Abstract
Background
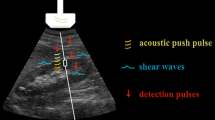
Acoustic radiation force impulse-imaging (ARFI) uses sound waves to interrogate the mechanical stiffness of a tissue.
Objective
To determine the usefulness of ARFI for estimating liver fibrosis in children.
Materials and methods
A prospective masked study of children with chronic liver disease (CLD) and/or before liver transplant (LT) comparing ARFI with histopathological analysis. Children with no history of liver disease served as a control group. ARFI was performed with Virtual Touch software using ACUSON S2000. Share wave velocities (SWV) of several regions within the liver were measured.
Results
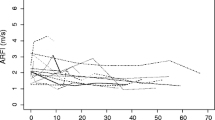
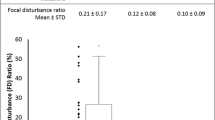
Fifty-two children were studied (mean age 8 years; range 1–16 years). The abnormal group included 10 children (31%) with CLD and 22 (69%) planned for LT. There were 20 normal controls. Mean SWV was 1.70 m/s in the abnormal group and 1.19 m/s in the controls. For diagnosis of fibrosis stage ≥ F1, ≥F2 and F4, the areas under the receiver-operator characteristics curves were 0.834, 0.818 and 0.983, respectively.
Conclusion
SWV is related to the degree of liver fibrosis in children, and may be a non-invasive alternative to biopsy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanif M, Raza J, Qureshi H et al (2004) Etiology of chronic liver disease in children. J Pak Med Assoc 54:119–122
Mews C, Sinatra F (1993) Chronic liver disease in children. Pediatr Rev 14:436–444
Berk PD, Brownstein AP (2002) Foreword: the impact of liver disease in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 35(1):S1–S2
Fahey BJ, Nightingale KR, Nelson RC et al (2005) Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging of the abdomen: demonstration of feasibility and utility. Ultrasound Med Biol 31(9):1185–1198
Lupsor M, Badea R, Stefanescu H et al (2009) Performance of a new elastographic method (ARFI technology) compared to unidimensional transient elastography in the noninvasive assessment of chronic hepatitis C. Preliminary results. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis 18(3):303–310
Nightingale K, Bentley R, Trahey G (2002) Observations of tissue response to acoustic radiation force: opportunities for imaging. Ultrasound Imaging 24:129–138
McAleavey SA, Menon M, Orszulak J (2007) Shearmodulus estimation by application of spatially modulated impulsive acoustic radiation force. Ultrasound Imaging 29:87–104
Nightingale K, Soo MS, Nightingale R et al (2002) Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging: in vivo demonstration of clinical feasibility. Ultrasound Med Biol 28:227–235
Nightingale K, McAleavey SA, Trahey G (2003) Shear-wave generation using acoustic radiation force: in vivo and ex vivo results. Ultrasound Med Biol 29:1715–1723
Batts KP, Ludwig J (1995) Chronic hepatitis. An update on terminology and reporting. Am J Surg Pathol 19:1409–1417
D’Onofrio, Gallotti A, Mucelli RP (2010) Tissue quantification with acoustic radiation force impulse imaging: measurement repeatability and normal values in the healthy liver. AJR 195:132–136
Friedrich-Rust M, Wunder K, Kriener S et al (2009) Liver fibrosis in viral hepatitis: noninvasive assessment with acoustic radiation force impulse imaging versus transient elastography. Radiology 252:595–604
Gatti E, Cabassa P, Gandolfi S et al (2009) Quantification of hepatic fibrosis with a new US technique (virtual touch analysis): correlation with pathologic findings. Eur Radiol 19:S308
Lees QR (2009) Acoustic radiation force imaging: a new method for quantifying hepatic fibrosis. Eur Radiol 19:S308
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noruegas, M.J., Matos, H., Gonçalves, I. et al. Acoustic radiation force impulse-imaging in the assessment of liver fibrosis in children. Pediatr Radiol 42, 201–204 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-011-2257-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-011-2257-2