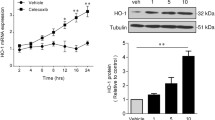
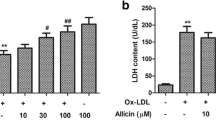
Abstract
Purpose
Statins and certain calcium channel blockers may improve nitric oxide (NO) release and endothelial function through various mechanisms, but their combined effects are not well understood.
Methods
The separate versus combined effects of amlodipine (AML) and atorvastatin (AT) on NO and peroxynitrite (ONOO−) were measured in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) in the presence and absence of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) using electrochemical nanosensors.
Results
The combination of AML (5 μmol/l) and AT (3-6 μmol/l) directly stimulated NO release that was about twofold greater than the sum of their separate effects (p < 0.05). This synergistic activity is attributed to enhanced endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) function and decreased cytotoxic ONOO−. LDL (100 mg/dl) caused a dysfunction of HUVEC manifested by a 60% reduction in NO and an almost twofold increase in ONOO−. Treatment with AML/AT partially reversed the effects of LDL on endothelial function, including a 90% increase in NO and 50% reduction in ONOO−. Small-angle X-ray diffraction analysis indicates that AML and AT are lipophilic and share an overlapping molecular location in the cell membrane that could facilitate electron transfer for antioxidant mechanisms.
Conclusion
These findings indicate a synergistic effect of AML and AT on an increase in NO concentration, reduction of nitroxidative stress. Also, AML/AT partially restored the NO level of LDL-induced dysfunctional endothelium. Their combined effects may be enhanced by antioxidant properties related to their intermolecular actions in the cell membrane and an increase in the expression and coupling of endothelial nitric oxide synthase.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. S. Oemar, M. R. Tschudi, N. Godoy, V. Brovkovich, T. Malinski, and T. F. Luscher. Reduced endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression and production in human atherosclerosis. Circulation 97(25):2494–2498 (1998).
D. G. Harrison, P. C. Freiman, M. L. Armstrong, M. L. Marcus, and D. D. Heistad. Alterations of vascular reactivity in atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 61:74–80 (1987).
J. K. Liao. Endothelium and acute coronary syndromes. Clin. Chem. 44:1799–1808 (1998).
G. Kojda and D. G. Harrison. Interactions between NO and reactive oxygen species: pathophysiological importance in atherosclerosis, hypertension, diabetes and heart failure. Cardiovasc. Res. 43:562–571 (1999).
M. R. Tschudi, M. Barton, N. A. Bersinger, P. Moreau, F. Cosentino, G. Noll, T. Malinski, and T. F. Luscher. Effect of age on kinetics of nitric oxide release in rat aorta and pulmonary artery. J. Clin. Invest. 98(4):899–905 (1996).
O. A. Paniagua, M. B. Bryant, and J. A. Panza. Role of endothelial nitric oxide in shear stress-induced vasodilation in human microvasculature. Diminished activity in hypertensive and hypercholesterolemic patients. Circulation 103:1752–1758 (2001).
J. A. Panza, A. A. Quyyumi, J. E. Brush, and S. E. Epstein. Abnormal endothelium-dependent vascular relaxation in patients with essential hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 323:22–27 (1990).
S. Taddei, A. Virdis, P. Mattei, and A. Salvetti. Vasodilation to acetylcholine in primary and secondary forms of human hypertension. Hypertension 21:929–933 (1993).
M. Rodriguez-Porcel, L. O. Lerman, J. Herrmann, T. Sawamura, C. Napoli, and A. Lerman. Hypercholesterolemia and hypertension have synergistic deleterious effects on coronary endothelial function. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23:885–891 (2003).
S. John and R. E. Schmieder. Impaired endothelial function in arterial hypertension and hypercholesterolemia: Potential mechanisms and differences. J. Hypertens. 18:363–374 (2000).
J. D. Neaton and D. Wentworth. Serum cholesterol, blood pressure, cigarette smoking, and death from coronary heart disease. Overall findings and differences by age for 316,099 white men. Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial Research Group. Arch. Intern. Med. 152:56–64 (1992).
F. Thomas, K. Bean, L. Guize, S. Quentzel, P. Argyriadis, and A. Benetos. Combined effects of systolic blood pressure and serum cholesterol on cardiovascular mortality in young (<55 years) men and women. Eur. Heart J. 23:528–535 (2002).
