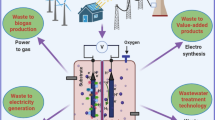
Abstract
Microbial fermentations are well recognized process for large-scale bioconversion of organic waste biomass into high-value organic acids. It requires processes optimization, i.e., that should reach at maximum productivity and no feedback inhibition, to reduce the cost of up- and down-stream processing for commercialization. To achieve this, triggered metabolic activities are often needed that maximize the conversion of organic carbon into organic acids under non-sterile conditions. By regulating the redox balance in-situ, the specific organic acid production could be tailored in fermentation systems under mixed/mono-culture conditions. In recent years, bio-electro-fermentations (BEF) has developed as a promising approach for organic waste conversion into value products due to its sustainable nature but yet required better understand for further development. In BEF, the fermentative metabolic pathways are enhanced with poising electrodes that facilitate effective electron transfers towards end-product recovery. It is expected to maintain the required redox conditions and buffer the system by regulating reducing equivalents e.g. NADH+ during fermentation. Moreover, microorganisms extract energy required to build biomass (anabolic process) from redox reactions (catabolism) through syntrophic interactions in BEF, while feedback inhibition of process could be overcome. In this chapter, we will elaborate the BEF process for organic acid production (mainly succinic, acetic, and muconic acids) and techno-economics of the process for commercialization.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
Acetic acid
- AD:
-
Anaerobic digestion
- BEF:
-
Bio-electro-fermentations
- CA:
-
Citric acid
- CAPEX:
-
Capital expenditure
- ccMA:
-
cis,cis-muconic acid
- ctMA:
-
cis,trans-muconic acid
- EET:
-
Extracellular electron transfer
- EF:
-
Electro-fermentation
- frd :
-
Fumarate reductase
- fum :
-
Fumarase
- LA:
-
Lactic acid
- LCA:
-
Life cycle assessment
- MA:
-
Muconic acid
- mdh :
-
Malate dehydrogenase
- MMC:
-
Mixed microbial cultures
- OW:
-
Organic waste
- ppc :
-
PEP carboxylase
- pck :
-
PEP carboxykinase
- pyc :
-
Pyruvate carboxylase
- SA:
-
Succinic acid
- TEA:
-
Techno-economic analysis
- ttMA:
-
trans,trans-muconic acid
References
Alexandri M, Venus J (2017) Feedstock flexibility in sustainable chemistry: bridging sectors still not sufficiently familiar with each other – showcases of ongoing and emerging initiatives. Curr Opin Green Sustain Chem 8:24–29
Alexandri M, Schneider R, Venus J (2018) Membrane technologies for lactic acid separation from fermentation broths derived from renewable resources. Membranes 8(4):94
Alves de Oliveira R, Komesu A, Vaz Rossell CE, Maciel Filho R (2018) Challenges and opportunities in lactic acid bioprocess design—from economic to production aspects. Biochem Eng J 133:219–239
Appels L, Baeyens J, Degre`ve J, Dewil R (2008) Principles and potential of the anaerobic digestion of waste-activated sludge. Prog Energ Combust Sci 34:755–781
Awate B, Steidl RJ, Hamlischer T, Reguera G (2017) Stimulation of electro-fermentation in single-chamber microbial electrolysis cells driven by genetically engineered anode bio films. J Power Sources 356:510–518
Batlle-Vilanova P, Puig S, Gonzalez-Olmos R, Colprim J (2016) Continuous acetate production through microbial electrosynthesis from CO with microbial mixed culture. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 91:921–927
Becker J, Wittmann C (2012) Systems and synthetic metabolic engineering for amino acid production-the heartbeat of industrial strain development. Curr Opin Biotechnol 23:718–726
Becker J, Kuhl M, Kohlstedt M, Starck S, Wittmann C (2018) Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for the production of cis,cis-muconic acid from lignin. Microb Cell Fact 17:115–128
Bentley GJ, Narayanan N, Jha RK et al (2020) Engineering glucose metabolism for enhanced muconic acid production in Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Metab Eng 59:64–75
Cao Y, Zhang R, Sun C, Cheng T, Liu Y, Xian M (2013) Fermentative succinate production: an emerging technology to replace the traditional petrochemical processes. Biomed Res Int 2013:1–12
Cavallo E, Charreau H, Cerrutti P, Foresti ML (2017) Yarrowia lipolytica: a model yeast for citric acid production. FEMS Yeast Res 17(8):84. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsyr/fox084
