Abstract
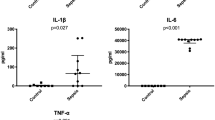
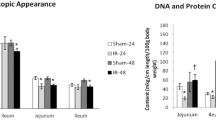
Postoperative complications in patients with obstructive jaundice remain increased when associated with endotoxemia and the inflammatory response due to gut barrier failure. Administration of glutamine has been proposed to maintain the integrity of the gut mucosa and thus reduce bacterial translocation (BT), but the effects of this pretreatment on apoptosis and histologic morphology of various organs affected by BT in obstructive jaundice have not been studied. We therefore studied the effects of oral glutamine supplementation on endotoxemia, BT, liver and terminal ileal morphology, and apoptosis in an experimental model of obstructive jaundice. A total of 60 male Wistar rats were randomly divided into four groups of 15 each: I, controls; II, sham-operated; III, bile duct ligation (BDL); IV, BDL + glutamine (4.5 g/kg/day in drinking water). Ileal samples for histology, DNA and protein content, liver biopsies, mesenteric lymph nodes (MLNs) for culture, and portal and systemic blood samples for endotoxin measurements were obtained 10 days later. Compared to the controls, a significant increase in contaminated MLN and liver samples and increased endotoxemia were noted in group III (p < 0.01) but were significantly reduced in group IV (p < 0.05). Group IV also had a significantly higher number of mitoses per crypt (M/c) (p < 0.05), less apoptotic body counts (ABCs) (p < 0.05), and a higher DNA content than did group III (p < 0.05). Liver biopsies from group III displayed typical changes of large duct obstruction that significantly improved after glutamine treatment, with decreased ductular proliferation.
We concluded that supplementation of oral glutamine in the presence of obstructive jaundice ameliorates BT, endotoxemia, and apoptosis and improves the ileal and liver histology.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dixon JM, Armstrong CP, Duffy SW, et al. Factors affecting morbidity and mortality after surgery for obstructive jaundice: a review of 373 patients. Gut 1983;24:845
Deitch EA, Sittig K, Li M, et al. Obstructive jaundice promotes bacterial translocation from the gut. Am. J. Surg. 1990;159:79
Deitch EA. Simple intestinal obstruction causes bacterial translocation in man. Arch. Surg. 1989;124:699
Lemaire LC, van Lanschot JJ, Stoutenbeek CP, et al. Bacterial translocation in multiple organ failure: cause or epiphenomenon still unproven. Br. J. Surg. 1997;84:1340
Newsholme P. Why is l-glutamine metabolism important to cells of the immune system in health, postinjury, surgery or infection? J. Nutr. 2001;131:2515S
Salvalaggio PR, Neto CZ, Tolazzi AR, et al. Oral glutamine does not prevent bacterial translocation in rats subjected to intestinal obstruction and Escherichia coli challenge but reduces systemic bacteria spread. Nutrition 2002;18:334
Souba WW, Klimberg VS, Hautamaki RD, et al. Oral glutamine reduces bacterial translocation following abdominal radiation. J. Surg. Res. 1990;48:1
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NS, Farr AL, et al. Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951;193:265
Giles KW, Myers M. Improved diphenylamine method for estimation of DNA. Nature 1965;206:93
Lee RG, Nakamura K, Tsamandas AC, et al. Pathology of human intestinal transplantation. Gastroenterology 1996;110:1820
Deitch EA. Bacterial translocation of the gut flora. J. Trauma 1990;30:S184
Scopa CD, Koureleas S, Tsamandas AC, et al. Beneficial effects of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor I on intestinal bacterial translocation, endotoxemia, and apoptosis in experimentally jaundiced rats. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2000;190:423
Assimakopoulos SF, Vagianos CE, Patsoukis N, et al. Evidence for intestinal oxidative stress in obstructive jaundice-induced gut barrier dysfunction in rats. Acta Physiol. Scand. 2004;180:177
Wells CL, Jechorek RP, Erlandsen SL. Inhibitory effect of bile on bacterial invasion of enterocytes: possible mechanism for increased translocation associated with obstructive jaundice. Crit. Care Med. 1995;23:301
Reeds PJ, Burrin DG. Glutamine and the bowel. J. Nutr. 2001;131:2505S
Labow BI, Souba WW. Glutamine. World J Surg 2000;24:1503
Kapadia CR, Colpoys MF, Jiang ZM, et al. Maintenance of skeletal muscle intracellular glutamine during standard surgical trauma. J.P.E.N. J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr. 1985;9:583
Greig JE, Keast D, Garcia-Webb P, et al. Inter-relationships between glutamine and other biochemical and immunoiogical changes after major vascular surgery. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 1996;53:116
Aldemir M, Geyik MF, Kokoglu OF, et al. Effects of ursodeoxycholic acid, glutamine and polyclonal immunoglobulins on bacterial translocation in common bile duct ligated rats. A.N.Z.J. Surg. 2003;73:722
Zulfikaroglu B, Zulfikaroglu E, Ozmen MM, et al. The effect of immunonutrition on bacterial translocation, and intestinal villus atrophy in experimental obstructive jaundice. Clin. Nutr. 2003;22:277
Fox AD, Kripke SA, De Paula J. Effect of a glutamine-supplemented enteral diet on methotrexate-induced enterocolitis. J.P.E.N. J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr. 1988;12:325
Karatzas T, Scopa S, Tsoni I, et al. Effect of glutamine on intestinal mucosal integrity and bacterial translocation after abdominal radiation. Clin. Nutr. 1991;10:188
Bertok L. Physico-chemical defense of vertebrate organisms: the role of bile acids in defense against bacterial endotoxins. Perspect. Biol. Med. 1977;21:70
Assimakopoulos SF, Scopa CD, Georgiou C, et al. Altered enterocyte occludin expression and intestinal oxidative stress in obstructive jaundice-induced gut barrier dysfunction. Eur. Surg. Res. 2003;35:105
Reynolds JV, Murchan P, Redmond HP, et al. Failure of macrophage activation in experimental obstructive jaundice: association with bacterial translocation. Br. J. Surg. 1995;82:534
Bemelmans MH, Gouma DJ, Greve JW, et al. Cytokines tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 in experimental biliary obstruction in mice. Hepatology 1992;15:1132
Steller H. Mechanisms and genes of cellular suicide. Science 1995;267:1445
Potten CS. Stem cells in gastrointestinal epithelium: numbers, characteristics and death. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1998;353:821
Thompson CB. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science 1995;267:1456
Parks RW, Stuart Cameron CH, Gannon CD, et al. Changes in gastrointestinal morphology associated with obstructive jaundice. J. Pathol. 2000;192:526
Karinch AM, Pan M, Lin CM, et al. Glutamine metabolism in sepsis and infection. J. Nutr. 2001;131:2535S
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Margaritis, V.G., Filos, K.S., Michalaki, M.A. et al. Effect of Oral Glutamine Administration on Bacterial Tanslocation, Endotoxemia, Liver and Ileal Morphology, and Apoptosis in Rats with Obstructive Jaundice. World J. Surg. 29, 1329–1334 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-005-7721-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-005-7721-4