Abstract
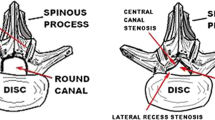
Lumbar spinal stenosis is a narrowing of spinal canal or neural foramina producing root ischaemia and neurogenic claudication[1–3]. Both the neural canal and foramen are narrowed with the spine in extension and opened in flexion. Patients are usually sixty years or over and present with unilateral or bilateral leg pain with or without back pain. The pain is worse on walking and if the patient is upright and relieved by sitting or bending forward[1–3]. With increasingly ageing population this is a common problem and difficult to deal with as many of the elderly patients have associated co-morbidities making them unsuitable for conventional decompressive surgery[4, 5]. Although lumbar spinal stenosis is one of the most frequent indications for spinal surgery in patients over 65 years of age[7], deciding the most appropriate procedure is a challenge to the clinicians. X-STOP interspinous implant is a titanium device. It was developed to prevent extension and also increase the dimension of spinal canal and neural foramina[5]. We are reporting the clinical outcome and patient satisfaction following indirect decompression with X-STOP.
Similar content being viewed by others
/+/ References
Epstein NE, Maldonado VC, Cusick JF (1998) Symptomatic lumbar spinal stenosis. Surg Neurol; 50:3–10
Hall S, Bartleson JD, Onofrio BM et al (1985) Lumbar spinal stenosis: clinical features, diagnostic procedures and result of surgical treatment in 68 patients. Ann Int Med; 103: 271–275
Alvarez JA, Hardy RH Jr (1998) Lumbar spinal stenosis: a common cause of back and leg pain. Am Fam Physician; 57: 1825–1840.
Szpalski M, Gunzburg R (2003) Lumbar spinal stenosis in the elderly: an overview. Eur Spine J; 12(suppl): 170–175.
Lee Jhangbo, Hida Kazutoshi et al (2004) An interspinous process distractor (XSTOP) for lumbar spinal stenosis in elderly patietns: Preliminary experience in 10 cosecutive cases. Journal of Spinal Disorder and Tecniques; 17(1): 72–77.
Amundsen T, Webber H et al (1995) Lumbar spinal stenosis: clinical and radiological features. Spine; 20: 1178–1186.
Katz LN, Lipson SJ, Chang LC et al (1996) Seven to 10 year outcome of decompressive surgery for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine; 21: 92–98.
de Graff I, Park A, et al (2006) Diagnosis of lumbar spinal stenosis: A systemic review of the accuracy of diagnostic tests. Spine; 31(10): 1168–1176.
Katz JN, Stucki G, Lipson SJ et al (1999) Predictors of surgical outcome in degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine; 24: 2229–2233.
Katz JN, Lipson SJ, Brick GW et al (1995) Clinical correlates of patient satisfaction after laminectomy for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine; 20:1155–1160.
Airaksinen o, Herno A, Turunen V et al (1997) Surgical outcome of 438 patients treated surgically for lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine; 22: 2278–2282.
Johnsson KE, Uden A, Rossen I (1991) The effect of decompression on the natural course of spinal stenosis. A comparison of surgically treated and untreated patients. Spine; 16: 615–619.
Gunzburg R, Keller TS, Szpalski M et al (2003) Clinical and psychofunctional measures of conservative decompression surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis: a prospective cohort study.Eur Spine J; 12: 197–204.
Jönsson B, Stromqvist B (1994) Lumbar spine surgery in the elderly. Complications and surgical results. Spine: 19: 1431–1435.
Benz RJ, Ibrahim ZG, Afshr P et al (2001) Predicting complications in elderly patients undergoing lumbar decompression. Clinical Orthop; 384: 116–121.
Reindl R, Steffen T, Cohen L et al (2003) Elective lumbar spinal decompression in the elderly: Is it a high risk operation? Can J Surgery; 46: 43–46.
Turner JA, Ersek M, Herron L et al (1992) Surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis. Attempted meta-analysis of literature. Spine; 17: 1–8.
Kalbarczyk A, Lukes A, Seiler RW (1998) Surgical treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis in the elderly. Acta Neurochir; 140: 637–641.
Galliano K, Obwegeser A, Gabl MV et al (2005) Long term outcome of laminectomy for spinal stenosis in Octagenarians. Spine; 30(3): 332–335.
Guiot BH, Khoo LT, Fessler RG (2002) A minimally invasive technique for decompression of the lumbar spine. Spine; 27: 432–438.
Zucherman, J; Hsu, K; Hartjen, C; Mehalic, Thomas F; Implicito, D et al (2005) Multicenter, Prospective, Randomized Trial Evaluating the X STOP Interspinous Process Decompression System for the Treatment of Neurogenic Intermittent Claudication: Two-Year Follow-Up Results. Spine. 30(12):1351–1358
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhadra, A.K., Raman, A.S., Tucker, S. et al. Interspinous implant in lumbar spinal stenosis: a prospective cohort. ArgoSpine News J 21, 142–144 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12240-009-0029-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12240-009-0029-8