Abstract
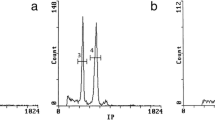
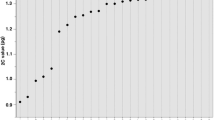
Two closely related spruces, Picea abies and Picea omorika, a Balkan paleoendemic species, often share habitats, yet never hybridize in nature. The present study adresses their characteristics such as nuclear DNA content, base composition, heterochromatin and rDNA pattern. The genome size of P. abies was 10% larger than that of P. omorika when assessed by flow cytometry, respectively 2C=37.2 pg and 33.8 pg; although when estimated as total chromosome length it was virtually the same. The heterochromatin Chromomycin-A (CMA)/ DAPI fluorochrome banding patterns of both P. abies and P. omorika are given here for the first time. Simultaneous FISH (fluorescent in situ hybridization) using 18S-26S and 5S rDNA probes revealed 16 18S rDNA sites in P. omorika, 12 18S rDNA sites in P. abies, and a single 5S rDNA locus in both species. The genomes have about 41% GC. The number and position of CMA/DAPI bands and rDNA loci provide good chromosome markers to clarify the karyotypes of the two species.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 18 October 2000 / 14 June 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siljak-Yakovlev, S., Cerbah, M., Coulaud, J. et al. Nuclear DNA content, base composition, heterochromatin and rDNA in Picea omorika and Picea abies . Theor Appl Genet 104, 505–512 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220100755
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220100755