Abstract
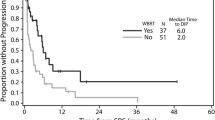
Patients with brain metastasis from melanoma have poor outcomes. Radiation is used both for prognostic and symptomatic value. We aimed to further clarify the role of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) and whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) as well as the prognostic implication of various sites of extracranial disease. The records of 73 consecutive patients treated at the University of Rochester Medical Center for brain-metastatic melanoma from January 2004 to October 2013 were reviewed. The median overall survival (OS) was 3.0 months. Patients treated with WBRT alone had decreased OS compared to those treated with SRS alone (HR = 0.38, p = 0.001) or WBRT and SRS (HR = 0.51, p = 0.039). The mean number of brain metastasis differed (p = 0.002) in patients in patients who received WBRT (4.0) compared to those who did not (2.0). Among patients with extracranial disease (n = 63), bone metastasis (HR = 1.86, p = 0.047, n = 15) was a negative prognostic factor; liver (HR = 1.59, p = 0.113, n = 17), lung (HR = 1.51, p = 0.23, n = 51) and adrenal metastasis (HR = 1.70, p = 0.15, n = 10) were not. In patients with concurrent brain and lung metastasis, those with disease limited to those two sites (OS = 8.7 mo, n = 13) had improved OS (HR = 0.44, p = 0.014) compared to those with additional disease (OS = 1.8 mo, n = 50). Based on this hypothesis-generating retrospective analysis, SRS may offer survival benefit compared to WBRT alone in patients with brain metastatic melanoma. Bone metastasis appears to confer a particularly poor prognosis. Those with disease confined to the lung and brain may represent a population with improved prognosis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gavrilovic IT, Posner JB (2005) Brain metastases: epidemiology and pathophysiology. J Neurooncol 75(1):5–14
Sperduto PW, Chao ST, Sneed PK et al (2010) Diagnosis-specific prognostic factors, indexes, and treatment outcomes for patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases: a multi-institutional analysis of 4,259 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77(3):655–661
Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D et al (2012) Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: an accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J Clin Oncol 30(4):419–425
Powell JW, Chung CT, Shah HR et al (2008) Gamma Knife surgery in the management of radioresistant brain metastases in high-risk patients with melanoma, renal cell carcinoma, and sarcoma. J Neurosurg 109(Suppl):122–128
Huttenlocher S, Dziggel L, Hornung D, Blanck O, Schild SE, Rades D (2014) A new prognostic instrument to predict the probability of developing new cerebral metastases after radiosurgery alone. Radiat Oncol 9:215
Mori Y, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Kirkwood JM, Agarwala S, Lunsford LD (1998) Stereotactic radiosurgery for cerebral metastatic melanoma: factors affecting local disease control and survival. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 42(3):581–589
Rades D, Sehmisch L, Huttenlocher S et al (2014) Radiosurgery alone for 1–3 newly-diagnosed brain metastases from melanoma: impact of dose on treatment outcomes. Anticancer Res 34(9):5079–5082
Selek U, Chang EL, Hassenbusch SJ 3rd et al (2004) Stereotactic radiosurgical treatment in 103 patients for 153 cerebral melanoma metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 59(4):1097–1106
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M et al (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 295(21):2483–2491
Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR et al (2009) Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10(11):1037–1044
Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U et al (2011) Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952–26001 study. J Clin Oncol 29(2):134–141
Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Regine WF et al (1998) Postoperative radiotherapy in the treatment of single metastases to the brain: a randomized trial. JAMA 280(17):1485–1489
Dyer MA, Arvold ND, Chen YH et al (2014) The role of whole brain radiation therapy in the management of melanoma brain metastases. Radiat Oncol 9:143
Hsu F, Kouhestani P, Nguyen S et al (2013) Population-based outcomes of boost versus salvage radiosurgery for brain metastases after whole brain radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 108(1):128–131
Brown PD, Asher AL, Ballman KV, et al. NCCTG N0574 (Alliance)(2015) A phase III randomized trial of whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) in addition to radiosurgery (SRS) in patients with 1 to 3 brain metastases. J Clin Oncol: Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 33(suppl):abstr LBA4
Fogarty G, Morton RL, Vardy J et al (2011) Whole brain radiotherapy after local treatment of brain metastases in melanoma patients—a randomised phase III trial. BMC Cancer 11:142
Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C et al (2011) Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. New Engl J Med 364(26):2507–2516
