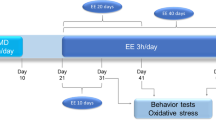
Abstract
Early life adversity has been associated with the development of various neuropsychiatric disorders in adulthood such as depression and anxiety. The aim of this study was to determine if stress during adulthood can exaggerate the depression-/anxiety-like behaviour observed in the widely accepted maternally separated (MS) Sprague–Dawley (SD) rat model of depression. A further aim was to determine whether the behavioural changes were accompanied by changes in hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and the protein profile of the prefrontal cortex (PFC). Depression-/anxiety-like behaviour was measured in the elevated plus maze, open field and forced swim test (FST) in the MS SD rats exposed to chronic restraint stress in adulthood. As expected, MS increased immobility of SD rats in the FST but restraint stress did not enhance this effect of MS on SD rats. A proteomic analysis of the PFC revealed a decrease in actin-related proteins in MS and non-separated rats subjected to restraint stress as well as a decrease in mitochondrial energy-related proteins in the stressed rat groups. Since MS during early development causes a disruption in the hypothalamic‐pituitary‐adrenal axis and long-term changes in the response to subsequent stress, it may have prevented restraint stress from exerting its effects on behaviour. Moreover, the decrease in proteins related to mitochondrial energy metabolism in MS rats with or without subsequent restraint stress may be related to stress per se and not depression-like behaviour, because rats subjected to restraint stress displayed similar decreases in energy-related proteins and spent less time immobile in the FST than control rats.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blaveri E, Kelly F, Mallei A, Harris K, Taylor A, Reid J, Razzoli M, Carboni L, Piubelli C, Musazzi L, Racagni G, Mathé A, Popoli M, Domenici E, Bates S (2010) Expression profiling of a genetic animal model of depression reveals novel molecular pathways underlying depressive-like behaviours. PLoS ONE 5:1–10
Brotto LA, Gorzalka BB, Barr AM (2001) Paradoxical effects of chronic corticosterone on forced swim behaviours in aged male and female rats. Eur J Pharmacol 424:203–209
Calabrese V, Scapagnini G, Giuffrida Stella AM, Bates TE, Clark JB (2001) Mitochondrial involvement in brain function and dysfunction: relevance to aging, neurodegenerative disorders and longevity. Neurochem Res 26:739–764
Caldji C, Tannenbaum B, Sharma S, Francis D, Plotsky PM, Meaney MJ (1998) Maternal care during infancy regulates the development of neural systems mediating the expression of fearfulness in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:5335–5340
Cancela LM, Rossi S, Molina VA (1991) Effect of different restraint schedules on the immobility in the forced swim test: modulation by an opiate mechanism. Brain Res Bull 26:671–675
Carboni L, Becchi S, Piubelli C, Mallei A, Giambelli R, Razzoli M, Mathé AA, Popoli M, Domenici E (2010) Early-life stress and antidepressants modulate peripheral biomarkers in a gene–environment rat model of depression. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 34:1037–1048
Castrén E, Rantamäki T (2010) Role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the aetiology of depression. CNS Drugs 24:1–7
Chiba S, Numakawa T, Ninomiya M, Richards MC, Wakabayashi C, Kunugi H (2012) Chronic restraint stress causes anxiety- and depression-like behaviors, downregulates glucocorticoid receptor expression, and attenuates glutamate release induced by brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the prefrontal cortex. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 39:112–119
Chourbaji S, Vogt MA, Fumagalli F, Sohr R, Frasca A, Brandwein C, Hörtnagl H, Riva MA, Sprengel R, Gass P (2008) AMPA receptor subunit 1 (GluR-A) knockout mice model the glutamate hypothesis of depression. FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 22:3129–3134