U. Landmesser, H. Cai, S. Dikalov, L. McCann, J. Hwang, H. Jo, S. M. Holland, and D. G. Harrison. Role of p47(phox) in vascular oxidative stress and hypertension caused by angiotensin II. Hypertension 40:511–515 (2002).
U. Landmesser, S. Dikalov, S. R. Price, L. McCann, T. Fukai, S. M. Holland, W. E. Mitch, and D. G. Harrison. Oxidation of tetrahydrobiopterin leads to uncoupling of endothelial cell nitric oxide synthase in hypertension. J. Clin. Invest. 111:1201–1209 (2003).
Y. Ohara, T. E. Peterson, and D. G. Harrison. Hypercholesterolemia increases endothelial superoxide anion production. J. Clin. Invest. 91(6):2546–2551 (1993).
J. K. Liao, W. S. Shin, W. Y. Lee, and S. L. Clark. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein decreases the expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 270:319–324 (1995).
L. Vergnani, S. Hatrik, F. Ricci, A. Passaro, N. Manzoli, G. Zuliani, V. Brovkovych, R. Fellin, and T. Malinski. Effect of native and oxidized low-density lipoprotein on endothelial nitric oxide and superoxide production: key role of l-arginine availability. Circulation 101(11):1261–1266 (2000).
R. P. Mason and R. F. Jacob. Membrane microdomains and vascular biology: Emerging role in atherogenesis. Circulation 107:2270–2273 (2003).
D. G. Harrison. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of endothelial cell dysfunction. J. Clin. Invest. 100:2153–2157 (1997).
X. Zhang and T. H. Hintze. Amlodipine releases nitric oxide from canine coronary microvessels: An unexpected mechanism of action of a calcium channel-blocking agent. Circulation 97:576–580 (1998).
T. J. Anderson, I. T. Meredith, A. C. Yeung, B. Frei, A. P. Selwyn, and P. Ganz. The effect of cholesterol-lowering and antioxidant therapy on endothelium-dependent coronary vasomotion. N. Engl. J. Med. 332:488–493 (1995).
G. B. Mancini, G. C. Henry, C. Macaya, B. J. O'Neill, A. L. Pucillo, R. G. Carere, T. J. Wargovich, H. Mudra, T. F. Luscher, M. I. Klibaner, H. E. Haber, A. C. Uprichard, C. J. Pepine, and B. Pitt. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition with quinapril improves endothelial vasomotor dysfunction in patients with coronary artery disease. The TREND (Trial on Reversing Endothelial Dysfunction) Study. Circulation 94(3):240–243 (1996).
S. Wolfrum, K. S. Jensen, and J. K. Liao. Endothelium-dependent effects of statins. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23:729–736 (2003).
R. P. Mason, M. F. Walter, and R. F. Jacob. Effects of HMG–CoA reductase inhibitors on endothelial function: Role of microdomains and oxidative stress. Circulation 109:II34–II41 (2004).
L. Kalinowski, I. T. Dobrucki, and T. Malinski. Cerivastatin potentiates nitric oxide release and eNOS expression through inhibition of isoprenoids synthesis. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 53:585–595 (2002).
R. P. Mason, L. Kalinowski, R. F. Jacob, A. M. Jacoby, and T. Malinski. Nebivolol reduces nitroxidative stress and restores nitric oxide bioavailability in endothelium of black Americans. Circulation 112:3795–3801 (2005).
R. P. Mason, P. Marche, and T. H. Hintze. Novel vascular biology of third-generation L-type calcium channel antagonists: Ancillary actions of amlodipine. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23:2155–2163 (2003).
R. P. Mason, M. F. Walter, C. A. Day, and R. F. Jacob. Intermolecular differences for HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors contribute to distinct pharmacologic and pleiotropic actions. Am. J. Cardiol. 96[suppl]:11F–23F (2005).
S. E. Nissen, E. M. Tuzcu, P. Libby, P. D. Thompson, M. Ghali, D. Garza, L. Berman, H. Shi, E. Buebendorf, and E. J. Topol. Effect of antihypertensive agents on cardiovascular events in patients with coronary disease and normal blood pressure: the CAMELOT study: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 292:2217–2226 (2004).