Hodi FS, O’Day SJ, McDermott DF et al (2010) Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. New Engl J Med 363(8):711–723
Gaudy-Marqueste C, Carron R, Delsanti C et al (2014) On demand Gamma-Knife strategy can be safely combined with BRAF inhibitors for the treatment of melanoma brain metastases. Ann Oncol 25(10):2086–2091
Knisely JP, Yu JB, Flanigan J, Sznol M, Kluger HM, Chiang VL (2012) Radiosurgery for melanoma brain metastases in the ipilimumab era and the possibility of longer survival. J Neurosurg 117(2):227–233
Silk AW, Bassetti MF, West BT, Tsien CI, Lao CD (2013) Ipilimumab and radiation therapy for melanoma brain metastases. Cancer Med 2(6):899–906
Postow MA, Callahan MK, Barker CA et al (2012) Immunologic correlates of the abscopal effect in a patient with melanoma. New Engl J Med 366(10):925–931
Stamell EF, Wolchok JD, Gnjatic S, Lee NY, Brownell I (2013) The abscopal effect associated with a systemic anti-melanoma immune response. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 85(2):293–295
Salama JK, Milano MT (2014) Radical irradiation of extracranial oligometastases. J Clin Oncol 32(26):2902–2912
Singh D, Chen Y, Hare MZ et al (2014) Local control rates with five-fraction stereotactic body radiotherapy for oligometastatic cancer to the lung. J Thorac Dis 6(4):369–374
Ashworth AB, Senan S, Palma DA et al (2014) An individual patient data metaanalysis of outcomes and prognostic factors after treatment of oligometastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 15(5):346–355
Biswas T, Sandhu AP, Singh DP et al (2003) Low-dose radiosurgery for benign intracranial lesions. Am J Clin Oncol 26(4):325–331
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J et al (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45(2):228–247
Ahmed KA, Freilich JM, Sloot S et al (2015) LINAC-based stereotactic radiosurgery to the brain with concurrent vemurafenib for melanoma metastases. J Neurooncol 122(1):121–126
Bernard ME, Wegner RE, Reineman K et al (2012) Linear accelerator based stereotactic radiosurgery for melanoma brain metastases. J Cancer Res Ther 8(2):215–221
Likhacheva A, Pinnix CC, Parikh N et al (2012) Validation of Recursive Partitioning Analysis and Diagnosis-Specific Graded Prognostic Assessment in patients treated initially with radiosurgery alone. J Neurosurg 117(Suppl):38–44
Kano H, Kondziolka D, Niranjan A, Flannery TJ, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2010) Repeat stereotactic radiosurgery for acoustic neuromas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76(2):520–527
Kim DH, Schultheiss TE, Radany EH, Badie B, Pezner RD (2013) Clinical outcomes of patients treated with a second course of stereotactic radiosurgery for locally or regionally recurrent brain metastases after prior stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurooncol 115(1):37–43
Mariya Y, Sekizawa G, Matsuoka Y, Seki H, Sugawara T, Sasaki Y (2011) Repeat stereotactic radiosurgery in the management of brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. Tohoku J Exp Med 223(2):125–131
Valentina P, Chiara O, Marcello M et al (2015) Radiosurgery reirradiation for high-grade glioma recurrence: a retrospective analysis. Neurol Sci. doi:10.1007/s10072-015-2172-7
Kocher M, Wittig A, Piroth MD et al (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery for treatment of brain metastases. A report of the DEGRO Working Group on Stereotactic Radiotherapy. Strahlenther Onkol 190(6):521–532
Xue J, Kubicek GJ, Grimm J et al (2014) Biological implications of whole-brain radiotherapy versus stereotactic radiosurgery of multiple brain metastases. J Neurosurg 121(Suppl):60–68
Hall MD, McGee JL, McGee MC et al (2014) Cost-effectiveness of stereotactic radiosurgery with and without whole-brain radiotherapy for the treatment of newly diagnosed brain metastases. J Neurosurg 121(Suppl):84–90
Balch CM, Gershenwald JE, Soong SJ et al (2009) Final version of 2009 AJCC melanoma staging and classification. J Clin Oncol 27(36):6199–6206
Fumagalli I, Bibault JE, Dewas S et al (2012) A single-institution study of stereotactic body radiotherapy for patients with unresectable visceral pulmonary or hepatic oligometastases. Radiat Oncol 7:164
Grimaldi AM, Simeone E, Giannarelli D et al (2014) Abscopal effects of radiotherapy on advanced melanoma patients who progressed after ipilimumab immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology 3:e28780
Kiess AP, Wolchok JD, Barker CA et al (2015) Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Melanoma Brain Metastases in Patients Receiving Ipilimumab: Safety Profile and Efficacy of Combined Treatment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 92:368
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical stands. For this type of study formal consent is not required. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bates, J.E., Youn, P., Usuki, K.Y. et al. Brain metastasis from melanoma: the prognostic value of varying sites of extracranial disease. J Neurooncol 125, 411–418 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1932-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1932-9