavecz, J. H., Marks, B. H., Dutta, S.: Arrhythmic effect of digitalis glycosides in relationship to Na++K+-ATPase of canine heart. Fed. Proc. 33, 518 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This investigation was supported in part by the United States Public Health Services Research Grant HE 07051 and The Central Ohio Heart Association Grant
A report of this study has been presented in the spring meetings of FASEB, April, 1974, Atlantic City, New Jersey and submitted by J. H. Zavecz in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy at the Ohio State University
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zavecz, J.H., Dutta, S. The relationship between Na+, K+-ATPase inhibition and cardiac glycoside-induced arrhythmia in dogs. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 297, 91–98 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00508815
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00508815