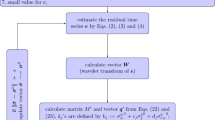
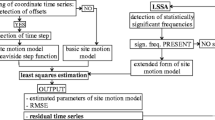
Abstract
The efficacy of robust M-estimators is a well-known issue when dealing with observational blunders. When the number of observations is considerably large—long time series for instance—one can take advantage of the asymptotic normality of the M-estimation and compute reasonable estimates for the unknown parameters of interest. A few leading M-estimators have been employed to identify the most likely functional model for GPS coordinate time series. This includes the simultaneous detection of periodic patterns and offsets in the GPS time series. Estimates of white noise, flicker noise, and random walk noise components are also achieved using the robust M-estimators of (co)variance components, developed in the framework of the least-squares variance component estimation (LS-VCE) theory. The method allows one to compute confidence interval for the (co)variance components in asymptotic sense. Simulated time series using white noise plus flicker noise show that the estimates of random walk noise fluctuate more than those of flicker noise for different M-estimators. This is because random walk noise is not an appropriate noise structure for the series. The same phenomenon is observed using the results of real GPS time series, which implies that the combination of white plus flicker noise is well described for GPS time series. Some of the estimated noise components of LS-VCE differ significantly from those of other M- estimators. This reveals that there are a large number of outliers in the series. This conclusion is also affirmed by performing the statistical tests, which detect (large) parts of the outliers but can also leave parts to be undetected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiri-Simkooei AR (2003) Formulation of L1 norm minimization in Gauss–Markov models. J Surv Eng 129(1): 37–43
Amiri-Simkooei AR (2007) Least-squares variance component estimation: theory and GPS applications, Ph.D. thesis, Delft University of Technology, Publication on Geodesy, 64, Netherlands, Geodetic Commission, Delft
Amiri-Simkooei AR, Tiberius CCJM, Teunissen PJG (2007) Assessment of noise in GPS coordinate time-series: methodology and results. J Geophys Res 112: B07413
Babu GJ (1989) Strong representations for LAD estimates in linear models. Probab Theory Relat Fields 83: 547–558
Bahadur RR (1966) A note on quantiles in large samples. Ann Math Stat 37: 577–580
Baselga S (2007) A global optimization solution of robust estimation. J Surv Eng 133(3): 123–128
Basseville M, Nikiforov IV (1993) Detection of abrupt changes: theory and application. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, p 469
Beutler G, Rothacher M, Schaer S, Springer TA, Kouba J, Neilan RE (1999) The International GPS Service (IGS): an interdisciplinary service in support of Earth sciences. Adv Space Res 23(4): 631–635
Calais E (1999) Continuous GPS measurements across the Western Alps 1996–1998. Geophys J Int 138: 221–230
Davis RA (1996) Gauss-Newton and M-estimation for ARMA processes with infinite variance. Stochas Process Appl 63: 75–95
Ding XL, Zheng DW, Dong DN, Ma C, Chen YQ, Wang GL (2005) Seasonal and secular positional variations at eight co-located GPS and VLBI stations. J Geod 79(1-3): 71–81
Dueck A, Lohr S (2005) Robust estimation of multivariate covariance components. Biometrics 61: 162–169
Efron B, Tibshirani RJ (1993) An introduction to the bootstrap. Chapman & Hall, London
Erenoglu RC, Hekimoglu S (2009) An investigation into robust estimation applied to GPS networks. In: International Association of Geodesy Symposia. vol 133. Springer, Berlin, pp 639-644
Gervini D, Yohai VJ (1998) Robust estimation of variance components. Can J Stat 26: 419–430
Gui Q, Zhang J (1998) Robust biased estimation and its application in geodetic adjustments. J Geod 72: 430–435
Hampel FR, Ronchetti EM, Rousseeuw PJ, Stahel WA (1986) Robust statistics: the approach based on influence functions. John Wiley & Sons, New York
He X, Shao Q (1996) A general Bahadur representation of M-estimators and its application to linear regression with nonstochastic designs. Ann Stat 24(6): 2608–2630
Hekimoglu S (1997) The finite sample breakdown points of conventional iterative outlier detection procedures. J Surv Eng 123(1): 15–31
Huber PJ (1981) Robust statistics. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Kenyeres A, Bruyninx C (2004) EPN coordinate time-series monitoring for reference frame. GPS Solut 8: 200–209
Khodabandeh A, Amiri-Simkooei AR (2010) Recursive algorithm for L1 norm estimation in linear models. J Surv Eng. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)SU.1943-5428.0000031
