Abstract
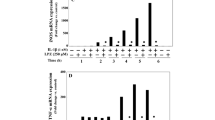
Surgery and infection are prominent risk factors for the development of obstructive cholestasis which in turn is associated with failure of the liver barrier. We studied the effects of oral Lactobacillus plantarum (LP) supplementation on endotoxemia, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and tight junctions of hepatocytes in an experimental model of obstructive jaundice. Fifty male Wistar rats were randomly divided into five groups of 10 each: group I, sham-operated; group II, ligation and division of the common bile duct (BDL); group III, BLD followed by oral LP treatment; group IV, BDL followed by internal biliary drainage (IBD); group V, BDL followed by IBD and oral LP treatment. Hepatocyte apoptosis, plasma reduced glutathione (GSH) and oxidized glutathione (GSSG) levels, and portal blood endotoxin levels were measured and changes in tight junction-associated proteins occludin, claudin-1, claudin-4, and ZO-1 were observed. Compared to the sham-operated group I, significant increases in endotoxemia, apoptosis, and GSSG were observed in group II and significant decreases were observed in group V. Tight junctions were destroyed in group II animals but were not in animals treated with oral LP (groups III and V). An increase in occludin, claudin-1, claudin-4, and ZO-1 mRNA and protein levels were detected in livers in LP-treated animals (group V) compared with group II levels. Oral LP treatment of rats with obstructive jaundice assisted in the return of active hepatic barrier function. These results may lead to treatments to prevent the deleterious effects of obstructive jaundice.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kismet K, Sabuncuoglu MZ, Kilicoglu SS et al (2008) Effect of propolis on oxidative stress and histomorphology of liver tissue in experimental obstructive jaundice. Eur Surg Res 41(2):231–237
Chuang JH, Chang NK, Huang CC et al (2004) Biliary intervention augments chemotactic reaction and aggravates cholestatic liver injury in rats. J Surg Res 120(2):210–218
Padillo FJ, Cruz A, Navarrete C et al (2004) Melatonin prevents oxidative stress and hepatocyte cell death induced by experimental cholestasis. Free Radic Res 38(7):697–704
Furuse M, Fujita K, Hiragi T et al (1998) Claudin-1 and -2: novel integral membrane proteins localizing at tight junctions with no sequence similarity to occludin. J Cell Biol 141(7):1539–1550
Anderson JM, van Itallie CM (1995) Tight junctions and the molecular basis for regulation of paracellular permeability. Am J Physiol 269(4):467–475
Schmitt M, Horbach A, Kubitz R et al (2004) Disruption of hepatocellular tight junctions by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF): a novel mechanism for tumor invasion. J Hepatol 41(2):333–335
Maly IP, Landmann L (2008) Bile duct ligation in the rat causes upregulation of ZO-2 and decreased colocalization of claudins with ZO-1 and occluding. Histochem Cell Biol 129(3):289–299
Kojima T, Yamamoto T, Murata M et al (2003) Regulation of the blood–biliary barrier: interaction between gap and tight junctions in hepatocytes. Med Electron Microsc 36(3):157–164
Lora L, Mazzon E, Martines D et al (1997) Hepatocyte tight-junctional permeability is increased in rat experimental colitis. Gastroenterology 113(4):1347–1354
Takakuwa Y, Kokai Y, Sasaki K et al (2002) Bile canalicular barrier function and expression of tight-junctional molecules in rat hepatocytes during common bile duct ligation. Cell Tissue Res 307(2):181–189
Adawi D, Kasravi FB, Molin G et al (1997) Effect of Lactobacillus supplementation with and without arginine on liver damage and bacterial translocation in an acute liver injury model in the rat. Hepatology 25(3):642–647
Molin G (2001) Probiotics in foods not containing milk or milk constituents, with special reference to Lactobacillus plantarum 299v. Am J Clin Nutr 73(2):380–385
Kasravi FB, Adawi D, Molin G et al (1997) Effect of oral supplementation of lactobacilli on bacterial translocation in acute liver injury induced by d-galactosamine. J Hepatol 26(2):417–424
Adawi D, Molin G, Jeppsson B (1998) Inhibition of nitric oxide production and the effects of arginine and Lactobacillus administration in an acute liver injury model. Ann Surg 228(6):748–755