Clemens MJ, Bushell M, Morley SJ (1998) Degradation of eukaryotic polypeptide chain initiation factor (eIF) 4G in response to induction of apoptosis in human lymphoma cell lines. Oncogene 17:2921–2931
Clemens MJ, Bushell M, Jeffrey IW, Pain VM, Morley SJ (2000) Translation initiation factor modifications and the regulation of protein synthesis in apoptotic cells. Cell Death Differ 7:603–615
Cryan JF, Markou A, Lucki I (2002) Assessing antidepressant activity in rodents: recent developments and future needs. TRENDS Pharmacol Sci 23:238–245
Daniels WMU, Pietersen CY, Carstens ME, Stein DJ (2004) Maternal separation in rats leads to anxiety-like behavior and a blunted ACTH response and altered neurotransmitter levels in response to a subsequent stressor. Metab Brain Dis 19:3–14
Daniels WMU, Marais L, Stein DJ, Russell VA (2012) Exercise normalizes altered expression of proteins in the ventral hippocampus of rats subjected to maternal separation. Exp Physiol 97:239–247
Desbonnet L, Garrett L, Clarke G, Kiely B, Cryan JF, Dinan TG (2010) Effects of the probiotic Bifidobacterium infantis in the maternal separation model of depression. Neuroscience 170:1179–1188
Dimatelis JJ, Russell VA, Stein DJ, Daniels WM (2012a) Effects of maternal separation and methamphetamine exposure on protein expression in the nucleus accumbens shell and core. Metab Brain Dis 27:363–375
Dimatelis JJ, Stein DJ, Russell VA (2012b) Behavioral changes after maternal separation are reversed by chronic constant light treatment. Brain Res 1480:61–71
Dimatelis JJ, Russell VA, Stein DJ, Daniels WM (2014) Methamphetamine reversed maternal separation-induced decrease in nerve growth factor in the ventral hippocampus. Metab Brain Dis 29:433–439
Diorio D, Viau V, Meaney MJ (1993) The role of the medial prefrontal cortex (cingulate gyrus) in the regulation of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal responses to stress. J Neurosci 13:3839–3847
Eiland L, McEwen BS (2012) Early life stress followed by subsequent adult chronic stress potentiates anxiety and blunts hippocampal structural remodeling. Hippocampus 22:82–91
Francis DD, Meaney MJ (1999) Maternal care and the development of stress responses. Curr Opin Neurobiol 9:128–134
Gale M Jr, Tan SL, Katze MG (2000) Translational control of viral gene expression in eukaryotes. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: MMBR 64:239–280
Gass P, Riva MA (2007) CREB, neurogenesis and depression. Bioessays: News Rev Mol Cell Dev Biol 29:957–961
Greisen MH, Altar CA, Bolwig TG, Whitehead R, Wörtwein G (2005) Increased adult hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor and normal levels of neurogenesis in maternal separation rats. J Neurosci Res 79:772–778
Han X, Shao W, Liu Z, Fan S, Yu J, Chen J, Qiao R, Zhou J, Xie P (2015) iTRAQ-based quantitative analysis of hippocampal postsynaptic density-associated proteins in a rat chronic mild stress model of depression. Neuroscience 298:220–292
Hansson AC, Rimondini R, Heilig M, Mathé AA, Sommer WH (2011) Dissociation of antidepressant-like activity of escitalopram and nortriptyline on behaviour and hippocampal BDNF expression in female rats. J Psychopharmacol 25:1378–1387
Harkness KL, Bruce AE, Lumley MN (2006) The role of childhood abuse and neglect in the sensitization to stressful life events in adolescent depression. J Abnorm Psychol 115:730–741
Herman JP, Cullinan WE (1997) Neurocircuitry of stress: central control of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical axis. Trends Neurosci 20:78–84
Hong IS, Lee HY, Kim HP (2014) Anti-oxidative effects of rooibos tea (Aspalathus linearis) on immobilization-induced oxidative stress in rat brain. PLoS ONE 9:1–9
Husum H, Wörtwein G, Andersson W, Bolwig TG, Mathé AA (2008) Gene-environment interaction affects substance P and neurokinin A in the entorhinal cortex and periaqueductal grey in a genetic animal model of depression: implications for the pathophysiology of depression. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 11:93–101
