Abstract
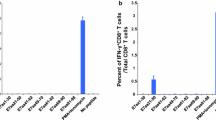
One of the critical steps in the progression to condyloma acuminatum (CA) is the establishment of a persistent human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, majority of HPV type 6 and 11. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL), which can be induced by the epitope-based peptides in vitro, are thought to be able to recognize and destroy virus-infected cells. In order to screen and identify HLA-A*0201 restricted HPV-11E7 CTL epitopes, five epitope peptides and tetramers were selected including HPV-11E7 7–15 (TLKDIVLDL), 15–23 (LQPPDPVGL), 47–55 (PLTQHYQIL), 81–89 (DLLLGTLNI) and 82–90 (LLLGTLNIV). Human monocyte-derived dendritic cells (DCs) from HLA-A*0201 healthy individuals were pulsed with these peptides to assess the expression of CD83, CD86, HLA-DR and the secretion of IL-12. The ability of peptide-loaded mature DCs to activate autologous T cells was evaluated by analyzing the frequency of specific tetramer+ CD8+ T cells using flow cytometry, and the level of IFN-γ secretion by ELISA. The ability of the epitope-specific CTLs to kill the target cells was also analysed. It was found that the immature DCs could be fully activated by all the five HPV-11E7 peptides and peptide-loaded mature DCs were able to stimulate the epitope-specific T cells in vitro. There was an increased frequency of CD8+ T cells specific for the E7 7–15 epitope when compared to other four predicted epitopes of HPV-11E7 (P < 0.05). The epitope-specific CTLs for E7 7–15 induced the strongest cytotoxicity to HPV-11E7 expressing cell line at an E:T ratio of 50:1 (P < 0.05). Taken together, these findings demonstrate that E7 7–15 (TLKDIVLDL) is an HLA-A*0201-restricted CTL epitope of HPV type 11. We propose that this epitope could be more helpful in the characterization of HPV control mechanism and be useful for the development of immunotherapeutic approaches for low-risk HPV infectious diseases such as CA.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appay V, Nixon DF, Donahoe SM, Gillespie GM, Dong T, King A, Ogg GS, Spiegel HM, Conlon C, Spina CA, Havlir DV, Richman DD, Waters A, Easterbrook P, McMichael AJ, Rowland-Jones SL (2000) HIV-specific CD8(+) T cells produce antiviral cytokines but are impaired in cytolytic function. J Exp Med 192:63
Buus S (1999) Description and prediction of peptide-MHC binding: the’human MHC project’. Curr Opin Immunol 11:209–213
Cheng WF, Hung CF, Chai CY, Hsu KF, He L, Ling M, Wu TC (2001) Tumor-specific immunity and antiangiogenesis generated by a DNA vaccine encoding calreticulin linked to a tumor antigen. J Clin Invest 108:669–678
de Villiers EM (1989) Heterogeneity of the human papillomavirus group. J Virol 63:4898–4903
Feltkamp MC, Smits HL, Vierboom MP, Minnaar RP, de Jongh BM, Drijfhout JW, ter Schegget J, Melief CJ, Kast WM (1993) Vaccination with cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitope-containing peptide protects against a tumor induced by human papillomavirus type 16-transformed cells. Eur J Immunol 23:2242–2249
Fernando GJ, Murray B, Zhou J, Frazer IH (1999) Expression, purification and immunological characterization of the transforming protein E7, from cervical cancer-associated human papillomavirus type 16. Clin Exp Immunol 115:397–403
Fonteneau JF, Larsson M, Somersan S, Sanders C, Munz C, Kwok WW, Bhardwaj N, Jotereau F (2001) Generation of high quantities of viral and tumor-specific human CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell clones using peptide pulsed mature dendritic cells. J Immunol Methods 258:111–126
Frazer IH, Thomas R, Zhou J, Leggatt GR, Dunn L, McMillan N, Tindle RW, Filgueira L, Manders P, Barnard P, Sharkey M (1999) Potential strategies utilised by papillomavirus to evade host immunity. Immunol Rev 168:131–142
Gallimore A, Dumrese T, Hengartner H, Zinkernage RM, Rammensee HG (1998) Protective immunity does not correlate with the hierarchy of virus-specific cytotoxic T cell responses to naturally processed peptides. J Exp Med 187:1647–1657
Giannini SL, Hubert P, Doyen J, Boniver J, Delvenne P (2002) Influence of the mucosal epithelium microenvironment on Langerhans cells: implications for the development of squamous intraepithelial lesions of the cervix. Int J Cancer 97:654–659
