Abstract
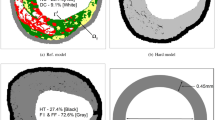
Balloon angioplasty followed by local delivery of antiproliferative drugs to target tissue is increasingly being considered for the treatment of obstructive arterial disease, and yet there is much to appreciate regarding pharmacokinetics in arteries of non-uniform disease. We developed a computational model capable of simulating drug-coated balloon delivery to arteries of heterogeneous tissue composition comprising healthy tissue, as well as regions of fibrous, fibro-fatty, calcified and necrotic core lesions. Image processing using an unsupervised clustering technique was used to reconstruct an arterial geometry from a single, patient-specific color image obtained from intravascular ultrasound-derived virtual histology. Transport of free drug was modeled using a time-dependent reaction-diffusion model and the bound, immobilized drug using the time-dependent reaction equation. The governing equations representing the transport of free as well as bound drug along with a set of initial settings and boundary conditions were solved numerically using an explicit finite difference scheme that satisfied the Courant-Friedrichs-Lewy stability criterion. Our results support previous findings related to the transport and binding of drug in arteries where tissue retention is strongly dependent on local pharmacologic properties. Additionally, modeling results indicate that non-uniform disease composition leads to heterogeneous arterial drug distribution patterns, although further validation using animal studies is required to fully appreciate pharmacokinetics in disease-laden arteries.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balakrishnan, B., A. R. Tzafriri, P. Seifert, A. Groothuis, C. Rogers, and E. R. Edelman. Strut position, blood flow, and drug deposition: implications for single and overlapping drug-eluting stents. Circulation 111:2958–2965, 2005.
Bozsak, F., J. M. Chomaz, AI. Barakat. Modeling the transport of drugs eluted from stents: physical phenomena driving drug distribution in the arterial wall. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 13:327–347, 2014.
Byrne, R. A., M. Joner, F. Alfonso, and A. Kastrati. Drug-coated balloon therapy in coronary and peripheral artery disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 11:13–23, 2014.
Cioppa, A., E. Stabile, G. Popusoi, L. Salemme, L. Cota, A. Pucciarelli, V. Ambrosini, G. Sorropago, T. Tesorio, A. Agresta, G. Biamino, and P. Rubino. Combined treatment of heavy calcified femoro-popliteal lesions using directional atherectomy and a paclitaxel coated balloon: one-year single centre clinical results. Cardiovasc. Revasc. Med. 13:219–223, 2012.
Creel, C., M. Lovich, and E. R. Edelman. Arterial paclitaxel distribution and deposition. Circ. Res. 86:879–884, 2000.
Feenstra, P. H., and C. A. Taylor. Drug transport in artery walls: a sequential porohyperelastic-transport approach. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 12:263–276, 2009.
Granada, J. F., M. Stenoien, P. P. Buszman, A. Tellez, D. Langanki, G. L. Kaluza, M. B. Leon, W. Gray, M. R. Jaff, and R. S. Schwartz. Mechanisms of tissue uptake and retention of paclitaxel-coated balloons: impact on neointimal proliferation and healing. Open Heart 1:e000117, 2014.
Gray, W. A., and J. F. Granada. Drug-coated balloons for the prevention of vascular restenosis. Circulation 121:2672–2680, 2010.
Guo, J., D. M. Saylor, E. P. Glaser, and D. V. Patwardhan. Impact of artificial plaque composition on drug transport. J. Pharm. Sci. 102:1905–1914, 2013.
Hossain, S. S., S. A. Hossainy, Y. Bazilevs, V. M. Calo, and T. J. R. Hughes. Mathematical modeling of coupled drug and drug-encapsulated nanoparticle transport in patient-specific coronary artery walls. Comput. Mech. 49:213–242, 2012.
Hwang, C. W., D. Wu, and E. R. Edelman. Physiological transport forces govern drug distribution for stent-based delivery. Circulation 104:822–829, 2001.
Hwang, C. W., D. Wu, and E. R. Edelman. Impact of transport and drug properties on the local pharmacology of drug-eluting stents. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Intervent. 90:7–12, 2003.
Ilea, D. E., and P. F. Whelan. Color image segmentation using a spatial k-means clustering algorithm. In: IMVIP 2006—10th International Machine Vision and Image Processing Conference, 30 August–1 September 2006, Dublin, Ireland, 2006.
Kolachalama, V. B., E. G. Levine, and E. R. Edelman. Luminal flow amplifies stent-based drug deposition in arterial bifurcations. PLoS ONE 4:e8105, 2009.
Kolachalama, V. B., S. D. Pacetti, J. W. Franses, J. J. Stankus, H. Q. Zhao, T. Shazly, A. Nikanorov, L. B. Schwartz, A. R. Tzafriri, and E. R. Edelman. Mechanisms of tissue uptake and retention in zotarolimus-coated balloon therapy. Circulation 127:2047–2055, 2013.
Kolachalama, V. B., A. R. Tzafriri, D. Y. Arifin, and E. R. Edelman. Luminal flow patterns dictate arterial drug deposition in stent-based delivery. J. Control Release 133:24–30, 2009.
Kolandaivelu, K., R. Swaminathan, W. J. Gibson, V. B. Kolachalama, K. L. Nguyen-Ehrenreich, V. L. Giddings, L. Coleman, G. K. Wong, and E. R. Edelman. Stent thrombogenicity early in high-risk interventional settings is driven by stent design and deployment and protected by polymer-drug coatings. Circulation 123:1400–1409, 2011.