Kendler KS, Karkowski LM, Prescott CA (1998) Stressful life events and major depression: risk period, long-term contextual threat, and diagnostic specificity. J Nerv Mental Dis 186:661–669
Kendler KS, Karkowski LM, Prescott CA (1999) Causal relationship between stressful life events and the onset of major depression. Am J Psychiatry 156:837–841
Kuroda Y, McEwen BS (1998) Effect of chronic restraint stress and tianeptine on growth factors, growth-associated protein-43 and microtubule-associated protein 2 mRNA expression in the rat hippocampus. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 59:35–39
Lambás-Señas L, Mnie-Filali O, Certin V, Faure C, Lemoine L, Zimmer L, Haddjeri N (2009) Functional correlates for 5-HT1A receptors in maternally deprived rats displaying anxiety and depression-like behaviors. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33:262–268
Larsen MH, Mikkelsen JD, Hay-Schmidt A, Sandi C (2010) Regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the chronic unpredictable stress rat model and the effects of chronic antidepressant treatment. J Psychiatr Res 44:808–816
Lee B, Sur B, Park J, Kim SH, Kwon S, Yeom M, Shim I, Lee H, Hahm DH (2013) Chronic administration of baicalein decreases depression-like behavior induced by repeated restraint stress in rats. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 17:393–403
Lees-Miller JP, Goodwin LO, Helfman DM (1990) Three novel brain tropomyosin isoforms are expressed from the rat alpha-tropomyosin gene through the use of alternative promoters and alternative RNA processing. Mol Cell Biol 10:1729–1742
Li X, Tizzano JP, Griffey K, Clay M, Lindstrom T, Skolnick P (2001) Antidepressant-like actions of an AMPA receptor potentiator (LY392098). Neuropharmacology 40:1028–1033
Lindvall O, Kokaia Z, Bengzon J, Elmér E, Kokaia M (1994) Neurotrophins and brain insults. Trends Neurosci 17:490–496
Liu SJ, Zukin RS (2007) Ca2+−permeable AMPA receptors in synaptic plasticity and neuronal death. Trends Neurosci 30:126–134
Liu D, Diorio J, Tannenbaum B, Caldji C, Francis D, Freedman A, Sharma S, Pearson D, Plotsky PM, Meaney MJ (1997) Maternal care, hippocampal glucocorticoid receptors, and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal responses to stress. Science (New York, NY) 277:1659–1662
Madrigal JL, Olivenza R, Moro MA, Lizasoain I, Lorenzo P, Rodrigo J, Leza JC (2001) Glutathione depletion, lipid peroxidation and mitochondrial dysfunction are induced by chronic stress in rat brain. Neuropsychopharmacol: Off Publ Am Coll Neuropsychopharmacol 24:420–429
Mallei A, Giambelli R, Gass P, Racagni G, Mathé AA, Vollmayr B, Popoli M (2011) Synaptoproteomics of learned helpless rats involve energy metabolism and cellular remodeling pathways in depressive-like behavior and antidepressant response. Neuropharmacology 60:1243–1253
Marais L, van Rensburg SJ, van Zyl JM, Stein DJ, Daniels WMU (2008) Maternal separation of rat pups increases the risk of developing depressive-like behavior after subsequent chronic stress by altering corticosterone and neurotrophin levels in the hippocampus. Neurosci Res 61:106–112
Martinez-Turrillas R, Frechilla D, Del Río J (2002) Chronic antidepressant treatment increases the membrane expression of AMPA receptors in rat hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 43:1230–1237
Martínez-Turrillas R, Del Río J, Frechilla D (2007) Neuronal proteins involved in synaptic targeting of AMPA receptors in rat hippocampus by antidepressant drugs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 353:750–755
Mathé AA, Husum H, Khoury AE, Jiménez-Vasquez P, Gruber SHM, Wörtwein G, Nikisch G, Baumann P, Ågren H, Andersson W, Södergren Å, Angelucci F (2007) Search for biological correlates of depression and mechanisms of action of antidepressant treatment modalities. Do neuropeptides play a role. Physiol Behav 92:226–231
