Abstract
Background
Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) imaging) is correlated with histopathological findings using METAVIR and semiquantitative scoring system (SSS) criteria for liver fibrosis.
Objective
To compare acoustic radiation force impulse imaging with biopsy results in the evaluation of liver fibrosis in children.
Materials and methods
Children with chronic liver disease and healthy children underwent acoustic radiation force impulse imaging liver measurements. ARFI gives a shear-wave velocity corresponding to tissue elasticity. In 39 children with liver disease, the values obtained were correlated with biopsy results. Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to determine the reliability of ARFI in estimating liver fibrosis in children.
Results
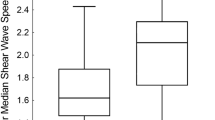
ARFI mean value was 1.12 in the healthy group and 1.99 in children with chronic liver disease. ROC curves show that an ARFI cutoff of 1.34 m/s is predictive of both METAVIR and SSS scores with a sensitivity of SSS > 2:0.85; METAVIR > F0:0.82. A cutoff of 2 m/s yielded a sensitivity of 100% to detect SSS > 4 or METAVIR > F2.
Conclusion
Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging is a reliable, noninvasive and rapid method to estimate moderate to severe liver fibrosis in children. It might prove useful to clinicians for fibrosis monitoring in children with liver disease and postpone the time of liver biopsy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jagadisan B, Srivastava A, Yachha SK et al (2012) Acute on chronic liver disease in children from the developing world: recognition and prognosis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 54:77–82
Mews C, Sinatra F (1993) Chronic liver disease in children. Pediatr Rev 14:436–444
El-Shabrawi MH, Kamal NM (2011) Medical management of chronic liver diseases in children (part I): focus on curable or potentially curable diseases. Paediatr Drugs 13:357–370
El-Shabrawi MH, Kamal NM (2011) Medical management of chronic liver diseases (CLD) in children (part II): focus on the complications of CLD, and CLD that require special considerations. Paediatr Drugs 13:371–383
Imbert-Bismut F, Ratziu V, Pieroni L et al (2001) Biochemical markers of liver fibrosis in patients with hepatitis C virus infection: a prospective study. Lancet 357:1069–1075
de Lédinghen V, Le Bail B, Rebouissoux L et al (2007) Liver stiffness measurement in children using FibroScan: feasibility study and comparison with Fibrotest, aspartate transaminase to platelets ratio index, and liver biopsy. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 45:443–450
Breton E, Bridoux-Henno L, Guyader D et al (2009) Value of transient elastography in noninvasive assessment in children’s hepatic fibrosis. Arch Pediatr 16:1005–1010
Friedrich-Rust M, Ong MF, Martens S (2008) Performance of transient elastography for the staging of liver fibrosis: a meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 134:960–974
Engelmann G, Gebhardt C, Wenning D et al (2012) Feasibility study and control values of transient elastography in healthy children. Eur J Pediatr 171:353–360
Hanquinet S, Courvoisier D, Kanavaki A et al. (2012) Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging (ARFI): normal values of liver stiffness in healthy children. Pediatr Radiol. doi:10.1007/s00247-012-2553-5
The French METAVIR Cooperative Study Group (1994) Intraobserver and interobserver variations in liver biopsy interpretation in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 20:15–20
Chevallier M, Guerret S, Chossegros P et al (1994) A histological semiquantitative scoring system for evaluation of hepatic fibrosis in needle liver biopsy specimens: comparison with morphometric studies. Hepatology 20:349–355
R Development Core Team (2012) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria ISBN 3-900051-07-0, URL http://www.R-project.org
Bedossa P, Carrat F (2009) Liver biopsy: the best, not the gold standard. J Hepatol 50:1–3
Sporea I (2011) Liver biopsy in the era of elastography. Med Ultrason 13:185–186
Castera L, Pinzani M (2010) Biopsy and non-invasive methods for the diagnosis of liver fibrosis: does it take two to tango? Gut 59:861–866
Nobili V, Monti L, Alisi A et al (2011) Transient elastography for assessment of fibrosis in paediatric liver disease. Pediatr Radiol 41:1232–1238
Nobili V, Parkes J, Bottazzo G et al (2009) Performance of ELF serum markers in predicting fibrosis stage in pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 136:160–167
Hermeziu B, Messous D, Fabre M et al (2010) Evaluation of FibroTest-ActiTest in children with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 34:16–22
Friedrich-Rust M, Wunder K, Kriener S et al (2009) Liver fibrosis in viral hepatitis: noninvasive assessment with acoustic radiation force impulse imaging versus transient elastography. Radiology 252:595–604
Lupsor M, Badea R, Stefanescu H et al (2009) Performance of a new elastographic method (ARFI technology) compared to unidimensional transient elastography in the noninvasive assessment of chronic hepatitis C. Preliminary results. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis 18:303–310
Boursier J, Isselin G, Fouchard-Hubert I et al (2010) Acoustic radiation force impulse: a new ultrasonographic technology for the widespread noninvasive diagnosis of liver fibrosis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 22:1074–1084
Haque M, Robinson C, Owen D et al (2010) Comparison of acoustic radiation force impulse imaging (ARFI) to liver biopsy histologic scores in the evaluation of chronic liver disease: a pilot study. Ann Hepatol 9:289–293
Sporea I, Sirli R, Popescu A et al (2010) Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI)—a new modality for the evaluation of liver fibrosis. Med Ultrason 12:26–31
Fierbinteanu-Braticevici C, Andronescu D, Usvat R et al (2009) Acoustic radiation force imaging sonoelastography for noninvasive staging of liver fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol 15:5525
Noruegas MJ, Matos H, Goncalves I et al (2012) Acoustic radiation force impulse-imaging in the assessment of liver fibrosis in children. Pediatr Radiol 42:201–204
Hubscher S (2009) What does the long-term liver allograft look like for the pediatric recipient? Liver Transpl 15(Suppl 2):S19–S24
Evans HM, Kelly DA, McKiernan PJ et al (2006) Progressive histological damage in liver allografts following pediatric liver transplantation. Hepatology 43:1109–1117
Batts KP, Ludwig J (1995) Chronic hepatitis. An update on terminology and reporting. Am J Surg Pathol 19:1409–1417
Friedrich-Rust M, Nierhoff J, Lupsor M et al (2012) Performance of acoustic radiation force impulse imaging for the staging of liver fibrosis: a pooled meta-analysis. J Viral Hepat 19:e212–e219
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanquinet, S., Rougemont, A., Courvoisier, D. et al. Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography for the noninvasive diagnosis of liver fibrosis in children. Pediatr Radiol 43, 545–551 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-012-2595-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-012-2595-8