Abstract
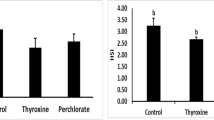
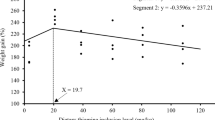
Juvenile red drum (Sciaenops ocellatus) were cultured at 25°C on a variety of diets and blood sampled over eight weeks to examine the relationship between growth and plasma thyroid hormone levels. Maximum growth rates were achieved on formulated experimental diets and a simulated natural shrimp diet. Associated with these maximal rates was a significant increase in triidothyronine (T3), but no consistent change in thyroxine (T4). Reduced rations of diets resulted in low growth rates associated with significantly lowered levels of T3 but not T4. To determine whether weight gain could be increased by application of exogeneous hormone, diets were supplemented with T3 or T4 at 2, 10, and 50 mg hormone/kg diet. Significantly elevated T3 was induced by supplementation with 10 and 50 mg T3/kg diet, although there were no indications of an anabolic effect of T3 incorporation, and 50 mg T3/kg diet was in fact associated with decreased weight gain. Incorporation of T4 into diets had no effect on growth or T3, and had effects on T4 which were small and inconsistent, indicating that T4 may not be effectively absorbed from the gut. No difference was found in response to hormone feeding between low (6 ppt) or high (35 ppt) water salinity. T3 levels thus appear to closely parallel growth in fish on unsupplemented diets, whereas T4 which were small and manipulation. Supplementation with T3 is not an effective means of stimulating growth in red drum fed optimum diets. Whereas thyroid hormones may function to regulate intermediary metabolism in red drum, elevated endogenous thyroid hormone levels appear adequate to supply tissue needs during juvenile growth in culture.
Résumé
Chez de jeunes corbes rouges (Sciaenops ocellatus), élevés à 25°C avec des régimes alimentaires variables, des prélèvements sanguins ont été effectués durant 8 semaines pour étudier les relations existantes entre la croissance et les niveaux des hormones thyroïdiennes. Les taux de croissance maximum sont obtenus grâce aux régimes artificiels et aux régimes simulant la consommation naturelle de crevettes. Parallèlement à ces taux de croissance élevés, on observe une augmentation des niveaux de T3, mais pas de modification nette des niveaux de T4. Une diminution de la ration alimentaire induit une diminution du taux de croissance associé à des niveaux plus faibles de T3, mais pas de T4. Pour vérifier si une augmentation de poids peut être obtenue grâce à une supplémentation hormonale, des additions de T3 et T4 à 2, 10 et 50 mg/kg d'aliment ont été effectuées. Une augmentation significative des niveaux plasmatiques de T3 est observée avec les régimes alimentaires contenant 10 et 50 mg T3/kg, cependant il n'y a pas d'effets anaboliques nets de la T3, et le régime contenant 50 mg T3/kg a été associé à une diminution du gain pondéral. Les régimes alimentaires contenant de la T4 n'a pas d'effet sur la croissance et sur les niveaux de T3 circulants, et présentent de faibles effets sur les niveaux de T4, ce qui indique que la T4 n'est pas absorbée efficacement par l'instestin. La salinité (6–35 ppm) ne modifie pas les réponses aux traitements hormonaux. Les niveaux de T3 sont étroitement liés à la croissance chez les animaux témoins, mais les niveaux de T4 demeurent insensibles aux variations des niveaux d'alimentation. La supplémentation en T3 n'est pas un moyen efficace pour stimuler la croissance du corbe rouge qui suit un régime alimentaire optimisé. Parce que les hormones thyroïdiennes réguleraient le métabolisme intermédiaire chez le corbe rouge, les niveaux endogènes élevés d'hormones thyroïdiennes apparaissent adéquats pour répondre aux besoins tissulaires durant la croissance des juvéniles en élevage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Brown, S.B. and Eales, J.G. 1977. Measurement of L-thyroxine and 3,5,3′-triiodo-L-thyronine levels in fish plasma by radioimmunoassay. Can. J. Zool. 55: 293–299.
Eales, J.G. 1988. The influence of nutritional state on thyroid function in various vertebrates. Am. Zool. 28: 351–362.
Eales, J.G. and Shostak, S. 1985. Correlations between food ration, somatic growth parameters and thyroid function in arctic charr, Salvelinus alpinus L. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 80A: 553–558.
Eales, J.G., Higgs, D.A., Uin, L.M., MacLatchy, D.L. Bres, O., McBride, J.R. and Dosanjh, B.S. 1990. Influence of dietary lipid and carbohydrate levels and chronic 3,5,3′-triiodo-L-thyronine treatment on thyroid function in immature rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 80: 146–154.
Eales, J.G., Hughes, M. and Uin, L. 1981. Effect of food intake on diel variation in plasma thyroid hormone levels in rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 45: 167–174.
