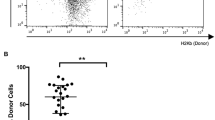
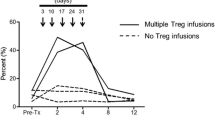
Abstract.
With donor and recipient matched at the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) locus, peripheral lymphoid tissue transplantation can be carried out without producing a graft-versus-host reaction or graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), thus correcting profound T cell immunodeficiencies of neonatally thymectomized mice. This analysis set the stage for clinical application of bone marrow transplantation (BMT) to provide for the first time cure of a human disease. With successful BMT, we cured immunologic deficiencies of a patient with XL severe combined immunodeficiency; thereafter we were the first to employ BMT to cure aplastic anemia. BMT regularly corrects immune and hematologic deficiencies caused by fatal irradiation without producing GVHD if the bone marrow (BM) used for the transplants has been purged of postthymic T cells. Over two decades in conjunction with Ikehara et al., we have shown that lethal total body irradiation (TBI) plus allogeneic BMT prevents or cures many organ-specific and systemic experimental autoimmune diseases. Animal models successfully treated by BMT include type I diabetes in nonobese diabetes (NOD) mice, type II diabetes in insulin-insensitive, glucose intolerant, diabetes mellitus (KK/Ay) mice, and autoimmune lupus erythematosus (LE) and glomerulonephritis in New Zealand Black × New Zealand White first generation hybrid (NZB × NZW)F1 females. El-Badri extended Ildstad's original research showing a high frequency of survival with a normal functioning immune system after stable mixed chimerism is produced by mixed BMT in C57BL/6 (normal long-lived black strain) mice transplanted with T cell-depleted marrow (TCDM) from BALB/c (“normal” long-lived strain) allogeneic donors and C57BL/6 syngeneic donors. We showed that osteoblasts act as facilitator cells for allogeneic BMT and promote engraftment of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cells. Wang et al. then showed that the autoimmunities and fulminating renal disease of BXSB (C57BL × SB cross and selective lupus-like systemic autoimmunity) male mice was prevented and could be cured by transplantation using TCDM from both BALB/c (resistant) and BXSB (susceptible) strains given to BXSB recipients after lethal TBI. This treatment produced mixed BMT and a stable mixed chimerism, increased longevity, corrected all manifestations of autoimmunity, and cured fulminant glomerulonephritis in these recipients. These studies generated a new perspective on the potential usefulness of BM and stem cell transplants to cure major diseases that can possibly be treated by BMT. Mixed BMT from TCD BALB/c and BXSB mice cured autoimmunities and fulminant glomerulonephritis in BXSB mice. LE disease plus coronary vascular disease that occurs in (NZW × BXSB)F1 mice, along with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, is also cured in lethally irradiated (NZW × BXSB)F1 mice by BMT from C57BL/6 donors. Furthermore, hemolytic anemia, autoimmune phenomena, and hyalinizing glomerular renal disease of New Zealand Black (NZB) mice were prevented or cured by stem cell transplants using purified stem cells from MHC-matched DBA/2 donors or NZB donors. Consequently, we reasoned that autoimmunities reside in stem cells. More recently, we found that transplants of both BM cells and bones can completely and permanently prevent otherwise highly resistant autoimmune diseases of MRL/lpr lpr mice and an autoimmune polyarthritis of NZB/Kn mice. Ildstad concluded that lethal preparative measures would not be acceptable for preparations to treat autoimmune diseases, so we now employ a gentle method for producing stable mixed chimerism described by Sharabi and Sachs to achieve mixed marrow transplantation and mixed hematopoietic chimerism. Other diseases we are approaching using this gentle manipulation include two forms of diabetes: insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) type I in NOD mice and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) type II in KK/Ay mice, atherosclerosis of apolipoprotein-E + knockout ApoE−/− knockout (K.O.) mutant mice that can be cured by BMT, and senility-accelerated disease in systemic amyloidosis and acceleration of aging model (SAM-P) mice accompanied by and driven by autoimmunities. Today, clinical BMT sometimes cures 75 otherwise lethal diseases, including acute and chronic resistant leukemias, lymphomas, aplastic anemias, cancers, hematologic anomalies, and inborn errors of metabolism. The new findings suggest that BMT may become an effective treatment for immunodeficiencies, autoimmunities, and hematologic diseases for which current treatments remain inadequate.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Good, R. Progress toward Production of Immunologic Tolerance with No or Minimal Toxic Immunosuppression for Prevention of Immunodeficiency and Autoimmune Diseases. World J. Surg. 24, 797–810 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002680010128
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002680010128