Abstract
Introduction
The study investigated sex differences in cortical thickness in middle-aged (MA, 44–48 years old, n = 397) and early old-aged (OA, 64–68 years old, n = 398) adults in a community-based sample.
Methods
T1-weighted three-dimensional structural magnetic resonance imaging scans were acquired in a Fast Field Echo sequence, and cortical thickness was measured with a surface-based segmentation procedure (http://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu).
Results
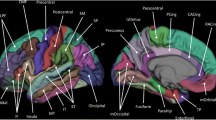
Results showed that after correcting for age, MA males had predominantly thicker superior temporal cortices, while MA females had thicker occipital, posterior cingulate, precentral, and postcentral cortices. Sex differences in OA adults were less prominent than those in MA adults with females showing thicker temporal and posterior cingulate cortices and males showing thicker rostral middle frontal regions. Between-cohort comparisons revealed that when compared with MA males, OA males showed many regions with significantly thinner cortices, but this pattern was less pronounced for OA females. Our results suggest that sex differences in cortical thickness are age specific, as larger differences in cortical thickness were found in MA compared to OA adults.
Conclusion
The results of the present study indicate that the inconsistencies in sexual dimorphism that have been reported in the literature are partly due to the variable and transitory nature of cortical thickness differences with age.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Resnick SM, Pham DL, Kraut MA, Zonderman AB, Davatzikos C (2003) Longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging studies of older adults: a shrinking brain. J Neurosci 23:3295–3301
Allen JS, Bruss J, Brown CK, Damasio H (2005) Normal neuroanatomical variation due to age: the major lobes and a parcellation of the temporal region. Neurobiology of Aging 26:1245–1260
Raz N et al (2005) Regional brain changes in aging healthy adults: general trends, individual differences and modifiers. Cerebral Cortex 15:1676–1689
Jernigan TL et al (2001) Effects of age on tissues and regions of the cerebrum and cerebellum. Neurobiology of Aging 22:581–594
Fjell AM et al (2009) High consistency of regional cortical thinning in aging across multiple samples. Cereb Cortex 19(9):2001–2012. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhn232
Chen X, Sachdev PS, Wen W, Anstey KJ (2007) Sex differences in regional gray matter in healthy individuals aged 44–48 years: a voxel-based morphometric study. NeuroImage 36:691–699
Lemaître H et al (2005) Age- and sex-related effects on the neuroanatomy of healthy elderly. NeuroImage 26:900–911
Sowell ER et al (2007) Sex differences in cortical thickness mapped in 176 healthy individuals between 7 and 87 years of age. Cerebral Cortex 17:1550–1560
Luders E et al (2006) Gender effects on cortical thickness and the influence of scaling. Human Brain Mapping 27:314–324
Carne RP, Vogrin S, Litewka L, Cook MJ (2006) Cerebral cortex: An MRI-based study of volume and variance with age and sex. J Clin Neurosci 13:60–72
Raz N et al (2004) Aging, sexual dimorphism, and hemispheric asymmetry of the cerebral cortex: replicability of regional differences in volume. Neurobiology of Aging 25:377–396
Nopoulos P, Flaum M, O'Leary D, Andreasen NC (2000) Sexual dimorphism in the human brain: evaluation of tissue volume, tissue composition and surface anatomy using magnetic resonance imaging. Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging 98:1–13. doi:10.1016/s0925-4927(99)00044-x
Good CD et al (2001) A voxel-based morphometric study of ageing in 465 normal adult human brains. NeuroImage 14:21–36
Sullivan EV, Rosenbloom M, Serventi KL, Pfefferbaum A (2004) Effects of age and sex on volumes of the thalamus, pons, and cortex. Neurobiology of Aging 25:185–192
Cowell PE et al (2007) Effects of sex and age on regional prefrontal brain volume in two human cohorts. Eur J Neurosci 25:307–318. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.05281.x
Curiati PK et al (2009) Brain structural variability due to aging and gender in cognitively healthy elders: results from the Sao Paulo ageing and health study. Am J Neuroradiol 30:1850–1856
Sowell ER et al (2004) Longitudinal mapping of cortical thickness and brain growth in normal children. J Neurosci 24:8223–8231
Shaw P et al (2006) Intellectual ability and cortical development in children and adolescents. Nature 440:676–679
Shaw P et al (2008) Neurodevelopmental trajectories of the human cerebral cortex. J Neurosci 28:3586–3594. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.5309-07.2008
Raznahan A et al (2010) Longitudinally mapping the influence of sex and androgen signaling on the dynamics of human cortical maturation in adolescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:16988–16993. doi:10.1073/pnas.1006025107
Fjell AM et al (2006) Selective increase of cortical thickness in high-performing elderly—structural indices of optimal cognitive aging. NeuroImage 29:984–994
Salat DH et al (2004) Thinning of the cerebral cortex in aging. Cerebral Cortex 14:721–730. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhh032
Greenberg DL et al (2008) Aging, gender, and the elderly adult brain: an examination of analytical strategies. Neurobiology of Aging 29:290–302
Barnes J et al (2010) Head size, age and gender adjustment in MRI studies: a necessary nuisance? NeuroImage 53:1244–1255
Gautam P, Cherbuin N, Sachdev PS, Wen W, Anstey KJ (2011) Relationships between cognitive function and frontal grey matter volumes and thickness in middle aged and early old-aged adults: the PATH through life study. NeuroImage 55(3):845–855. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.01.015
Anstey K et al (2011) Cohort profile: the PATH through life project. International Journal of Epidemiology 41(4):951–960. doi:10.1093/ije/dyr025
