Abstract
Objective
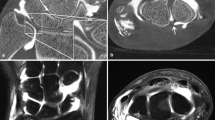
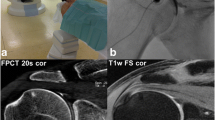
To determine the optimal intra-articular iodine concentration for C-arm flat-panel computed tomography (FPCT) arthrography using advanced joint phantoms and to evaluate its application in human cadaveric wrists and elbows. Multi-detector (MD) CT served as the standard of reference.
Materials and methods
Joint phantoms and 10 human cadaveric wrist and elbow joints were scanned with C-arm FPCT (5-s, 8-s, and 20-s runs) and standard MDCT using different and optimal concentrations of iodinated contrast material. CT numbers of contrast material, tissue, and noise were measured and contrast-to-noise ratios (CNR) calculated for quantitative analysis. Image and depiction of cartilage, bone, and soft tissues were rated. Radiation doses were compared.
Results
In FPCT, iodine concentrations positively correlated with CT numbers and noise of contrast material and with radiation dose (r = 0.713–0.996, p < 0.05 each). At an iodine concentration of 45 mg/ml, CNR of cartilage and soft tissues were highest for all FPCT acquisitions and higher than in MDCT. The 20-s FPCT run performed best for image quality and depiction of anatomical structures and was rated overall equal to MDCT (p = 0.857).
Conclusion
The optimal iodine concentration for C-arm FPCT arthrography in this study is 45 mg/ml, leading to superior CNR and image quality for an optimal FPCT protocol compared with standard MDCT arthrography in human cadaveric joints.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roemer FW, Crema MD, Trattnig S, Guermazi A. Advances in imaging of osteoarthritis and cartilage. Radiology. 2011;260(2):332–54.
De Filippo M, Bertellini A, Pogliacomi F, Sverzellati N, Corradi D, Garlaschi G, et al. Multidetector computed tomography arthrography of the knee: diagnostic accuracy and indications. Eur J Radiol. 2009;70(2):342–51.
De Filippo M, Pogliacomi F, Bertellini A, Araoz PA, Averna R, Sverzellati N, et al. MDCT arthrography of the wrist: diagnostic accuracy and indications. Eur J Radiol. 2010;74(1):221–5.
Cochet H, Pele E, Amoretti N, Brunot S, Lafenetre O, Hauger O. Anterolateral ankle impingement: diagnostic performance of MDCT arthrography and sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010;194(6):1575–80.
Fischer W, Bohndorf K, Kreitner KF, Schmitt R, Wortler K, Zentner J. Indications for CT and MR arthrography–recommendations of the musculoskeletal workgroup of the DRG. Rofo. 2009;181(5):441–6.
El-Khoury GY, Alliman KJ, Lundberg HJ, Rudert MJ, Brown TD, Saltzman CL. Cartilage thickness in cadaveric ankles: measurement with double-contrast multi-detector row CT arthrography versus MR imaging. Radiology. 2004;233(3):768–73.
Prokop M. General principles of MDCT. Eur J Radiol. 2003;45 Suppl 1:S4–10.
De Filippo M, Bertellini A, Sverzellati N, Pogliacomi F, Costantino C, Vitale M, et al. Multidetector computed tomography arthrography of the shoulder: diagnostic accuracy and indications. Acta Radiol. 2008;49(5):540–9.
Kyriakou Y, Struffert T, Dorfler A, Kalender WA. Basic principles of flat detector computed tomography (FD-CT). Radiologe. 2009;49(9):811–9.
Kalender WA, Kyriakou Y. Flat-detector computed tomography (FD-CT). Eur Radiol. 2007;17(11):2767–79.
De Cock J, Mermuys K, Goubau J, Van Petegem S, Houthoofd B, Casselman JW. Cone-beam computed tomography: a new low dose, high resolution imaging technique of the wrist, presentation of three cases with technique. Skeletal Radiol. 2012;41(1):93–6.
Ramdhian-Wihlm R, Le Minor JM, Schmittbuhl M, Jeantroux J, Mahon PM, Veillon F, et al. Cone-beam computed tomography arthrography: an innovative modality for the evaluation of wrist ligament and cartilage injuries. Skeletal Radiol. 2012;41(8):963–9.