Feist, G. and Schreck, C.B. 1990. Hormonal content of commercial fish diets and of young coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) fed these diets. Aquaculture 86: 63–75.
Fagerlund, U.H.M., McCallum, I., Higgs, D.A., McBride, J.R., Plotnikoff, M.D. and Dosanjh, B.S. 1984. Diet composition as a factor in the anabolic efficacy of 3,5,3′-triiodo-L-thyronine administered orally to steelhead trout (Salmo gairdneri). Aquaculture 36: 49–59.
Flood, C.G. and Eales, J.G. 1983. Effects of starvation and refeeding on plasma T4 and T3 levels and T4 deiodination in rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. Can. J. Zool. 61: 1949–1953.
Gannam, A.L. and Lovell, R.T. 1991. Effects of feeding 17α-methyltestosterone, 11-ketotestesterone, 17β-estradiol, and 3,5,3′-triiodothyronine to channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus. Aquaculture 92: 377–388.
Higgs, D.A., Fagerlund, U.H.M., McBride, J.R., Plotnikoff, M.D., Dosanjh, B.S., Markert, J.R. and Davidson, J. 1983. Protein quality of Altex canola meal for juvenile chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) considering dietary protein and 3,5,3′-triiodo-L-thyronine content. Aquaculture 34: 213–238.
Higgs, D.A., Fagerlund, U.H.M. and McBride, J.R. 1979. Influence of orally administered L-thyroxine or 3,5,3′-triiodo-L-thyronine on growth, food consumption, and food conversion of underyearling coho salmon (Oncorhynhcus kisutch). Can. J. Zool. 57: 1974–1979.
Himick, B.A., Higgs, D.A. and Eales, J.G. 1991. The acute effects of alteration in the dietary concentrations of carbohydrate, protein, and lipid on plasma T4, T3, and glucose levels in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 82: 451–458.
Leatherland, J.F., Hilton, J.W. and Slinger, S.J. 1987. Effects of thyroid hormone supplementation of canola meal-based diets on growth, and interrenal and thyroid gland physiology of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 3: 73–82.
Leatherland, J.F., Cho, Y. and Hilton, J. 1984. Effect of diet on serum thyroid hormone levels in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri Richardson). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 78A: 601–605.
Leatherland, J.F., Cho, C.Y., Hilton, J.W. and Slinger, S.J. 1980. Further studies on the effect of diet on serum thyroid hormone concentrations and thyroid histology in rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri (Pisces Salmonidae). Env. Biol. Fish. 5: 175–179.
Leatherland, J.F., Cho, C.Y. and Slinger, S.J. 1977. Effects of diet, ambient temperature, and holding conditions on plasma thyroxine levels in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 34: 677–682.
Lin, R.J., Rivas, R.J., Nishioka, R.S., Grau, E.G. and Bern, H.A. 1985. Effects of feeding triiodothyronine (T3) on thyroxin (T4) levels in the steelhead trout, Salmo gairdneri. Aquaculture 45: 133–142.
McCormick, S.D. and Saunders, R.L. 1990. Influence of ration level and salinity on circulating thyroid hormones in juvenile Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 78: 224–230.
MacKenzie, D.S. 1988. Thyroid function in red drum. Contrib. Mar. Sci., Suppl. to Vol. 30: 139–146.
Moon, H.Y. and Gatlin, D.M., III. 1991. Total sulfur amino acid requirement of juvenile red drum, Sciaenops ocellatus. Aquaculture 95: 97–106.
Saunders, R.L., McCormick, S.D., Henderson, E.B., Eales, J.G. and Johnston, C.E. 1985. The effect of orally administered 3,5,3′-triiodo-L-thyronine on growth and salinity tolerance of the Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 45: 143–156.
Serrano, J.A., Nematipour, G.R. and Gatlin, D.M., III. 1992. Dietary protein requirement of the red drum (Sciaenops ocellatus) and relative use of dietary carbohydrate and lipid. Aquaculture 101: 283–291.
Soengas, J.L., Rey, P., Rozas, G., Andrés, M.D. and Aldegunde, M. 1992. Effects of cortisol and thyroid hormone treatment on the glycogen metabolism of selected tissues of domesticated rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquaculture 101: 317–328.
Woo, N.Y.S., Chung, A.S.B. and Ng, T.B. 1991. Influence of oral administration of 3,5,3′-triiodo-L-thyronine on growth, digestion, food conversion and metabolism in the underyearling red sea bream, Chrysophrys major (Temminck and Schlegel). J. Fish Biol. 39: 459–468.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MacKenzie, D.S., Moon, H.Y., Gatlin, D.M. et al. Dietary effects on thyroid hormones in the red drum, Sciaenops ocellatus . Fish Physiol Biochem 11, 329–335 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00004582
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00004582