Abstract
In this article, we developed a membrane-based enzyme micro-reactor by directly using commercial polystyrene–divinylbenzene cation–exchange membrane as the support for trypsin immobilization via electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions and successfully applied it for protein digestion. The construction of the reactor can be simply achieved by continuously pumping trypsin solution through the reactor for only 2 min, which was much faster than the other enzyme immobilization methods. In addition, the membrane reactor could be rapidly regenerated within 35 min, resulting in a “new” reactor for the digestion of every protein sample, completely eliminating the cross-interference of different protein samples. The amount and the activity of immobilized trypsin were measured, and the repeatability of the reactor was tested, with an RSD of 3.2% for the sequence coverage of cytochrome c in ten digestion replicates. An integrated platform for protein analysis, including online protein digestion and peptide separation and detection, was established by coupling the membrane enzyme reactor with liquid chromatography–quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. The performance of the platform was evaluated using cytochrome c, myoglobin, and bovine serum albumin, showing that even in the short digestion time of several seconds the obtained sequence coverages was comparable to or higher than that with in-solution digestion. The system was also successfully used for the analysis of proteins from yeast cell lysate.

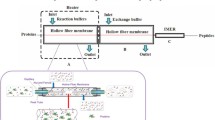
Schemes of the designed ion-exchange-membrane-based enzyme micro-reactor (a) and the online coupling system of the enzyme micro-reactor with LC-QTOF MS (b)




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duan JC, Liang Z, Yang C, Zhang J, Zhang LH, Zhang WB, Zhang YK (2006) Proteomics 6:412–419
Duan JC, Sun LL, Liang Z, Zhang J, Wang H, Zhang LH, Zhang WB, Zhang YK (2006) J Chromatogr A 1106:165–174
Feng S, Ye ML, Jiang XG, Jin WH, Zou HF (2006) J Proteome Res 5:422–428
Křenková J, Bilková Z, Foret F (2005) J Sep Sci 28:1675–1684
Krenkova J, Lacher NA, Svec F (2009) Anal Chem 81:2004–2012
Palm AK, Novotny MV (2004) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 18:1374–1382
Palms AK, Novotny MV (2005) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 19:1730–1738
Sproß J, Sinz A (2010) Anal Chem 82:1434–1443
Zhang K, Wu S, Tang XT, Kaiser NK, Bruce JE (2007) J Chromatogr B 849:223–230
Cooper JW, Chen JZ, Li Y, Lee CS (2003) Anal Chem 75:1067–1074
Gao J, Xu JD, Locascio LE, Lee CS (2001) Anal Chem 73:2648–2655
Jiang Y, Lee CS (2001) J Chromatogr A 924:315–322
Li Y, Cooper JW, Lee CS (2002) J Chromatogr A 979:241–247
Xu F, Wang WH, Tan YJ, Bruening ML (2010) Anal Chem 82:10045–10051
Liu Y, Lu HJ, Zhong W, Song PY, Kong JL, Yang PY, Girault HH, Liu BH (2006) Anal Chem 78:801–808
Amounas M, Innocent C, Cosnier S, Seta P (2000) J Membr Sci 176:169–176
Pugazhenthi G, Kumar A (2004) J Membr Sci 228:187–197
Tang ZM, Kang JW (2006) Anal Chem 78:2514–2520
Tang ZM, Wang TD, Kang JW (2007) Electrophoresis 28:2981–2987
Zhou Y, Shen H, Yi T, Wen D, Pang N, Liao J, Liu H (2008) Anal Chem 80:8920–8929
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 20975005 and 21027012) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities. We thank Dr. Peng Chen and Ph.D. student Jie Li from Peking University for providing the yeast cell lysate.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 579 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Z., Yang, Y., Zhang, J. et al. Ion-exchange-membrane-based enzyme micro-reactor coupled online with liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry for protein analysis. Anal Bioanal Chem 403, 239–246 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-5812-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-5812-2