P. S. Sever, B. Dahlof, and N. R. Poulter. Prevention of coronary and stroke events with atorvastatin in hypertensive patients who have average or lower-than-average cholesterol concentrations, in the Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial-Lipid Lowering Arm (ASCOT-LLA): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 361:1149–1158 (2003).
H. M. Colhoun, D. J. Betteridge, P. N. Durrington, G. A. Hitman, Neil HAW, S. J. Livingstone, M. J. Thomason, M. I. Mackness, V. Charlton-Menys, and J. H. Fuller. Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease with atorvastatin in type 2 diabetes in the Collaborative Atorvastatin Diabetes Study (CARDS): Multicentre randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 364:685–696 (2004).
P. Sever, B. Dahlof, N. Poulter, H. Wedel, G. Beevers, M. Caulfield, R. Collins, S. Kjeldsen, A. Kristinsson, G. McInnes, J. Mehlsen, M. Niemenem, E. O'Brien, and J. Ostergren. Potential synergy between lipid-lowering and blood-pressure-lowering in the Anglo-Scadinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trail. Eur. Heart J. 27:2982–2988 (2006).
D. J. M. Delsing, J. W. Jukema, M. A. van de Wiel, J. J. Emeis, A. van der Laarse, L. M. Havekes, and H. M. G. Princen. Differential effects of amlodipine and atorvastatin treatment and their combination on atherosclerosis in ApoE*3-Leiden transgenic mice. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 42:63–70 (2003).
L. Kalinowski, L. W. Dobrucki, V. Brovkovich, and T. Malinski. Increased nitric oxide bioavailability in endothelial cells contributes to the pleiotropic effect of cerivastatin. Circulation 105:933–938 (2002).
J. Xue, X. Ying, J. Chen, Y. Xian, and L. Jin. Amperometric ultramicrosensors for peroxynitrite detection and its application toward single myocardial cells. Anal. Chem. 72:5313–5321 (2000).
V. Lvovich and A. Scheeline. Amperometric sensors for simultaneous superoxide and hydrogen peroxide detection. Anal. Chem. 69:454–462 (1997).
T. Malinski, and Z. Taha. Nitric oxide release from a single cell measured in situ by a porphyrinic-based microsensor. Nature 358:676–678 (1992).
P. Vallance, S. Patton, K. Bhagat, R. MacAllister, M. Radomski, S. Moncada, and T. Malinski. Direct measurement of nitric oxide in human beings. Anal. Chem. 346:153–154 (1995).
J. E. Bennett and T. Malinski. Conductive polymeric porphyrin films: application in the electrocatalytic oxidation of hydrazine. Chem. Mater. 3:490–495 (1991).
A. D. Bangham, M. M. Standish, and J. C. Watkins. Diffusion of univalent ions across the lamellae of swollen phospholipids. J. Mol. Biol. 13:238–252 (1965).
D. W. Chester, L. G. Herbette, R. P. Mason, A. F. Joslyn, D. J. Triggle, and D. E. Koppel. Diffusion of dihydropyridine calcium channel antagonists in cardiac sarcolemmal lipid multibilayers. Biophys. J. 52(6):1021–1030 (1987).
R. P. Mason, G. E. Gonye, D. W. Chester, and L. G. Herbette. Partitioning and location of Bay K 8644, 1,4-dihydropyridine calcium channel agonist, in model and biological membranes. Biophys. J. 55(4):769–778 (1989).
R. P. Mason and R. F. Jacob. X-ray diffraction analysis of membrane structure changes with oxidative stress. In D. Armstrong (ed.), Methods in Molecular Biology: Ultrastructural and Molecular Biology Protocols. Vol 193. Humana Press Inc., Totowa, NJ, 2002, pp. 71–80.
T. N. Tulenko, M. Chen, P. E. Mason, and R. P. Mason. Physical effects of cholesterol on arterial smooth muscle membranes: Evidence of immiscible cholesterol domains and alterations in bilayer width during atherogenesis. J. Lipid. Res. 39:947–956 (1998).