Caxiano IN, Junqueira PG, Mangili PV, Prata DM (2020) Eco-efficiency analysis and intensification of the acetic acid purification process. Chem Eng Process - Process Intensif 147:107784
Chavas J-P, Kim K (2010) Economies of diversification: a generalization and decomposition of economies of scope. Int J Prod Econ 126:229–235
Cheng S, Xing D, Call DF, Logan BE (2009) Direct biological conversion of electrical current into methane by electromethanogenesis. Environ Sci Technol 43:3953–3958
Choi O, Sang BI (2016) Extracellular electron transfer from cathode to microbes: application for biofuel production. Biotechnol Biofuel 9(1):11
Choi KS, Kondaveeti S, Min B (2017) Bioelectrochemical methane (CH4) production in anaerobic digestion at different supplemental voltages. Bioresour Technol 245:826–883
Christodoulou X, Velasquez-Orta SB (2016) Microbial electrosynthesis and anaerobic fermentation: an economic evaluation for acetic acid production from CO2 and CO. Environ Sci Technol 50(20):11234–11242
Chu N, Liang Q, Jiang Y, Zeng RJ (2020) Microbial electrochemical platform for the production of renewable fuels and chemicals. Biosens Bioelectron 150:111922
Chua JW, Hsieh JH (1990) Oxidative bioconversion of toluene to 1,3-butadiene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid (cis,cis-muconic acid). World J Microbiol Biotechnol 6:127–143
De Corato U, De Bari I, Viola E, Pugliese M (2018) Assessing the main opportunities of integrated biorefining from agro-bioenergy co/by-products and agroindustrial residues into high-value added products associated to some emerging markets: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 88:326–346
Desloover J, Arends JB, Hennebel T, Rabaey K (2012) Operational and technical considerations for microbial electrosynthesis. Biochem Soc Trans 40:1233–1238
Frost JW, Miermont A, Schweitzer D, Bui V (2013) Preparation of trans, trans muconic acid and trans, trans muconates. US Patent US8426639B2
Ghaffar T, Irshad M, Anwar Z et al (2014) Recent trends in lactic acid biotechnology: a brief review on production to purification. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 7:222–229
Gorby YA, Yanina S, McLean JS, Rosso KM, Moyles D et al (2006) Electrically conductive bacterial nanowires produced by Shewanella oneidensis strain MR-1 and other exoelectrogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:11358–11363
Grootscholten TIM, Borgo F, Hamelers HVM, Buisman CJN (2013) Promoting chain elongation in mixed culture acidification reactors by addition of ethanol. Biomass Bioenerg 48:10–16
Jiang Y, Su M, Zhang Y, Zhan G, Tao Y, Li D (2013a) Bioelectrochemical systems for simultaneously production of methane and acetate from carbon dioxide at relatively high rate. Int J Hydrogen Energy 38:3497–3502
Jiang J, Zhang Y, Li K, Wang Q, Gong C, Li M (2013b) Volatile fatty acids production from food waste: effects of pH, temperature and organic loading rate. Bioresour Technol 143:525–530
Jiang Y, Lu L, Wang H et al (2018) Electrochemical control of redox potential arrests methanogenesis and regulates products in mixed culture electro-fermentation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:8650–8658
Jiang Y, May HD, Lu L et al (2019) Carbon dioxide and organic waste valorization by microbial electrosynthesis and electro-fermentation. Water Res 149:42–55
Jiang Y, Chu N, Zhang W et al (2020) Electro-fermentation regulates mixed culture chain elongation with fresh and acclimated cathode. Energy Convers Manag 204:112285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.112285
Karthikeyan OP, Visvanathan C (2013) Bio-energy recovery from high-solid organic substrates by dry anaerobic bio-conversion processes: a review. Rev Environ Sci Bio/Technol 12(3):257–284
Khalil I, Quintens G, Junkers T, Dusselier M (2020) Muconic acid isomers as platform chemicals and monomers in the biobased economy. Green Chem 22:1517–1541
Khosravanipour Mostafazadeh A, Drogui P, Brar SK et al (2017) Microbial electrosynthesis of solvents and alcoholic biofuels from nutrient waste: A review. J Environ Chem Eng 5:940–954
Kiely PD, Regan JM, Logan BE (2011) The electric picnic: synergistic requirements for exoelectrogenic microbial communities. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22:378–385
Kotloski NJ, Gralnick JA (2013) Flavin electron shuttles dominate extracellular electron transfer by Shewanella oneidensis. mBio 4:00553-12