Hammerling GJ, Vogt AB, Kropshofer H (1999) Antigen processing and presentation—towards the millennium. Immunol Rev 172:5–11
Hirano N, Butler MO, Xia Z, Berezovskaya A, Murray AP, Ansén S, Nadler LM (2006) Efficient presentation of naturally processed HLA class I peptides by artificial antigen-presenting cells for the generation of effective antitumor responses. Clin Cancer Res 12:2967–2975
Hoffmann TK, Arsov C, Schirlau K, Bas M, Friebe-Hoffmann U, Klussmann JP, Scheckenbach K, Balz V, Bier H, Whiteside TL (2006) T cells specific for HPV16 E7 epitopes in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the oropharynx. Int J Cancer 118:1984–1991
Ishiji T (2000) Molecular mechanism of carcinogenesis by human papillomavirus-16. J Dermatol 27:73–86
Kast W, Brandt R, Sidney J, Drijfhout J, Kubo RT, Grey HM, Melief C, Sette A (1994) Role of HLA-A motifs in identification of potential CTL epitopes in human papillomavirus type-16 E6 and E7 proteins. J Immunol 152:3904–3912
Mork J, Lie AK, Glattre E, Hallmans G, Jellum E, Koskela P, Moller B, Pukkala E, Schiller JT, Youngman L, Lehtinen M, Dillner J (2001) Human papillomavirus infection as a risk factor for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med 344:1125–1131
Münger K, Werness BA, Dyson N, Phelps WC, Harlow E, Howley PM (1989) Complex formation of human papillomavirus E7 proteins with the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor gene product. EMBO J 8:4099–4105
Nakagawa M, Kim KH, Moscicki AB (2004) Different methods of identifying new antigenic epitopes of human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 proteins. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 11:889–896
Nakagawa M, Kim KH, Moscicki AB (2005) Patterns of CD8 T-cell epitopes within the human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV 16) E6 protein among young women whose HPV 16 infection has become undetectable. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 12:1003–1005
Nakagawa M, Stites DP, Patel S, Farhat S, Scott M, Hills NK, Palefsky JM, Moscicki AB (2000) Persistence of human papillomavirus type 16 infection is associated with lack of cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to the E6 antigens. J Infect Dis 182:595–598
Ohlschlager P, Pes M, Osen W, Durst M, Schneider A, Gissmann L, Kaufmann AM (2006) An improved rearranged human papillomavirus type 16 E7 DNA vaccine candidate (HPV-16 E7SH) induces an E7 wildtype-specific T cell response. Vaccine 24:2880–2893
Osen W, Peiler T, Ohlschlager P, Caldeira S, Faath S, Michel N, Muller M, Tommasino M, Jochmus I, Gissmann L (2001) A DNA vaccine based on a shuffled E7 oncogene of the human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV 16) induces E7-specific cytotoxic T cells but lacks transforming activity. Vaccine 19:4276–4286
Parker KC, Bednarek MA, Coligan JE (1994) Scheme for ranking potential HLA-A2 binding peptides based on independent binding of individual peptide side-chains. J Immunol 152:163–175
Passmore JA, Milner M, Denny L, Sampson C, Marais DJ, Allan B, Gumbi PP, Hitzeroth II, Rybicki EP, Williamson AL (2006) Comparison of cervical and blood T-cell responses to human papillomavirus-16 in women with human papillomavirus-associated cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Immunology 119:507–514
Peng S, Ji H, Trimble C, He L, Tsai YC, Yeatermeyer J, Boyd DA, Hung CF, Wu TC (2004) Development of a DNA vaccine targeting human papsillomavirus type 16 oncoprotein E6. J Virol 78:8468–8476
Ressing ME, Sette A, Brandt RM, Ruppert J, Wentworth PA, Hartman M, Oseroff C, Grey HM, Melief CJ, Kast WM (1995) Human CTL epitopes encoded by human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 identified through in vivo and in vitro immunogenicity studies of HLA-A *0201 binding peptides. J Immunol 154:5934–5943
Ruppert J, Sidney J, Esteban C, Kubo RT, Grey HM, Sette A (1993) Prominent role of secondary anchor residues in peptide binding to HLA-A2.1. Mol Cell 74:929–938
Sadovnikova E, Zhu X, Collins SM, Zhou J, Vousden K, Crawford L, Beverley P, Stauss HJ (1994) Limitations of predictive motifs revealed by cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitope mapping of the human papilloma virus E7 protein. Int Immunol 6:289–296