Mao Y, Nobaek S, Kasravi B et al (1996) The effects of Lactobacillus strains and oat fiber on methotrexate-induced enterocolitis in rats. Gastroenterology 111(2):334–344
Safwat GM, Pisanò S, D’Amore E et al (2009) Induction of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance by feeding a high-fat diet in rats: does coenzyme Q monomethyl ether have a modulatory effect? Nutrition. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2009.02.009
Krafchak CM, Pawar H, Moroi SE et al (2005) Mutations in TCF8 cause posterior polymorphous corneal dystrophy and ectopic expression of COL4A3 by corneal endothelial cells. Am J Hum Genet 77(5):694–708
Sheen-Chen SM, Ho HT, Chia-Pei L et al (2008) Z-LLY-FMK can attenuate hepatocyte apoptosis after bile duct ligation in rat. Dig Dis Sci 53(11):2975–2979
Papakostas C, Bezirtzoglou E, Pitiakoudis M et al (2003) Endotoxinemia in the portal and the systemic circulation in obstructive jaundice. Clin Exp Med 3(2):124–128
Pain JA, Cahill CJ, Bailey ME (1985) Perioperative complications in obstructive jaundice: therapeutic considerations. Br J Surg 72(12):942–945
Roughneen PT, Kumar SC, Pellis NR et al (1988) Endotoxemia and cholestasis. Surg Gynecol Obstet 167(3):205–210
Margaritis VG, Filos KS, Michalaki MA et al (2005) Effect of oral glutamine administration on bacterial translocation, endotoxemia, liver and ileal morphology, and apoptosis in rats with obstructive jaundice. World J Surg 29(10):1329–1334
Assimakopoulos SF, Scopa CD, Georgiou C et al (2003) Altered enterocyte occludin expression and intestinal oxidative stress in obstructive jaundice-induced gut barrier dysfunction. Eur Surg Res 35:105
Katsube T, Tsuji H, Onoda M (2007) Nitric oxide attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced barrier disruption and protein tyrosine phosphorylation in monolayers of intestinal epithelial cell. Biochim Biophys Acta 1773(6):794–803
Basuroy S, Seth A, Elias B et al (2006) MAPK interacts with occludin and mediates EGF-induced prevention of tight junction disruption by hydrogen peroxide. Biochem J 393(pt 1):69–77
Lutgendorff F, Nijmeijer RM, Sandström PA et al (2009) Probiotics prevent intestinal barrier dysfunction in acute pancreatitis in rats via induction of ileal mucosal glutathione biosynthesis. PLoS ONE 4(2):e4512
Steller H (1995) Mechanisms and genes of cellular suicide. Science 267(5203):1445–1449
Miyoshi H, Rust C, Roberts PJ et al (1999) Hepatocyte apoptosis after bile duct ligation in the mouse involves Fas. Gastroenterology 117(3):669–677
Yan F, Polk DB (2002) Probiotic bacterium prevents cytokine-induced apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 277(52):50959–50965
De Vos R, Desmet VJ (1978) Morphologic changes of the junctional complex of the hepatocytes in rat liver after bile duct ligation. Br J Exp Pathol 59(2):220–227
Fanning AS, Mitic LL, Anderson JM (1999) Transmembrane proteins in the tight junction barrier. J Am Soc Nephrol 10(6):1337–1345
Kawaguchi T, Sakisaka S, Sata M et al (1999) Different lobular distributions of altered hepatocyte tight junctions in rat models of intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholestasis. Hepatology 29(1):205–216
Schmitz H, Fromm M, Bentzel CJ et al (1999) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFalpha) regulates the epithelial barrier in the human intestinal cell line HT-29/B6. J Cell Sci 112(pt 1):137–146
Assimakopoulos SF, Scopa CD, Charonis A et al (2004) Experimental obstructive jaundice disrupts intestinal mucosal barrier by altering occludin expression: beneficial effect of bombesin and neurotensin. J Am Coll Surg 198(5):748–757
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our deep and sincere gratitude to the Professor M. Michael Wolf (Boston University School of Medicine, USA) for his advice about this manuscript. This work was financially supported by the Grants from National Key Basic Research Program (No. 2008CB517400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Wang, XQ., Zhou, YK. et al. Effects of oral Lactobacillus plantarum on hepatocyte tight junction structure and function in rats with obstructive jaundice. Mol Biol Rep 37, 2989–2999 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9866-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9866-y