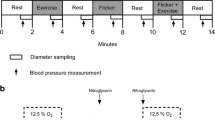
Summary
The effects of a blockade of the action or synthesis of endothelium-derived nitric oxide (EDRF) on vascular resistance and reactivity, platelet cGMP and tissue oxygenation were studied. Experiments were performed in isolated perfused rabbit hearts as well as in rabbit hindlimbs in vivo. In isolated hearts, perfusion with hemoglobin (6 μM) or NG-nitro-L-arginine (30 μM) significantly increased vascular resistance. The cGMP level in platelets passing through the coronary bed was found to be more than 50% lower than with intact EDRF production. EDRF inhibition also resulted in a reduced peak reactive hyperemia, an enhanced reactive vasoconstriction after a rapid increase in perfusion pressure (myogenic response), and in abolition of flow-dependent dilation of coronary resistance vessels. In rabbit hindlimbs, local blockade of EDRF-mediated dilations by gossypol resulted also in an increased vascular resistance and abolition of the increase in platelet cGMP induced by intraarterial infusion of acetylcholine. In addition, the oxygen uptake of the hindlimb (−46%) and the skeletal muscle pO2 were significantly reduced. It is concluded that continuously released EDRF has a functional role in maintaining adequate tissue perfusion and oxygen supply. Furthermore, the adaption of the vascular bed to rapid changes in flow and pressure is impaired after inhibition of EDRF.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amezcua JL, Palmer RMJ, Desouza BM, Moncada S (1989) Nitric oxide synthesized form L-arginine regulates vascular tone in the coronary circulation of the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol 97:1119–1124
Azuma H, Ishikawa M, Sekizaki S (1986) Endothelium dependent inhibition of platelet aggregation. Br J Pharmacol 88:411–415
Busse R, Trogisch G, Bassenge E (1985) The role of endothelium in the control of vascular tone. Basic Res Cardiol 80:475–190
Busse R, Lückhoff A, Bassenge E (1978) Endothelium-derived relaxant factor inhibits platelet activation. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 336:566–571
Drexler H, Zeiher AM, Wollschläger H, Meinertz T, Just H, Bonzel T (1989) Flow-dependent coronary artery dilatation in humans. Circulation 80:466–474
Furchgott RF (1983) Role of endothelium in responses of vascular smooth muscle. Circ Res 53:557–573
Gardiner SM, Sompton AM, Bennett T, Palmer RMJ, Moncada S (1990) Control of regional blood flow by endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Hypertension 15:486–492
Griffith TM, Edwards D, Davies RLI, Harrison TJ, Evans KT (1987) EDRF coordinates the behaviour of vascular resistance vessels. Nature 329:442–445
Hogan JC, Lewis MJ, Henderson AH (1988) In vivo EDRF activity influences platelet function. Br J Pharmacol 94:1020–1022
Holtz J, Förstermann U, Pohl U, Giesler M, Bassenge E (1984) Flow-dependent, endothelium-mediated dilation of epicardial coronary arteries in conscious dogs: effects of cyclooxygenase inhibition. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 6:1161–1169
Hull SS, Kaiser L, Jaffe MD, Sparks HV (1986) Endothelium-dependent flow induced dilation of canine femoral and saphenous arteries. Blood Vessels 23:183–198
Koller A, Messina EJ, Wolin MS, Kaley G (1989) Effects of endothelial impairment on arteriolar dilator responses in vivo. Am J Physiol 257:H1485–H1489
Ludmer PL, Selwyn AP, Shook TL, Wayne RR, Mudge GH, Alexander RW, Ganz P (1986) Paradoxical vasoconstriction induced by acetylcholine in atherosclerotic coronary arteries. N Engl J Med 315:1046–1051
Maseri A, Kaski JC (1989) Pathogenetic mechanisms of coronary artery spasm. J Am Coll Cardiol 14:610–612
Melkumyants AM, Balashov SA, Veselova ES, Khayutin VM (1987) Continuous control of the lumen of feline conduit arteries by blood flow rate. Cardiovasc Res 21:863–870
Palmer RMJ, Ashton DS, Moncada S (1988) Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from L-arginine. Nature 333:664–666
Pohl U, Busse R, Kuon E, Bassenge E (1986) Pulsatile perfusion stimulates the release of endothelial autacoids. J Appl Cardiol 1:215–235
Pohl U, Holtz J, Busse R, Bassenge E (1986) Crucial role of endothelium in the vasodilator response to increased flow in vivo. Hypertension 8:37–44
Pohl U, Dézsi L, Simon B, Busse R (1987) Selective inhibition of endothelium-dependent dilation in resistance-sized vessels in vivo. Am J Physiol 253:H234–H239
Pohl U, Busse R (1989) EDRF increases cyclic GMP in platelets during passage through the coronary vascular bed. Circ Res 65:1798–1803
Pohl U, Busse R (1989) Hypoxia stimulates the release of endothelium-derived relaxant factor (EDRF). Am J Physiol 256:H1595–H1600
Pohl U, Herlan K, Huang A, Bassenge E (1990) EDRF-mediated, shear-induced dilation opposes myogenic vasoconstriction. Am J Physiol (in press)
Pohl U, Lamontagne D, Bassenge E, Busse R (1990) EDRF augments coronary conductivity through attenuation of myogenic autoregulation. Pflüger Arch 415 (Suppl 1):1262
Rees DD, Palmer RMJ, Moncada S (1989) Role of endothelium-derived nitric oxide in the regulation of blood pressure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:3375–3378
Rosenblum WI (1986) Endothelial dependent relaxation demonstrated in vivo in cerebral arterioles. Stroke 17:494–497
Rubanyi GM, Romero JC, Vanhoutte PM (1986) Flow-induced release of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Am J Physiol 250:H1145–H1149
Shimokawa H, Flavahan NA, Sheperd JT, Vanhoutte PM (1989) Endothelium-dependent inhibition of ergonovine-induced contraction is impaired in porcine coronary arteries with regenerated endothelium. Circulation 80:643–650
Stewart DJ, Holtz J, Pohl U, Bassenge E (1987) Balance between endothelium-mediated dilator and direct constrictor actions of serotonin on resistance vessels in the isolated rabbit heart. Eur J Pharmacol 143:131–134
Stewart DJ, Pohl U, Bassenge E (1988) Free radicals inhibit endothelium-dependent dilation in the coronary resistance bed. Am J Physiol 255:H765–H769
Vallance P, Collier J, Moncada S (1989) Effects of endothelium-derived nitric oxide on peripheral arteriolar tone in man. Lancet 2:997–1000
Yamamoto Y, Tomoike H, Egashira K, Kobayashi T, Kawasaki T, Nakamura M (1987) Pathogenesis of coronary artery spasm in miniature swine with regional intimai thickening after balloon denudation. Circ Res 60:113–121
Zeiher AM, Drexler H, Wollschläger H, Sambier B, Just H (1989) Coronary vasomotion in response to sympathetic Stimulation in humans — importance of the functional integrity of the endothelium. J Am Coll Cardiol 14:1181–1190
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Dr. Dietrich Steinkopff Verlag GmbH & Co. KG, Darmstadt
About this paper
Cite this paper
Pohl, U., Lamontagne, D. (1991). Impaired tissue perfusion after inhibition of endothelium-derived nitric oxide. In: Drexler, H., Zeiher, A.M., Bassenge, E., Just, H. (eds) Endothelial Mechanisms of Vasomotor Control. Steinkopff. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-72461-9_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-72461-9_11
Publisher Name: Steinkopff
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-72463-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-72461-9
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive