Abstract
Background
Receptors of the ErbB family are involved in the development of various cancers, and the inhibition of these receptors represents an attractive therapeutic concept. Upon ligand binding, ErbB receptors become activated as homo- or heterodimers, leading to the activation of downstream signaling cascades that result in the facilitation of cell proliferation and migration. A region of the extracellular part of the receptor, termed the ‘dimerization arm’, is important for the formation of receptor dimers and represents an attractive target for the design of ErbB inhibitors.
Methods
An ErbB1 targeting peptide, termed Herfin-1, was designed based on a model of the tertiary structure of the EGF-EGFR ternary complex. The binding kinetics of this peptide were determined employing surface plasmon resonance analyses. ErbB1-4 expression and phosphorylation in human glioblastoma cell lines U87 and U118 were determined by Western blotting using specific antibodies. Cell proliferation was determined by MTS staining. Cell migration was examined using a Chemotaxis Migration Kit. Neurite outgrowth from primary cerebellar granule neurons was evaluated by fluorescence microscopy and image processing.
Results
The present study shows that Herfin-1 functions as an ErbB1 antagonist. It binds to the extracellular domain of ErbB1 with a KD value of 361 nM. In U87 and U118 cells, both expressing high levels of ErbB1, Herfin-1 inhibits EGF-induced ErbB1 phosphorylation and cell migration. Additionally, Herfin-1 was found to increase neurite outgrowth in cerebellar granule neurons, likely through the inhibition of a sustained weak ErbB1 activation.
Conclusions
Targeting the ErbB1 receptor dimerization interface is a promising strategy to inhibit receptor activation in ErbB1-expressing glioma cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Normanno, C. Bianco, L. Strizzi et al., The ErbB receptors and their ligands in cancer: an overview. Curr. Drug Targets 6, 243–257 (2005)
N.E. Hynes, H.A. Lane, ERBB receptors and cancer: the complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Cancer 5, 341–354 (2005)
P.M. Guy, J.V. Platko, L.C. Cantley, R.A. Cerione, K.L. Carraway III, Insect cell-expressed p180erbB3 possesses an impaired tyrosine kinase activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 91, 8132–8136 (1994)
N.E. Hynes, G. MacDonald, ErbB receptors and signaling pathways in cancer. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 21, 177–184 (2009)
T.P. Garrett, N.M. McKern, M. Lou et al., Crystal structure of a truncated epidermal growth factor receptor extracellular domain bound to transforming growth factor alpha. Cell 110, 763–773 (2002)
H. Ogiso, R. Ishitani, O. Nureki et al., Crystal structure of the complex of human epidermal growth factor and receptor extracellular domains. Cell 110, 775–787 (2002)
J. Schlessinger, Ligand-induced, receptor-mediated dimerization and activation of EGF receptor. Cell 110, 669–672 (2002)
H.S. Cho, D.J. Leahy, Structure of the extracellular region of HER3 reveals an interdomain tether. Science 297, 1330–1333 (2002)
S. Bouyain, P.A. Longo, S. Li, K.M. Ferguson, D.J. Leahy, The extracellular region of ErbB4 adopts a tethered conformation in the absence of ligand. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 102, 15024–15029 (2005)
F. Walker, S.G. Orchard, R.N. Jorissen et al., CR1/CR2 interactions modulate the functions of the cell surface epidermal growth factor receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 22387–22398 (2004)
K.M. Ferguson, M.B. Berger, J.M. Mendrola, H.S. Cho, D.J. Leahy, M.A. Lemmon, EGF activates its receptor by removing interactions that autoinhibit ectodomain dimerization. Mol. Cell 11, 507–517 (2003)
A.W. Burgess, H.S. Cho, C. Eigenbrot et al., An open-and-shut case? Recent insights into the activation of EGF/ErbB receptors. Mol. Cell 12, 541–552 (2003)
R.N. Jorissen, F. Walker, N. Pouliot, T.P. Garrett, C.W. Ward, A.W. Burgess, Epidermal growth factor receptor: mechanisms of activation and signalling. Exp. Cell Res. 284, 31–53 (2003)
D.S. Salomon, R. Brandt, F. Ciardiello, N. Normanno, Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their receptors in human malignancies. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 19, 183–232 (1995)
N. Normanno, L.A. De, C. Bianco et al., Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling in cancer. Gene 366, 2–16 (2006)
A.J. Ekstrand, N. Sugawa, C.D. James, V.P. Collins, Amplified and rearranged epidermal growth factor receptor genes in human glioblastomas reveal deletions of sequences encoding portions of the N- and/or C-terminal tails. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 89, 4309–4313 (1992)
S.V. Sharma, D.W. Bell, J. Settleman, D.A. Haber, Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 7, 169–181 (2007)
J. Marshall, Clinical implications of the mechanism of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Cancer 107, 1207–1218 (2006)
B.W. Park, H.T. Zhang, C. Wu et al., Rationally designed anti-HER2/neu peptide mimetic disables P185HER2/neu tyrosine kinases in vitro and in vivo. Nat. Biotechnol. 18, 194–198 (2000)
T. Nakamura, H. Takasugi, T. Aizawa et al., Peptide mimics of epidermal growth factor (EGF) with antagonistic activity. J. Biotechnol. 116, 211–219 (2005)
A. Berezov, J. Chen, Q. Liu, H.T. Zhang, M.I. Greene, R. Murali, Disabling receptor ensembles with rationally designed interface peptidomimetics. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 28330–28339 (2002)
R. Xu, G.K. Povlsen, V. Soroka, E. Bock, V. Berezin, A peptide antagonist of the ErbB1 receptor inhibits receptor activation, tumor cell growth and migration in vitro and xenograft tumor growth in vivo. Cell. Oncol. 32, 259–274 (2010)
R.W. Wong, L. Guillaud, The role of epidermal growth factor and its receptors in mammalian CNS. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 15, 147–156 (2004)
C. Birchmeier, ErbB receptors and the development of the nervous system. Exp. Cell Res. 315, 611–618 (2009)
M. Ozaki, S. Kishigami, R. Yano, Expression of receptors for neuregulins, ErbB2, ErbB3 and ErbB4, in developing mouse cerebellum. Neurosci. Res. 30, 351–354 (1998)
M. Yamada, T. Ikeuchi, H. Hatanaka, The neurotrophic action and signalling of epidermal growth factor. Prog. Neurobiol. 51, 19–37 (1997)
F. Gomez-Pinilla, D.J. Knauer, M. Nieto-Sampedro, Epidermal growth factor receptor immunoreactivity in rat brain. Development and cellular localization. Brain Res. 438, 385–390 (1988)
M. Sibilia, J.P. Steinbach, L. Stingl, A. Aguzzi, E.F. Wagner, A strain-independent postnatal neurodegeneration in mice lacking the EGF receptor. EMBO J. 17, 719–731 (1998)
G.K. Povlsen, V. Berezin, E. Bock, Neural cell adhesion molecule-180-mediated homophilic binding induces epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) down-regulation and uncouples the inhibitory function of EGFR in neurite outgrowth. J. Neurochem. 104, 624–639 (2008)
V. Koprivica, K.S. Cho, J.B. Park et al., EGFR activation mediates inhibition of axon regeneration by myelin and chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans. Science 310, 106–110 (2005)
A. Schousboe, A. Meier, J. Drejer, L. Hertz, Preparation of Primary Cultures of Mouse (rat) Cerebellar Granule Cells (Alan R Liss, New York, 1989), pp. 203–206
C. Lu, L.Z. Mi, M.J. Grey et al., Structural evidence for loose linkage between ligand binding and kinase activation in the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 30, 5432–5443 (2010)
P.C. Burger, D.K. Pearl, K. Aldape et al., Small cell architecture–a histological equivalent of EGFR amplification in glioblastoma multiforme? J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 60, 1099–1104 (2001)
H. Ohgaki, P. Kleihues, Genetic pathways to primary and secondary glioblastoma. Am. J. Pathol. 170, 1445–1453 (2007)
P.S. Ritch, S.L. Carroll, H. Sontheimer, Neuregulin-1 enhances survival of human astrocytic glioma cells. Glia 51, 217–228 (2005)
R.V. LaRocca, M. Rosenblum, B. Westermark, M.A. Israel, Patterns of proto-oncogene expression in human glioma cell lines. J. Neurosci. Res. 24, 97–106 (1989)
E. Carrasco-Garcia, M. Saceda, S. Grasso et al., Small tyrosine kinase inhibitors interrupt EGFR signaling by interacting with erbB3 and erbB4 in glioblastoma cell lines. Exp. Cell Res. 317, 1476–1489 (2011)
M.K. Ghosh, P. Sharma, P.C. Harbor, S.O. Rahaman, S.J. Haque, PI3K-AKT pathway negatively controls EGFR-dependent DNA-binding activity of Stat3 in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Oncogene 24, 7290–7300 (2005)
P.H. Huang, A.M. Xu, F.M. White, Oncogenic EGFR signaling networks in glioma. Sci. Signal. 2, re6 (2009)
Z. Liu, J. Klominek, Inhibition of proliferation, migration, and matrix metalloprotease production in malignant mesothelioma cells by tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Neoplasia 6, 705–712 (2004)
S.H. Kim, Y.C. Song, S.H. Kim, H. Jo, Y.S. Song, Effect of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor alone and in combination with cisplatin on growth of vulvar cancer cells. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1171, 642–648 (2009)
S.M. Huang, J. Li, P.M. Harari, Molecular inhibition of angiogenesis and metastatic potential in human squamous cell carcinomas after epidermal growth factor receptor blockade. Mol. Cancer Ther. 1, 507–514 (2002)