L. G. Herbette, T. MacAlister, T. F. Ashavaid, and R. A. Colvin. Structure-function studies of canine cardiac sarcolemmal membranes. II. Structural organization of the sarcolemmal membrane as determined by electron microscopy and lamellar X-ray diffraction. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 812(3):609–623 (1985).
K. K. Koh, M. J. Quon, S. H. Han, W. J. Chung, J. Y. Ahn, Y. H. Seo, M. H. Kang, T. H. Ahn, I. S. Choi, and E. K. Shin. Additive beneficial effects of losartan combined with simvastatin in the treatment of hypercholesterolemic, hypertensive patients. Circulation 110:3687–3692 (2004).
H. E. Andrews, K. R. Bruckdorfer, R. C. Dunn, and M. Jacobs. Low-density lipoproteins inhibit endothelium-dependent relaxation in rabbit aorta. Nature 327(6119):237–239 (1987).
K. A. Pritchard, L. Groszek, D. M. Smalley, W. C. Sessa, M. Wu, P. Villalon, M. S. Wolin, and M. B. Stemerman. Native low-density lipoprotein increases endothelial cell nitric oxide synthase generation of superoxide anion. Circ. Res. 77(3):510–518 (1995).
D. W. Stepp, J. Ou, A. W. Ackerman, S. Welak, D. Klick, K. A. Pritchard Jr. Native LDL and minimally oxidized LDL differentially regulate superoxide anion in vascular endothelium in situ. Am J Physiol, Heart Circ Physiol. 283(2):H750–H759 (2002).
F. Vidal, C. Colome, J. Martinez-Gonzalez, and L. Badimon. Atherogenic concentrations of native low-density lipoproteins down-regulate nitric-oxide-synthase mRNA and protein levels in endothelial cells. Eur. J. Biochem. 252(3):378–384 (1998).
J. Martinez-Gonzalez, B. Raposo, C. Rodriguez, and L. Badimon. 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase inhibition prevents endothelial NO synthase downregulation by atherogenic levels of native LDLs: balance between transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 21(5):804–809 (2001).
Z. Ou, J. Ou, A. W. Ackerman, K. T. Oldham, K. A. Pritchard Jr. L-4F, an apolipoprotein A-1 mimetic, restores nitric oxide and superoxide anion balance in low-density lipoprotein-treated endothelial cells. Circulation 107(11):1520–1524 (2003).
U. Laufs, V. La Fata, J. Plutzky, and J. K. Liao. Upregulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase by HMG CoA reductase inhibitors. Circulation 97(12):1129–1135 (1998).
A. H. Wagner, T. Kohler, U. Ruckschloss, I. Just, and M. Hecker. Improvement of nitric oxide-dependent vasodilation by HMG–CoA reductase inhibitors through attenuation of endothelial superoxide anion formation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 20:61–69 (2000).
S. Wassmann, U. Laufs, K. Muller, C. Konkol, K. Ahlbory, A. T. Baumer, W. Linz, M. Bohm, and G. Nickenig. Cellular antioxidant effects of atorvastatin in vitro and in vivo. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 22:300–305 (2002).
O. Feron, C. Dessy, J. P. Desager, and J. L. Balligand. Hydroxy-methylgluataryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibition promotes endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation through a decrease in caveolin abundance. Circulation 103:113–118 (2001).
R. P. Mason, M. F. Walter, M. W. Trumbore, E. G. Olmstead Jr., and P. E. Mason. Membrane antioxidant effects of the charged dihydropyridine calcium antagonist amlodipine. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 31:275–281 (1999).
F. Franzoni, G. Santoro, F. Regoli, Y. Plantinga, F. R. Femia, A. Carpi, and F. Galetta. An in vitro study of the peroxyl and hydroxyl radical scavenging capacity of the calcium antagonist amlodipine. Biomed. Pharmacother. 58:423–426 (2004).
M. McIntyre, C. A. Hamilton, D. D. Rees, J. L. Reid, and A. F. Dominiczak. Sex differences in the abundance of endothelial nitric oxide in a model of genetic hypertension. Hypertension 30:1517–1524 (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mason, R.P., Kubant, R., Heeba, G. et al. Synergistic Effect of Amlodipine and Atorvastatin in Reversing LDL-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction. Pharm Res 25, 1798–1806 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-007-9491-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-007-9491-1