König, A., and V. Klauss. Virtual histology. Heart 93:977–982, 2007.
König, A., M. P. Margolis, R. Virmani, D. Holmes, and V. Klauss. Technology Insight: in vivo coronary plaque classification by intravascular ultrasonography radiofrequency analysis. Nat. Clin. Pract. Cardiovasc. Med. 5:219–229, 2008.
Levin, A. D., N. Vukmirovic, C. W. Hwang, and E. R. Edelman. Specific binding to intracellular proteins determines arterial transport properties for Rapamycin and Paclitaxel. Proc. Natl Acad .Sci. USA. 101:9463–9467, 2004.
Levitt, D. Heterogeneity of human blood flow. BMC Clin. Pharmacol. 7, 2007. doi:10.1186/1472-6904-7-1.
Loh, J. P., I. M. Barbash, and R. Waksman. The current status of drug-coated balloons in percutaneous coronary and peripheral interventions. EuroIntervention 9:979–988, 2013.
Lovich, M. A., C. Creel, K. Hong, C. W. Hwang, and E. R. Edelman. Carrier proteins determine local pharmacokinetics and arterial distribution of Paclitaxel. J. Pharm. Sci. 90:1324–1335, 2001.
McKittrick, C. M., S. Kennedy, K. G. Oldroyd, S. McGinty, and C. McCormick. Modelling the impact of atherosclerosis on drug release and distribution from coronary stents. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 44:477–487, 2016.
Nair, A., B. D. Kuban, E. M. Tuzcu, P. Schoenhagen, S. E. Nissen, and D. G. Vince. Coronary plaque classification with intravascular ultrasound radiofrequency data analysis. Circulation 106:2200–2206, 2002.
Nissen, S. E. Application of intravascular ultrasound to characterize coronary artery disease and assess the progression or regression of atherosclerosis. Am. J. Cardiol. 89:24B–31B, 2002 .
Nissen, S. E., and P. Yock. Intravascular ultrasound: novel pathophysiological insights and current clinical applications. Circulation 103:604–616, 2001.
O’Brien, C. C., V. B. Kolachalama, T. J. Barber, A. Simmons, and E. R. Edelman. Impact of flow pulsatility on arterial drug distribution in stent-based therapy. J .Control Release 168:115–124, 2013.
O’Brien, C. C., K. Kolandaivelu, J. Brown, A. C. Lopes, M. Kunio, V. B. Kolachalama, and E. R. Edelman. Constraining OCT with knowledge of device design enables high accuracy hemodynamic assessment of endovascular implants. PLoS One 11:e0149178, 2016.
O’Connell, B. M., and M. T. Walsh Demonstrating the influence of compression on artery wall mass transport. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38:1354–1366, 2010.
Sarode, K., D. A. Spelber, D. L. Bhatt, A. Mohammad, A. Prasad, E. S. Brilakis, and S. Banerjee. Drug delivering technology for endovascular management of infrainguinal peripheral artery disease. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 7:827–839, 2014.
Sixt, S., O. G.Carpio Cancino, A. Treszl, U. Beschorner, R. Macharzina, A. Rastan, H. Krankenberg, F. J. Neumann, and T. Zeller. Drug-coated balloon angioplasty after directional atherectomy improves outcome in restenotic femoropopliteal arteries. J. Vasc. Surg. 58:682–686, 2013.
Stefanini, G. G., and D. R. Holmes, Jr. Drug-eluting coronary artery stents. N .Engl. J. Med. 368:254–265, 2013.
Strikwerda, J. C. Finite Difference Schemes and Partial Differential Equations (2\(^{\rm nd}\) edition), SIAM Publication, 2004.
Tedgui, A., and M. J. Lever. 1984 Filtration through damaged and undamaged rabbit thoracic aorta. Am. J. Physiol. 247:H784–H791.
Tzafriri, A. R., A. D. Levin, and E. R. Edelman. Diffusion-limited binding explains binary dose response for local arterial and tumour drug delivery. Cell. Prolif. 42:348–363, 2009.
Tzafriri, A. R., N. Vukmirovic, V. B. Kolachalama, I. Astafieva, and E. R. Edelman. Lesion complexity determines arterial drug distribution after local drug delivery. J. Control Release 142:332–338, 2010.
Waksman, R., and R. Pakala. Drug-eluting balloon: the comeback kid? Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2:352–358, 2009.
Woods, T. C., and A. R. Marks. Drug-eluting stents. Annu. Rev. Med 55:169–178, 2004.
Zotarolimus, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/9876378.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mr. Gweltaz Lever, University of Glasgow, UK for his assistance on border detection of the patient-specific IVUS image. This work was supported by funding from the Charles Stark Draper Laboratory to VBK and in part by funding from Special Assistance Programme (SAP-III) (Grant No. F.510/3/DRS-III/2015 (SAPI)) sponsored by the University Grants Commission, New Delhi, India to PKM.
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Statement of Human Studies
No human subjects were used for this study.
Statement of Animal Studies
No animal subjects were used for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Francesco Migliavacca and Editor-in-Chief Ajit P. Yoganathan oversaw the review of this article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandal, P.K., Sarifuddin & Kolachalama, V.B. Computational Model of Drug-Coated Balloon Delivery in a Patient-Specific Arterial Vessel with Heterogeneous Tissue Composition. Cardiovasc Eng Tech 7, 406–419 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13239-016-0273-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13239-016-0273-y