Cherbuin N, Anstey KJ, Reglade-Meslin C, Sachdev PS (2009) In vivo hippocampal measurement and memory: a comparison of manual tracing and automated segmentation in a large community-based sample. PLoS ONE [Electronic Resource] 4:e5265
Fischl B, Sereno MI, Dale AM (1999) Cortical surface-based analysis. II: Inflation, flattening, and a surface-based coordinate system. NeuroImage 9:195–207
Dale AM, Fischl B, Sereno MI (1999) Cortical surface-based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. NeuroImage 9:179–194
Desikan RS et al (2006) An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. NeuroImage 31:968–980
Han X et al (2006) Reliability of MRI-derived measurements of human cerebral cortical thickness: the effects of field strength, scanner upgrade and manufacturer. NeuroImage 32:180–194
Lv B et al (2010) Gender consistency and difference in healthy adults revealed by cortical thickness. NeuroImage 53:373–382. doi:310.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.1005.1020
Brun CC et al (2009) Sex differences in brain structure in auditory and cingulate regions. Neuroreport 20:930–935
Raz N, Rodrigue KM (2006) Differential aging of the brain: patterns, cognitive correlates and modifiers. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 30:730–748
Witte AV, Savli M, Holik A, Kasper S, Lanzenberger R (2010) Regional sex differences in grey matter volume are associated with sex hormones in the young adult human brain. NeuroImage 49:1205–1212. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.09.046
Abe O et al (2008) Aging in the CNS: comparison of gray/white matter volume and diffusion tensor data. Neurobiology of Aging 29:102–116
Gur RC, Gunning-Dixon FM, Turetsky BI, Bilker WB, Gur RE (2002) Brain region and sex differences in age association with brain volume: a quantitative MRI study of healthy young adults. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 10:72–80
Chen X, Wen W, Anstey KJ, Sachdev PS (2006) Effects of cerebrovascular risk factors on gray matter volume in adults aged 60–64 years: a voxel-based morphometric study. Psychiatry Research. Neuroimaging 147:105–114. doi:10.1016/j.pscychresns.2006.01.009
Khaw K-T et al (2007) Endogenous testosterone and mortality due to all causes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer in men: European Prospective Investigation Into Cancer in Norfolk (EPIC-Norfolk) prospective population study. Circulation 116:2694–2701. doi:10.1161/circulationaha.107.719005
Stein DG, Wright DW, Kellermann AL (2008) Does progesterone have neuroprotective properties? Ann Emerg Med 51:164–172
Cherbuin N, Reglade-Meslin C, Kumar R, Sachdev P, Anstey KJ (2010) Mild cognitive disorders are associated with different patterns of brain asymmetry than normal ageing: the PATH through life study. Frontiers in Psychiatry 1:12. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2010.00011
Chen JJ, Rosas HD, Salat DH (2011) Age-associated reductions in cerebral blood flow are independent from regional atrophy. NeuroImage 55(2):468–478. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.12.032(2010
Im K et al (2008) Brain size and cortical structure in the adult human brain. Cerebral Cortex 18:2181–2191. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhm244
Plant C et al (2010) Automated detection of brain atrophy patterns based on MRI for the prediction of Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage 50:162–174. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.11.046
Salat DH et al (2009) Age-associated alterations in cortical gray and white matter signal intensity and gray to white matter contrast. NeuroImage 48:21–28
Westlye LT et al (2009) Increased sensitivity to effects of normal aging and Alzheimer’s disease on cortical thickness by adjustment for local variability in gray/white contrast: a multi-sample MRI study. NeuroImage 47:1545–1557. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.05.084
Westlye LT et al (2010) Differentiating maturational and aging-related changes of the cerebral cortex by use of thickness and signal intensity. NeuroImage 52:172–185. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.03.056
Tang Y, Nyengaard JR, Pakkenberg B, Gundersen HJG (1997) Age-induced white matter changes in the human brain: a stereological investigation. Neurobiology of Aging 18:609–615. doi:10.1016/s0197-4580(97)00155-3
Davis SW et al (2009) Assessing the effects of age on long white matter tracts using diffusion tensor tractography. NeuroImage 46:530–541
Fjell AM et al (2009) Minute effects of sex on the aging brain: a multisample magnetic resonance imaging study of healthy aging and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 29:8774–8783. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.0115-09.2009
Wallentin M (2009) Putative sex differences in verbal abilities and language cortex: a critical review. Brain and Language 108:175–183
Beaucousin V et al (2011) Sex-dependent modulation of activity in the neural networks engaged during emotional speech comprehension. Brain Research 1390:108–117. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2011.03.043
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Anthony Jorm, Bryan Rodgers, Helen Christensen, Patricia Jacomb, Karen Maxwell, and the PATH interviewers. This research was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) of Australia Unit grant no. 973302, program grant no. 179805, project grant no. 157125, grants from the Australian Rotary Health Research Fund and the Australian Brewers Foundation, and a processing grant from the National Computational Infrastructure. NC is funded by NHMRC Research Fellowship no. 471501. KA is funded by NHMRC Research Fellowship no. 1002560.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 2143 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gautam, P., Cherbuin, N., Sachdev, P.S. et al. Sex differences in cortical thickness in middle aged and early old-aged adults: Personality and Total Health Through Life study. Neuroradiology 55, 697–707 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-013-1144-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-013-1144-y