McAllister AK, Katz LC, Lo DC (1999) Neurotrophins and synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci 22:295–318
McEwen BS (2000) The neurobiology of stress: from serendipity to clinical relevance. Brain Res 886:172–189
McEwen BS (2008) Central effects of stress hormones in health and disease: understanding the protective and damaging effects of stress and stress mediators. Eur J Pharmacol 583:174–185
Meaney MJ (2001) Maternal care, gene expression, and the transmission of individual differences in stress reactivity across generations. Ann Rev Neurosci 24:1161–1192
Mochida S (1995) Role of myosin in neurotransmitter release: functional studies at synapses formed in culture. J Physiol, Paris 89:83–94
Mu J, Xie P, Yang ZS, Yang DL, Lv FJ, Luo TY, Li Y (2007) Neurogenesis and major depression: implications from proteomic analyses of hippocampal proteins in a rat depression model. Neurosci Lett 416:252–256
Naert G, Ixart G, Maurice T, Tapia-Arancibia L, Givalois L (2011) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis adaptation processes in a depressive-like state induced by chronic restraint stress. MCN: Mol Cell Neurosci 46:55–66
O’Connor TM, O’Halloran DJ, Shanahan F (2000) The stress response and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis: from molecule to melancholia. QJM: Mon J Assoc Phys 93:323–333
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain on stereotaxic co-ordinates, 2nd edn. Academic, San Diego
Pickering C, Gustafsson L, Cebere A, Nylander I, Liljequist S (2006) Repeated maternal separation of male Wistar rats alters glutamate receptor expression in the hippocampus but not the prefrontal cortex. Brain Res 1099:101–108
Pigino G, Kirkpatrick LL, Brady ST (2006) The cytoskeleton of neurons and glia. In: Siegel G, Albers RW, Brady S, Price D (eds) Basic neurochemistry: molecular, cellular, and medical aspects. Elsevier Academic Press, USA, pp 123–137
Piubelli C, Vighini M, Mathé AA, Domenici E, Carboni L (2011) Escitalopram modulates neuron-remodelling proteins in a rat gene-environment interaction model of depression as revealed by proteomics. Part I: genetic background. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 14:796–833
Platt JE, Stone EA (1982) Chronic restraint stress elicits a positive antidepressant response on the forced swim test. Eur J Pharmacol 82:179–181
Popoli M, Mori S, Brunello N, Perez J, Gennarelli M, Racagni G (2001) Serine/threonine kinases as molecular targets of antidepressants: implications for pharmacological treatment and pathophysiology of affective disorders. Pharmacol Ther 89:149–170
Raison CL, Miller AH (2003) When not enough is too much: the role of insufficient glucocorticoid signaling in the pathophysiology of stress-related disorders. Am J Psychiatry 160:1554–1565
Rasmusson AM, Shi L, Duman R (2002) Downregulation of BDNF mRNA in the hippocampal dentate gyrus after re-exposure to cues previously associated with footshock. Neuropsychopharmacology 27:133–142
Ray B, Gaskins DL, Sajdyk TJ, Spence JP, Fitz SD, Shekhar A, Lahiri DK (2011) Restraint stress and repeated corticotrophin-releasing factor receptor activation in the amygdala both increase amyloid-b precursor protein and amyloid-b peptide but have divergent effects on brain-derived neurotrophic factor and pre-synaptic proteins in the prefrontal cortex of rats. Neuroscience 184:139–150
Reagan LP, Hendry RM, Reznikov LR, Piroli GG, Wood GE, McEwen BS, Grillo CA (2007) Tianeptine increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in the rat amygdala. Eur J Pharmacol 565:68–75
Réus GZ, Abelaira HM, Maciel AL, dos Santos MA, Carlessi AS, Steckert AV, Ferreira GK, De Prá SD, Streck EL, Macêdo DS, Quevedo J (2014) Minocycline protects against oxidative damage and alters energy metabolism parameters in the brain of rats subjected to chronic mild stress. Metab Brain Dis 30:545–553