Koch KR (1996) Robuste Parameterschatzung. Allgemeine Vermessungs-Nachrichten 103: 1–18
Koch KR (1999) Parameter estimation and hypothesis testing in linear models. Springer, Berlin
Krarup T, Juhl J, Kubik K (1980) Götterdämmerung over least squares adjustment. Proc.14th congress of the international society of photogrammetry, Hamburg, vol B3, pp 369–378
Krarup T, Kubik K (1983) The danish method: experience and Philosophy. DGK Reihe A.Heft 98: 131–134
Langbein J (2008) Noise in GPS displacement measurements from Southern California and Southern Nevada. J Geophys Res 113(B5): B05405
Magnus JR (1988) Linear structures. London School of Economics and Political Science. Charles Griffin & Company LTD, London, Oxford University Press, , New York
Mao A, Harrison CGA, Dixon TH (1999) Noise in GPS coordinate time-series. J Geophys Res 104(B2): 2797–2816
Maronna RA, Martin RD, Yohai VJ (2006) Robust statistics: theory and methods. Wiley series in probability and statistics, England
Martin RD (1981) Robust methods for time-series. In: Findley DF (eds) Applied time-series analysis II. Academic Press, New York, pp 683–759
Martin RD, Yohai VJ (1986) Influence functionals for time-series. Ann Stat 14: 781–818
Martin RD, Yohai VJ (1991) Bias robust estimation of autoregression parameters. In: Stahel W, Weisberg S (eds) Directions in robust statistics and diagnostics Part I, IMA Volumes in Mathematics and its Applications, vol 30.. Springer, Berlin
Peng JH (2005) The asymptotic variance-covariance matrix, Baarda testing and the reliability of L1 norm estimates. J Geod 78: 668–682
Peng JH (2009) Jointly robust estimation of unknown parameters and variance components based on expectation- maximization algorithm. J Surv Eng 135(1): 1–9
Perfetti N (2006) Detection of station coordinate discontinuities within the Italian GPS Fiducial Network. J Geod 80(7): 381–396
Pope AJ (1976) The statistics of residuals and the detection of outliers. NOAA technical report NOS65 NGS1, US Department of commerce, National Geodetic Survey, Rockville, Maryland
Ray J, Altamimi Z, Collilieux X, van Dam T (2008) Anomalous harmonics in the spectra of GPS position estimates. GPS Solut 12: 55–64
Rousseuw PJ, Leroy AM (1987) Robust regression and outlier detection. Wiley, New York
Shao J (2003) Mathematical Statistics, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Teunissen PJG (1988) Towards a least-squares framework for adjusting and testing of both functional and stochastic model. Internal research memo, Geodetic Computing Centre, Delft
Teunissen PJG (2000) Testing theory: an introduction. Delft University press, Series on mathematical Geodesy and positioning, The Netherlands
Teunissen PJG, Simons DG, Tiberius CCJM (2005) Probability and observation theory. In: Lecture notes AE2-E01, Delft University of technology, Delft, The Netherlands
Teunissen PJG, Amiri-Simkooei AR (2008) Least-squares variance component estimation. J Geod 82(2): 65–82
Vanicek P (1969) Approximate spectral analysis by least-squares fit. Astrophys Space Sci 4: 387–391
Williams SDP (2003a) The effect of coloured noise on the uncertainties of rates estimated from geodetic time-series. J Geod 76: 483–494
Williams SDP (2003b) Offsets in global positioning system time-series. J Geophys Res 108(B6): 2310
Williams SDP, Bock Y, Fang P, Jamason P, Nikolaidis RM, Prawirodirdjo L, Miller M, Johnson DJ (2004) Error analysis of continuous GPS position time-series. J Geophys Res 109: B03412
Yang Y (1994) Robust estimation for dependent observations. Manuscr Geod 19: 10–17
Yang Y (1999) Robust estimation of geodetic datum transformation. J Geod 73: 268–274
Yang Y, Song L, Xu T (2001) robust estimator for the adjustment of correlated GPS networks. In: Carosio A, Kutterer H (eds) First International Symposium on Robust Statistics and Fuzzy Techniques in Geodesy and GIS, vol 295, pp 199–207
Yang Y, Xu TH, Song LJ (2005) Robust estimation of variance components with application in global positioning system network adjustment. J Surv Eng 131(4): 107–112
Zhang J, Bock Y, Johnson H, Fang P, Williams S, Genrich J, Wdowinski S, Behr J (1997) Southern California permanent GPS geodetic array: error analysis of daily position estimates and site velocitties. J Geophys Res 102: 18035–18055
Zumberge JF, Heflin MB, Jefferson DC, Watkins MM, Webb FH (1997) Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J Geophys Res 102: 5005–5017
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khodabandeh, A., Amiri-Simkooei, A.R. & Sharifi, M.A. GPS position time-series analysis based on asymptotic normality of M-estimation. J Geod 86, 15–33 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-011-0489-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-011-0489-4