Abstract
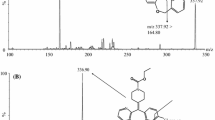
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive degenerative disorder of the central nervous system. Levodopa (L-dopa), dopamine precursor is the most effective therapeutic drug for PD patients. Levodopa (LDP) and its three metabolites in rat plasma were determined using high performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS). Method validation was conducted in terms of linearity, accuracy, precision, recovery, specificity, limit of detection, limit of quantification and stability. Correlation coefficients (r 2) were above 0.9965. The intra-day accuracy values at LLOQ (low limit of quantification), LQC (low quality control), MQC (medium quality control) and HQC (high quality control) levels were 85.7–103.3, 96.5–105.1, 90.7–100.1 and 94.2–101.3 %, respectively. The inter-day accuracy values at LLOQ, LQC, MQC and HQC levels were 77.6–112.0, 91.1–109.3, 84.3–101.0 and 88.2–103.9 %, respectively. The coefficient of variation (RSD) values of both intra- and inter-day results were within 6.7 and 8.5 %, respectively. The recoveries (mean ± %SD) for LLOQ, LQC, MQC and HQC were 82.7 ± 3.7–113 ± 2.8 %, 86.6 ± 5.7–110.3±3.4 %, 90.9 ± 3.6–106 ± 6.5 and 89.7 ± 4.5–97.4 ± 6.7 %, respectively. The coefficient of variation (RSD) values of both intra- and inter-day results were within 6.7 and 8.5 %, respectively. The validated LC–MS/MS method was applied successfully to the measurement of LDP and its metabolites in the rat plasma samples.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
de la Fuente-Fernandez R, Calne DB (2002) Evidence for environmental causation of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 8:235–241
Dingemanse J (2000) Issues important for rational COMT inhibition. Neurology 55:S24–S32
Forno LS (1996) Neuropathology of Parkinson’s disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:259–272
http://www/fda.gov/cder/guidance/index.htm. Accessed 2 November 2012
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parkinson's_disease, Accessed November 2, 2012
Igarashi K, Hotta K, Kasuyaa F, Abe K, Sakoda S (2003) Determination of cabergoline and L-dopa in human plasma using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chrom B 792:55–61
Kim HG, Kim G-S, Lee JH, Park S, Jeong WY, Kim Y-H et al (2011) Determination of the change of flavonoid components as the defence materials of Citrus unshiu Marc. fruit peel against Penicillium digitatum by liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem 128:49–54
Lee SJ, Choi JY, Park S, Chung JI, Jin JS, Lee SJ, Sung N-J, Bae DW, Shin SC (2010) Determination of phospholipids in soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr) cultivars by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Food Compost Anal 23:314–318
Licker V, Kövari E, Hochstrasser DF, Burkhard PR (2009) Proteomics in human Parkinson’s disease research. J Proteomics 73:10–29
Männistö PT, Kaakkola S (1989) New selective COMT inhibitors: useful adjuncts for Parkinson’s disease? Trends Pharmacol Sci 10:54–56
Maranis S, Tsouli S, Konitsiotis S (2011) Treatment of motor symptoms in advanced Parkinson’s disease: a practical approach. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35:1795–1807
Muzzi C, Bertocci E, Terzuoli L, Porcelli B, Ciari I, Pagani R, Guerranti R (2008) Simultaneous determination of serum concentrations of levodopa, dopamine, 3-O-methyldopa and a-methyldopa by HPLC. Biomed Pharmacother 62:253–258
Nutt JG, Fellman JH (1984) Pharmacokinetics of levodopa. Clin Neuropharmacol 7:35–49
Orr CF, Rowe DB, Halliday GM (2002) An inflammatory review of Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 68:325–340
Pan L, Guo Y, Li Z, Chen J, Jiang T, Yu Y (2010) Simultaneous determination of Levodopa, Benserazide and 3-O-Methyldopa in Human serum by LC–MS–MS. Chromatography 72:627–633
Poewe W, Wenning G (2002) The differential diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Neurol 9:23–30
Tsouli S, Konitsiotis S (2010) How should we treat a patient with early Parkinson’s disease? Int J Clin Pract 64:1210–1219
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, Y.A., Park, S., Seo, O.N. et al. Development and validation of an LC–ESI–MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of levodopa, dopamine, L-α-methyldopa and 3-O-methyldopa in rat plasma. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 42, 361–368 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-012-0048-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-012-0048-x