Roceri M, Cirulli F, Pessina C, Peretto P, Racagni G, Riva MA (2004) Postnatal repeated maternal deprivation produces age-dependent changes of brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in selected rat brain regions. Biol Psychiatry 55:708–714
Rosenbrock H, Koros E, Bloching A, Podhorna J, Borsini F (2005) Effect of chronic intermittent restraint stress on hippocampal expression of marker proteins for synaptic plasticity and progenitor cell proliferation in rats. Brain Res 1040:55–63
Rüedi-Bettschen D, Pedersen EM, Feldon J, Pryce CR (2005) Early deprivation under specific conditions leads to reduced interest in reward in adulthood in Wistar rats. Behav Brain Res 156:297–310
Rutter M (2007) Psychopathological development across adolescence. J Youth Adolesc 36:101–110
Rutter M (2010) Gene–environment interplay. Depress Anxiety 27:1–4
Ryan B, Musazzi L, Mallei A, Tardito D, Gruber SHM, El Khoury A, Anwyl R, Racagni G, Mathé AA, Rowan MJ, Popoli M (2009) Remodelling by early-life stress of NMDA receptor-dependent synaptic plasticity in a gene-environment rat model of depression. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 12:553–559
Serang O, Cansizoglu AE, Käll L, Steen H, Steen JA (2013) Nonparametric Bayesian evaluation of differential protein quantification. J Proteome Res 12:4556–4565
Sheikh MS, Fornace AJ (1999) Regulation of translation initiation following stress. Oncogene 18:6121–6128
Suvrathan A, Tomar A, Chattarji S (2010) Effects of chronic and acute stress on rat behaviour in the forced-swim test. Stress: Int J Biol Stress 13:533–540
Swiergiel AH, Zhou Y, Dunn AJ (2007) Effects of chronic footshock, restraint and corticotropin-releasing factor on freezing, ultrasonic vocalization and forced swim behavior in rats. Behav Brain Res 183:178–187
Tabassum I, Siddiqui ZN, Rizvi SJ (2010) Effects of Ocimum sanctum and Camellia sinensis on stress-induced anxiety and depression in male albino Rattus norvegicus. Indian J Pharm 42:283–288
Tamburella A, Micale V, Leggio GM, Drago F (2010) The beta3 adrenoceptor agonist, amibegron (SR58611A) counteracts stress-induced behavioral and neurochemical changes. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol: J Eur Coll Neuropsychopharmacol 20:704–713
Tobe EH (2013) Mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and major depressive disorder. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 9:567–573
Uchida S, Hara K, Kobayashi A, Funato H, Hobara T, Otsuki K, Yamagata H, McEwen BS, Watanabe Y (2010) Early life stress enhances behavioral vulnerability to stress through the activation of REST4-mediated gene transcription in the medial prefrontal cortex of rodents. J Neurosci 30:15007–15018
Ulloa JL, Castañeda P, Berríos C, Díaz-Veliz G, Mora S, Bravo JA, Araneda K, Menares C, Morales P, Fiedler JL (2010) Comparison of the antidepressant sertraline on differential depression-like behaviors elicited by restraint stress and repeated corticosterone administration. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 97:213–221
Uys JDK, Hattingh S, Stein DJ, Daniels WMU (2008) Large scale hippocampal cellular distress may explain the behavioral consequences of repetitive traumatic experiences: a proteomic approach. Neurochem Res 33:1724–1734
van Heerden JH, Russell V, Korff A, Stein DJ, Illing N (2010) Evaluating the behavioural consequences of early maternal separation in adult C57BL/6 mice; the importance of time. Behav Brain Res 207:332–342
van Veen T, Wardenaar KJ, Carlier IVE, Spinhoven P, Penninx BWJH, Zitman FG (2013) Are childhood and adult life adversities differentially associated with specific symptom dimensions of depression and anxiety? Testing the tripartite model. J Affect Disord 146:238–245
Wang F, Qiao M, Xue L, Wei S (2015) Possible involvement of μ opioid receptor in the antidepressant-like effect of Shuyu formula in restraint stress-induced depression-like rats. Evid-based Complement Alternat Med (eCAM) 2015:1–11
