Abstract
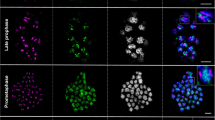
The structure and organization of the 5S ribosomal DNA units of the silver fir, Abies alba Mill., as well as their position in the chromosome complement were investigated. PCR amplification of the gene and nontranscribed spacer region, sequence analysis and Southern hybridization, using a homologous probe, detected DNA sequences of approximately 550 bp and 700 bp. Sequence analysis of the spacers revealed that the difference in length between the sequences occurred in the middle spacer region as a result of the amplification of a 75-bp sequence of the short unit class, which is organized in four 54- to 68-bp tandem repeats in the long spacer unit. The 5S rDNA transcribed region is 120 bp long and shows high sequence similarity with other gymnosperm species. The comparative analysis of 5′ and 3′ flanking sequences of 5S rRNA genes of silver fir and other gymnosperms indicates that A. alba spacer units have the same rate of evolution and are more closely related to Larix and Pseudotsuga than to Pinus and Picea. Southern hybridization and fluorescence in situ hybridization of metaphase chromosomes of A. alba suggest that the short and long spacer units are organized as separate tandem arrays at two chromosomal loci on chromosomes V and XI.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amarasinghe V, Carlson JE (1998) Physical mapping and characterization of 5S rRNA genes in Douglas-fir. J Hered 89:495–500
Basten CJ, Ohta T (1992) Simulation study of a multigene family, with special reference to the evolution of compensatory advantageous mutations. Genetics 132:247–252
Brown GR, Carlson JE (1997) Molecular cytogenetics of the genes encoding 18S–5.8S–26S rRNA and 5S rRNA in two species of spruce (Picea). Theor Appl Genet 95:1–9
Campell BR, Song Y, Posch TE, Cullis CA, Town CD (1992) Sequence and organization of 5S ribosomal RNA-encoding genes of Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene 112:225–228
Cronn RC, Zhao X, Paterson AH, Wendel JF (1996) Polymorphism and concerted evolution in a tandemly repeated gene family: 5S ribosomal DNA in diploid and allopolyploid cottons. J Mol Evol 42:685–705
Doudrick RL, Heslop-Harrison JS, Nelson CD, Schmidt T, Nance WL, Schwarzacher T (1995) Karyotype of slash pine (Pinus elliottii var. elliottii) using patterns of fluorescence in situ hybridization and fluorochrome banding. J Hered 86:289–296
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Farjon A (1990) Pinaceae. Koelltz Scientific, Königstein, p 340
Fulnaček J, Lim KY, Leitch AR, Kovařik A, Matyášek R (2002) Evolution and structure of 5S rDNA loci in allotetraploid Nicotiana tabacum and its putative parental species. Heredity 88:19–25
Gorman SW, Teasdale RD, Cullis CA (1992) Structure and organization of the 5S rRNA genes (5S DNA) in Pinus radiata (Pinaceae). Plant Syst Evol 183:223–234
Gottlob-McHugh SG, Lévesque M, MakKenzie K, Olson M, Yarosh O, Johnson DA (1990) Organization of the 5S rRNA genes in the soybean Glycine max (L.) Merill and conservation of the 5S rDNA repeat structure in higher plants. Genome 33:486–494
Hayes JJ, Tullius TD (1992) Structure of the TF-IIIA-5S DNA complex. J Mol Biol 227:407–417
Hizume M, Shibata F, Kondo K, Hoshi Y, Kondo T, Ge S, Yang QE, Hong DY (1999) Identification of chromosomes in two Chinese spruce species by multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization. Chrom Sci 3:37–41
Hori H, Lim B-L, Osawa S (1985) Evolution of green plants as deduced from 5S rRNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:820–823
Liepelt S, Bialozyt R, Ziegenhagen B (2002) Wind-dispersed pollen mediates postglacial gene flow among refugia. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 99:14590–14594
Liu T-S (1971) A monograph of the genus Abies. National Taiwan University, Taipei, p 608
Liu Z-L, Zhang D, Hong D-Y, Wang X-R (2003a) Chromosomal localization of 5S and 18S–25S ribosomal DNA sites in five Asian pines using fluorescent in situ hybridization. Theor Appl Genet 106:198–204
Liu Z-L, Zhang D, Wang X-Q, Ma X-F, Wang X-R (2003b) Intragenomic and interspecific 5S rDNA sequence variation in five Asian pines. Am J Bot 90(1):17–24
Lubaretz O, Fuchs J, Ahne R, Meister A, Schubert I (1996) Karyotyping of tree Pinaceae species via fluorescent in situ hybridization and computer-aided chromosome analysis. Theor Appl Genet 92:411–416