Wang G, Crawford CR, Kalender WA. Multirow detector and cone-beam spiral/helical CT. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2000;19(9):817–21.
Schulze R, Heil U, Gross D, Bruellmann DD, Dranischnikow E, Schwanecke U, et al. Artefacts in CBCT: a review. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2011;40(5):265–73.
Jelinek J, Overton TR. Simulation of CT reconstruction artifacts associated with multiple-rotation fan-beam data collection. Comput Radiol. 1986;10(1):23–36.
Schindera ST, Diedrichsen L, Muller HC, Rusch O, Marin D, Schmidt B, et al. Iterative reconstruction algorithm for abdominal multidetector CT at different tube voltages: assessment of diagnostic accuracy, image quality, and radiation dose in a phantom study. Radiology. 2011;260(2):454–62.
Struffert T, Deuerling-Zheng Y, Kloska S, Engelhorn T, Strother CM, Kalender WA, et al. Flat detector CT in the evaluation of brain parenchyma, intracranial vasculature, and cerebral blood volume: a pilot study in patients with acute symptoms of cerebral ischemia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31(8):1462–9.
Penzkofer T, Isfort P, Bruners P, Wiemann C, Kyriakou Y, Kalender WA, et al. Robot arm based flat panel CT-guided electromagnetic tracked spine interventions: phantom and animal model experiments. Eur Radiol. 2010;20(11):2656–62.
Struffert T, Richter G, Engelhorn T, Doelken M, Goelitz P, Kalender WA, et al. Visualisation of intracerebral haemorrhage with flat-detector CT compared to multislice CT: results in 44 cases. Eur Radiol. 2009;19(3):619–25.
Suzuki S, Yamaguchi I, Kidouchi T, Yamamoto A, Masumoto T, Ozaki Y. Evaluation of effective dose during abdominal three-dimensional imaging for three flat-panel-detector angiography systems. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2011;34(2):376–82.
Phan CM, Macklin EA, Bredella MA, Dadrich M, Flechsig P, Yoo AJ, et al. Trabecular structure analysis using C-arm CT: comparison with MDCT and flat-panel volume CT. Skeletal Radiol. 2010;40(8):1065–72.
Walsh CJ, Phan CM, Misra M, Bredella MA, Miller KK, Fazeli PK, et al. Women with anorexia nervosa: finite element and trabecular structure analysis by using flat-panel volume CT. Radiology. 2010;257(1):167–74.
Bredella MA, Misra M, Miller KK, Madisch I, Sarwar A, Cheung A, et al. Distal radius in adolescent girls with anorexia nervosa: trabecular structure analysis with high-resolution flat-panel volume CT. Radiology. 2008;249(3):938–46.
Guggenberger R, Fischer MA, Hodler J, Pfammatter T, Andreisek G. Flat-panel CT arthrography: feasibility study and comparison to multidetector CT arthrography. Invest Radiol. 2012;47(5):312–8.
Moser T, Dosch JC, Moussaoui A, Buy X, Gangi A, Dietemann JL. Multidetector CT arthrography of the wrist joint: how to do it. Radiographics. 2008;28(3):787–800. quiz 911.
Steinbach LS, Schwartz M. Elbow arthrography. Radiol Clin North Am. 1998;36(4):635–49.
Cohen J. Weighted kappa: nominal scale agreement with provision for scaled disagreement or partial credit. Psychol Bull. 1968;70(4):213–20.
Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33(1):159–74.
Huda W, Scalzetti EM, Levin G. Technique factors and image quality as functions of patient weight at abdominal CT. Radiology. 2000;217(2):430–5.
Nakayama Y, Awai K, Funama Y, Hatemura M, Imuta M, Nakaura T, et al. Abdominal CT with low tube voltage: preliminary observations about radiation dose, contrast enhancement, image quality, and noise. Radiology. 2005;237(3):945–51.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guggenberger, R., Morsbach, F., Alkadhi, H. et al. C-arm flat-panel CT arthrography of the wrist and elbow: first experiences in human cadavers. Skeletal Radiol 42, 419–429 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-012-1501-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-012-1501-7