Wörtwein G, Husum H, Andersson W, Bolwig TG, Mathé AA (2006) Effects of maternal separation on neuropetide Y and calcitonin gene-related peptide in ‘depressed’ Flinders sensitive line rats: a study of gene-environment interactions. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 30:684–693
Wu WW, Wang G, Baek SJ, Shen RF (2006) Comparative study of three proteomic quantitative methods, DIGE, cICAT, and iTRAQ, using 2D gel- or LC-MALDI TOF/TOF. J Proteome Res 5:651–658
Xu H, Luo C, Richardson JS, Li XM (2004) Recovery of hippocampal cell proliferation and BDNF levels, both of which are reduced by repeated restraint stress, is accelerated by chronic venlafaxine. Pharmacogenomics J 4:322–331
Xu H, Chen Z, He J, Haimanot S, Li X, Dyck L, Li XM (2006) Synergetic effects of quetiapine and venlafaxine in preventing the chronic restraint stress-induced decrease in cell proliferation and BDNF expression in rat hippocampus. Hippocampus 16:551–559
Yan Q, Rosenfeld RD, Matheson CR, Hawkins N, Lopez OT, Bennett L, Welcher AA (1997) Expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein in the adult rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 78:431–448
Yoo SB, Kim BT, Kim JY, Ryu V, Kang DW, Lee JH, Jahng JW (2013) Adolescence fluoxetine increases serotonergic activity in the raphe-hippocampus axis and improves depression-like behaviors in female rats that experienced neonatal maternal separation. Psychoneuroendocrinology 38:777–788
Zimmerberg B, Sageser KA (2011) Comparison of two rodent models of maternal separation on juvenile social behavior. Front Psychiatry 2:39–49
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Institute for the Study of Affective Neuroscience (ISAN) and the National Research Foundation (NRF) for financial support. The authors would like to acknowledge the contributions of the Centre for Proteomic and Genomic Research (CPGR), University of Cape Town (UCT) who performed the proteomic analysis. We would also like to thank Ms Estella Minnaar for breeding the rats and performing the MS as well as the Animal Unit and Nuraan Ismail for taking care of the animals. Any opinion, finding and conclusion or recommendation expressed in this material is that of the authors and the NRF does not accept any liability in this regard.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest or other disclosures to report.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. 3
Time spent in the open and closed arms of the EPM by control SD, MS SD, restraint stressed SD and restraint stressed MS SD rats. The EPM revealed no difference between Ctr, MS, RS, and MS + RS rats in time spent in the open arms (a) and closed arms (b) (n = 12-13/group). Data presented as mean ± SEM (GIF 35 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 4
BDNF levels in the ventral hippocampus of control SD, MS SD, restraint stressed SD and restraint stressed MS SD rats. No significant difference found in BDNF levels in the ventral hippocampus between Ctr, MS, RS and MS + RS rats (n = 10/group). Data presented as mean ± SEM (GIF 41 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
Proteomic (8-plex) profile of the PFC of Ctr, MS and restraint stressed (RS) rats. Data presented as a ratio to Ctr 1. The average Ctr ratio (Avg) was calculated and normalized to 1.0 (grey). * Data differed from the normalized Ctr/Ctr by more than 20 % (1.2-fold increase or decrease) (DOCX 278 kb)
Supplementary Table 4
Proteomic (4-plex) profile of the PFC of Ctr and MS + RS rats. Data presented as ratio to Ctr 1. The average Ctr ratio (Avg) was calculated and normalized to 1.0 (grey). * Data differed from the normalized Ctr/Ctr by more than 20 % (1.2-fold increase or decrease) (DOCX 224 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Zyl, P.J., Dimatelis, J.J. & Russell, V.A. Behavioural and biochemical changes in maternally separated Sprague–Dawley rats exposed to restraint stress. Metab Brain Dis 31, 121–133 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-015-9757-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-015-9757-y