Scholten KB, Schreurs MW, Ruizendaal JJ, Kueter EW, Kramer D, Veenbergen S, Meijer CJ, Hooijberg E (2005) Preservation and redirection of HPV16E7-specific T cell receptors for immunotherapy of cervical cancer. Clin Immunol 114:119–129
Schreurs MW, Scholten KB, Kueter EW, Ruizendaal JJ, Meijer CJ, Hooijberg E (2003) In Vitro Generation and Life Span Extension of Human Papillomavirus Type 16-Specific, Healthy Donor-Derived CTL Clones. J Immunol 171:2912–2921
Smith KL, Tristram A, Gallagher KM, Fiander AN, Man S (2005) Epitope specificity and longevity of a vaccine-induced human T cell response against HPV18. Int Immunol 17:167–176
Tarpey I, Stacey S, Hickling J, Birley HD, Renton A, McIndoe A, Davies DH (1994) Human cytotoxic T lymphocytes stimulated by endogenously processed human papillomavirus type 11 E7 recognize a peptide containing a HLA-A2 (A*0201) motif. Immunology 81:222–227
Telusma G, Datta S, Mihajlov I, Ma W, Li J, Yang H, Newman W, Messmer BT, Minev B, Schmidt-Wolf IG, Tracey KJ, Chiorazzi N, Messmer D (2006) Dendritic cell activating peptides induce distinct cytokine profiles. Int Immunol 18:563–573
Tindle RW (2002) Immune evasion in human papillomavirus-associated cervical cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2:59–65
Toes RE, van der Voort EI, Schoenberger SP, Drijfhout JW, van Bloois L, Storm G, Kast WM, Offringa R, Melief CJ (1998) Enhancement of tumor outgrowth through CTL tolerization after peptide vaccination is avoided by peptide presentation on dendritic cells. J Immunol 160:4449–4456
Tsai V, Kawashima I, Keogh E, Daly K, Sette A, Celis E (1998) In vitro immunization and expansion of antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes for adoptive immunotherapy using peptide-pulsed dendritic cells. Crit Rev Immunol 18:65–75
Tuting T, DeLeo AB, Lotze MT, Storkus WJ (1997) Genetically modified bone marrow-derived dendritic cells expressing tumor-associated viral or “self” antigens induce antitumor immunity in vivo. Eur J Immunol 27:2702–2707
Vambutas A, DeVoti J, Nouri M, Drijfhout JW, Lipford GB, Bonagura VR, van der Burg SH, Melief CJ (2005) Therapeutic vaccination with papillomavirus E6 and E7 long peptides results in the control of both established virus-induced lesions and latently infected sites in a pre-clinical cottontail rabbit papillomavirus model. Vaccine 23:5271–5280
Wang P, Wang Q, Sims PF, Hyde JE (2002) Rapid positive selection of stable integrants following transfection of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol 123:1–10
Wan T, Zhou XY, Chen GY, An HZ, Chen TY, Zhang WP, Liu SX, Jiang YM, Yang F, Wu YF, Cao XT (2004) Novel heat shock protein Hsp70L1 activates dendritic cells and acts as a Th1 polarizing adjuvant. Blood 103:1747–1754
Yoon H, Chung MK, Min SS, Lee HG, Yoo WD, Chung KT, Jung NP, Park SN (1998) Synthetic peptides of human papillomavirus type 18 E6 harboring HLA-A2.1 motif can induce peptide-specific cytotoxic T-cells from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of healthy donors. Virus Res 54:23–29
Youde SJ, Dunbar PR, Evans EM, Fiander AN, Borysiewicz LK, Cerundolo V, Man S (2000) Use of Fluorogenic Histocompatibility Leukocyte Antigen-A*0201/HPV 16 E7 Peptide Complexes to Isolate Rare Human Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte- recognizing Endogenous Human Papillomavirus Antigens. Cancer Res 60:365–371
Acknowledgments
We gratefully thank Dr. Jie He for her technical help. This work was supported by Science Foundation of Ministry of Education of China and High-level Innovation Personal Project of Health Bureau of Zhejiang Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The abstract was accepted by 23rd HPV International Conference and by the American Academy of Dermatology Academy 2007.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Zhu, KJ., Chen, XZ. et al. Mapping of cytotoxic T lymphocytes epitopes in E7 antigen of human papillomavirus type 11. Arch Dermatol Res 300, 235–242 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-008-0837-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-008-0837-2