Kucek LA, Xu J, Nguyen M, Angenent LT (2016) Waste conversion into n-Caprylate and n-Caproate: resource recovery from wine lees using anaerobic reactor microbiomes and in-line extraction. Front Microbiol 7:1892
Kumar P, Pant DC, Mehariya S et al (2014a) Ecobiotechnological strategy to enhance efficiency of bioconversion of wastes into hydrogen and methane. Indian J Microbiol 54:262–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-014-0467-7
Kumar P, Singh M, Mehariya S et al (2014b) Ecobiotechnological approach for exploiting the abilities of bacillus to produce co-polymer of polyhydroxyalkanoate. Indian J Microbiol 54:151–157
Kumar A, Hsu LHH, Paul K, Barriere F, Lens PNL et al (2017) The ins and outs of microorganism-electrode electron transfer reactions. Nat Rev Chem 1:0024
LaBelle EV, May HD (2017) Energy efficiency and productivity enhancement of microbial electrosynthesis of acetate. Front Microbiol 8:756. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00756
Lee WS, Chua ASM, Yeoh HK, Ngoh GC (2014) A review of the production and applications of waste-derived volatile fatty acids. Chem Eng J 235:83–99
Liu H, Grot S, Logan BE (2005) Electrochemically assisted microbial production of hydrogen from acetate. Environ Sci Technol 39:4317–4320
Lovley DR (2011) Electrosynthesis of organic compounds from carbon dioxide is catalyzed by a diversity of acetogenic microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:2882–2886
Marshall CW, Ross DE, Fichot EB, Norman RS, May HD (2012) Electrosynthesis of commodity chemicals by an autotrophic microbial community. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(23):8412–8420
Mehariya S, Patel AK, Obulisamy PK et al (2018) Co-digestion of food waste and sewage sludge for methane production: current status and perspective. Bioresour Technol 265:519–531
Mika LT, Cséfalvay E, Németh Á (2018) Catalytic conversion of carbohydrates to initial platform chemicals: chemistry and sustainability. Chem Rev 118:505–613. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00395
Mizuno S, Yoshikawa N, Seki M, Mikawa T, Imada Y (1988) Microbial production of cis, cis-muconic acid from benzoic acid. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 28:20–25
Mohanakrishna G, Seelam JS, Vanbroekhoven K, Pant D (2015) An enriched electroactive homoacetogenic biocathode for the microbial electrosynthesis of acetate through carbon dioxide reduction. Faraday Discuss 183:445–462
Moscoviz R, Toledo-Alarcn J, Trably E, Bernet N (2016) Electro-fermentation: how to drive fermentation using electrochemical systems. Trends Biotechnol 34:856–865
Moscoviz R, Trably E, Bernet N (2018) Electro-fermentation triggering population selection in mixed-culture glycerol fermentation. Microb Biotechnol 11:74–83
Nevin KP, Hensley SA, Franks AE, Summers ZM, Ou J, Woodard TL, Lovley DR (2011) Electrosynthesis of organic compounds from carbon dioxide is catalyzed by a diversity of acetogenic microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbial 77(9):2882–2886
Nevin KP, Hensley SA, Franks AE, Summers ZM, Ou J, Woodard TL, Snoeyenbos-West OL, Nikhil GN, Subhash GV, Dileep Y, Venkata Mohan S (2015) Synergistic yield of dual energy forms through biocatalyzed electrofermentation of waste: stoichiometric analysis of electron and carbon distribution. Energy 88:281–191
Nevin KP, Woodard TL, Franks AE, Summers ZM, Lovley DR (2010) Microbial electrosynthesis: feeding microbes electricity to convert carbon dioxide and water to multicarbon extracellular organic compounds. MBio 1:e00103–e00110. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00103-10
Park DH, Zeikus JG (1999) Utilization of electrically reduced neutral Red by Actinobacillus succinogenes: physiological function of neutral Red in membrane-driven fumarate reduction and energy conservation. J Bacteriol 181(8):2403–2410
Patil SA, Arends JBA, Vanwonterghem I, van Meerbergen J, Guo K, Tyson GW, Rabaey K (2015) Selective enrichment establishes a stable performing community for microbial electrosynthesis of acetate from CO2. Environ Sci Technol 49:8833–8843
Rabaey K, Rozendal RA (2010) Microbial electrosynthesis - revisiting the electrical route for microbial production. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:706–716
Rabaey K, Girguis P, Nielsen LK (2011) Metabolic and practical considerations on microbial electrosynthesis. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22:371–377