J.L. Eller, S.L. Longo, D.J. Hicklin, G.W. Canute, Activity of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody C225 against glioblastoma multiforme. Neurosurgery 51, 1005–1013 (2002)
G. Karpel-Massler, U. Schmidt, A. Unterberg, M.E. Halatsch, Therapeutic inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor in high-grade gliomas: where do we stand? Mol. Cancer Res. 7, 1000–1012 (2009)
S. Kobayashi, T.J. Boggon, T. Dayaram et al., EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 352, 786–792 (2005)
J. Mendelsohn, J. Baselga, Status of epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists in the biology and treatment of cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 21, 2787–2799 (2003)
M. Kirsch, G. Schackert, P.M. Black, Metastasis and angiogenesis. Cancer Treat. Res. 117, 285–304 (2004)
D. Kedrin, J. Wyckoff, P.J. Boimel et al., ERBB1 and ERBB2 have distinct functions in tumor cell invasion and intravasation. Clin. Cancer Res. 15, 3733–3739 (2009)
T. Turner, P. Chen, L.J. Goodly, A. Wells, EGF receptor signaling enhances in vivo invasiveness of DU-145 human prostate carcinoma cells. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 14, 409–418 (1996)
M. Fedor-Chaiken, P.W. Hein, J.C. Stewart, R. Brackenbury, M.S. Kinch, E-cadherin binding modulates EGF receptor activation. Cell Commun. Adhes. 10, 105–118 (2003)
P. Reddy, L. Liu, C. Ren et al., Formation of E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion activates AKT and mitogen activated protein kinase via phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase and ligand-independent activation of epidermal growth factor receptor in ovarian cancer cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 19, 2564–2578 (2005)
J. Gavard, S. Gutkind, in Cancer Drug Discovery and Development: EGFR Signaling Networks in Cancer Therapy eds. by J. D. Haley, W. J. Gullick. A Molecular Crosstalk between E-cadherin and EGFR Signaling Networks (Humana Press, 2008), pp. 139–154
M. Xia, M. Hu, J. Wang et al., Identification of the role of Smad interacting protein 1 (SIP1) in glioma. J. Neurooncol. 97, 225–232 (2010)
M. Gotz, W.B. Huttner, The cell biology of neurogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6, 777–788 (2005)
A. Fiederling, R. Ewert, A. Andreyeva, K. Jungling, K. Gottmann, E-cadherin is required at GABAergic synapses in cultured cortical neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 501, 167–172 (2011)
S.A. Oblander, S.E. Ensslen-Craig, F.M. Longo, S.M. Brady-Kalnay, E-cadherin promotes retinal ganglion cell neurite outgrowth in a protein tyrosine phosphatase-mu-dependent manner. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 34, 481–492 (2007)
K. Shimamura, T. Takahashi, M. Takeichi, E-cadherin expression in a particular subset of sensory neurons. Dev. Biol. 152, 242–254 (1992)
Acknowledgments
Help from the Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Protein Research (Copenhagen, Denmark) with the binding studies performed using the Biacore T200 instrument is greatly appreciated.
Funding
This work was supported by the Lundbeck Foundation (R13-A1398 to V.B.) and the Danish Research Council (09–065919 to V.B., 09–071033 to E.B.).
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest for all authors
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material

Supplementary Fig. 1
Schematic presentation of the Herfin-1 peptide tetramer (JPEG 15 kb)

Supplementary Fig. 2
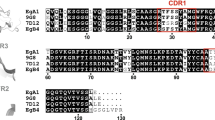
Sequence alignment of the extended part of the C-terminal (Herfin motifs) and N-terminal (Herfin counter-motifs involved in hydrophobic interactions with the Herfin motif) regions of the dimerization arm of four ErbB receptors (ErbB1, ErbB2, ErbB3, and ErbB4; UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot accession no. P00533, P04626, P21860, and Q15303, respectively) (JPEG 47 kb)

Supplementary Fig. 3
Sequence alignment of the N-terminal region of the ErbB1 dimerization arm and N-terminal region of E-cadherin extracellular domain 3 (UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot accession no. P00533 and P09803, respectively). The advanced BLAST program was used (http://www.ch.embnet.org/software/bBLAST.html; accessed June 6, 2012) (JPEG 11 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Staberg, M., Riemer, C., Xu, R. et al. Identification of a novel antagonist of the ErbB1 receptor capable of inhibiting migration of human glioblastoma cells. Cell Oncol. 36, 201–211 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-013-0128-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-013-0128-6