Mashkova TD, Barciszewska MZ, Joachimiak A, Nalaskowska M, Barciszewski J (1990) Molecular evolution of plants as deduced from changes in free energy of 5S ribosomal RNAs. Int J Biol Macromol 12:247–250
Melekhovets YF, Troitsky AV, Valiejo-Roman KM, Bobrova VK, Antonov AS (1988) Nucleotide sequences of cytosolic 5S ribosomal RNAs from two gymnosperms, Gnetum gnemon and Ephedra kokanica. Nucleic Acid Res 16:4155
Moran GF, Smith D, Bell JC, Appels R (1992) The 5S RNA genes in Pinus radiata and the spacer region as a probe for relationships between Pinus species. Plant Syst Evol 183:209–221
Rushforth KD (1987) Conifers. Facts on File, New York, p 232
Sastri DC, Hilu K, Appels R, Lagudah ES, Playford J, Baum BR (1992) An overview of evolution in plant 5S DNA. Plant Syst Evol 183:169–181
Schlötterer C, Tautz D (1994) Chromosomal homogeneity of Drosophila ribosomal DNA arrays suggests intrachromosomal exchanges drive concerted evolution. Curr Biol 4:777–783
Schwarzacher T, Heslop-Harrison JS (2000) Practical in situ hybridization. Bios Scientific, Oxford, p 203
Scoles GJ, Gill BS, Xin Z-Y, Clarke BC, McIntyre CL, Chapman C, Appels R (1988) Frequent duplication and deletion events in the 5S RNA genes and the associated space regions of the Triticae. Plant Syst Evol 160:105–122
Shibata F, Hizume M (2002) Evolution of 5S rDNA units and their chromosomal localization in Allium cepa and Allium schoenoprasum revealed by microdissection and FISH. Theor Appl Genet 105:167–172
Siljak-Yakovlev S, Cerbah M, Coulaud J, Stoian V, Brown SC, Zoldoš V, Jelenić S, Papeš D (2002) Nuclear DNA content, base composition, heterochromatin and rDNA in Picea omorika and Picea abies. Theor Appl Genet 104:505–512
Smith GP (1976) Evolution of repeated DNA sequences by unequal crossover. Science 191:528–535
Soltis DE, Soltis PS, Doyle JJ (1998) Molecular systematics of plants: DNA sequencing. Kluwer, Boston, p 574
Swofford DL (1998) PAUP. Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and or other methods). Version 4.0. Sinauer, Sunderland
Szymanski M, Specht T, Barciszewska MZ, Barciszewski J, Erdmann VA (1998) 5S rRNA data bank. Nucleic Acid Res 26:156–159
Toress-Ruiz RA, Hemleben V (1994) Pattern and degree of methylation in ribosomal RNA genes of Cucurbita pepo L. Plant Mol Biol 26:1167–1179
Trontin J-F, Grandemange C, Favre J-M (1999) Two highly divergent 5S rDNA unite size classes occur in composite tandem array in European larch (Larix decidua Mill.) and Japanese larch [Larix kaempferi (Lamb.) Carr]. Genome 42:837–848
Van de Peer Y, De Baere R, Cauwenbergh J, De Watcher R (1990) Evolution of green plants and their relationship with other photosynthetic eukaryotes as deduced from 5S ribosomal RNA sequences. Plant Syst Evol 170:85–96
Vendramin GG, Degen B, Petit RJ, Anzidei M, Madaghiele A, Ziegenhagen B (1999) High level of variation at Abies alba chloroplast microsatellite loci in Europe. Mol Ecol 8:1117–1126
Vidaković M (1982) Četinjače. Sveučilišna naklada Liber, Zagreb, p 710
Volkov RA, Borisjuk NV, Panchuk II, Schweizer D, Hemleben V (1999) Elimination and rearrangement of parental rDNA in the allotetraploid Nicotiana tabacum. Mol Biol Evol 16:311–320
Wang X-Q, Tank DC, Sang T (2000) Phylogeny and divergence times in Pinaceae: evidence from three genomes. Mol Biol Evol 17:773–781
Acknowledgements
The authors thank M. Gradečki from the Forestry Research Institute ‘Jasrebarsko’ for preparing the plant material used in the cytogenetic study and K. Vlahoviček for sequence analysis and suggestions in the interpretation of the phylogeny results. This work was supported by research grant no. 119112 from the Ministry of Science, Education and Sport of the Republic of Croatia. Jasna Puizina acknowledges the support of the Gregor Mendel Institute, Vienna, Austria.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by D.B. Neale
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Besendorfer, V., Krajačić-Sokol, I., Jelenić, S. et al. Two classes of 5S rDNA unit arrays of the silver fir, Abies alba Mill.: structure, localization and evolution. Theor Appl Genet 110, 730–741 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1899-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1899-y