Rago L, Pant D, Schievano A (2019) Chapter 14 - electro-fermentation—microbial electrochemistry as new frontier in biomass refineries and industrial fermentations. In: Hosseini M (ed) Advanced bioprocessing for alternative fuels, biobased chemicals, and bioproducts. Woodhead Publishing, Sawston, pp 265–287
Reguera G, Nevin KP, Nicoll JS, Covalla SF, Woodard TL, Lovley DR (2006) Biofilm and nanowire production leads to increased current in Geobacter sulfurreducens fuel cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:7345–7348
Sasaki K, Sasaki D, Kamiya K et al (2018) Electrochemical biotechnologies minimizing the required electrode assemblies. Curr Opin Biotechnol 50:182–188
Schievano A, PepéSciarria T, Vanbroekhoven K, De Wever H, Puig S, Andersen SJ, Rabaey K, Pant D (2016) Electro-fermentation-merging electrochemistry with fermentation in industrial applications. Trends Biotechnol 34:866–878
Schmidt FR (2005) Optimization and scale up of industrial fermentation processes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 68(4):425–435
Shanthi Sravan J, Butti SK, Sarkar O et al (2018) Electrofermentation of food waste – regulating acidogenesis towards enhanced volatile fatty acids production. Chem Eng J 334:1709–1718
Srikanth S, Maesen M, Dominguez-Benetton X, Vanbroekhoven K, Pant D (2014) Enzymatic electrosynthesis of formate through CO2 sequestration/reduction in a bioelectrochemical system (BES). Bioresour Technol 165:350–354
Srikanth S, Kumar M, Singh MP, Das BP (2016) Bioelectro chemical systems: a sustainable and potential platform for treating waste. Procedia Environ Sci 35:853–859
Stamenkovic VR, Strmcnik D, Lopes PP, Markovic NM (2016) Energy and fuels from electrochemical interfaces. Nat Mater 16:57–69
Steinbusch KJJ, Hamelers HVM, Plugge CM, Buisman CJN (2011) Biological formation of caproate and caprylate from acetate: fuel and chemical production from low grade biomass. Energ Environ Sci 4:216
Su M, Jiang Y, Li D (2013) Production of acetate from carbon dioxide in bioelectrochemical systems based on autotrophic mixed culture. J Microbiol Biotechnol 23:1140–1146
Summers ZM, Fogarty HE, Leang C, Franks AE, Malvankar NS, Lovley DR (2010) Direct exchange of electrons within aggregates of an evolved syntrophic coculture of Anaerobic bacteria. Science 330:1413–1415
Teigiserova DA, Hamelin L, Thomsen M (2019) Review of high-value food waste and food residues biorefineries with focus on unavoidable wastes from processing. Resour Conserv Recycl 149:413–426
Uçkun Kiran E, Trzcinski AP, Ng WJ, Liu Y (2014) Enzyme production from food wastes using a biorefinery concept. Waste Biomass Valoriz 5:903–917
Van Eerten-Jansen MC, TerHeijne A, Grootscholten TI, Steinbusch KJ et al (2013) Bioelectrochemical production of caproate and caprylate from acetate by mixed cultures. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 1:513–518
Venkata Mohan S, Butti SK, Amulya K, Dahiya S, Modestra JA (2016) Waste biorefinery: a new paradigm for a sustainable bioelectro economy. Trends Biotechnol 34:852–855
Villano M, Paiano P, Palma E, Miccheli A, Majone M (2017) Electrochemically-driven fermentation of organic substrates with undefined mixed microbial cultures. Chem Sus Chem. 10(15):3091–3097. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201700360
Xafenias N, Kmezik C, Mapelli V (2017) Enhancement of anaerobic lysine production in Corynebacterium glutamicum electrofermentations. Bioelectrochemistry 117:40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2017.06.001
Zhao Y, Cao W, Wang Z, Zhang B, Chen K, Ouyang P (2016) Enhanced succinic acid production from corncob hydrolysate by microbial electrolysis cells. Bioresour Technol 202:152–157
Zhou M, Yan B, Wong JWC, Zhang Y (2017) Enhanced volatile fatty acids production from anaerobic fermentation of food waste: a mini-review focusing on acidogenic metabolic pathways. Bioresour Technol 248:68–78
Competing Interests
All the authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Nagendranatha Reddy, C. et al. (2020). Electro-Fermentation of Biomass for High-Value Organic Acids. In: Verma, P. (eds) Biorefineries: A Step Towards Renewable and Clean Energy. Clean Energy Production Technologies. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-9593-6_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-9593-6_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-9592-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-9593-6
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)