Abstract
Background
In view of the role of fibronectin in adhesion, signal transduction pathways and the infectious disease process, changes in serum fibronectin levels may influence disease evolution and severity in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS).
Methods
The levels of fibronectin were measured in serum samples from 112 patients with HFRS at various phases, and 30 healthy individuals were monitored as controls.
Results
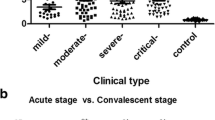
The serum levels of fibronectin in patients with HFRS at all clinical phases were higher than those in the controls, with the levels of patients at the fever, oliguric and polyuric phases of disease significantly different from controls (P < 0.01). The serum fibronectin concentration in the patients with more severe clinical disease types was higher than that in those with milder types. The serum fibronectin level in the more severe patient group was significantly higher than that in milder patient group at the oliguric phase (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
Serum fibronectin concentration in patients with HFRS was increased and associated with disease phases and severity, suggesting the value of detection of fibronectin levels for evaluating HFRS disease progression and severity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee HW, Lee PW, Johnson KM. Isolation of the etiologic agent of Korean hemorrhagic fever. J Infect Dis. 1978;137:298–308.
Cosgriff TM. Mechanisms of disease in Hantavirus infection: pathophysiology of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Rev Infect Dis. 1991;13:97–107.
Krüger DH, Ulrich R, Lundkvist AA. Hantavirus infections and their prevention. Microbes Infect. 2001;3:1129–44.
Lednicky JA. Hantaviruses. A short review. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2003;127:30–5.
Peters CJ, Simpson GL, Levy H. Spectrum of hantavirus infection: hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome and hantavirus pulmonary syndrome. Annu Rev Med. 1999;50:531–45.
Schmaljohn C, Hjelle B. Hantaviruses: a global disease problem. Emerg Infect Dis. 1997;3:95–104.
Chen HX, Qiu FX, Dong BJ, Ji SZ, Li YT, Wang Y, et al. Epidemiological studies on hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in China. J Infect Dis. 1986;154:394–8.
Liang M, Li D, Xiao SY, Hang C, Rossi CA, Schmaljohn CS. Antigenic and molecular characterization of hantavirus isolates from China. Virus Res. 1994;31:219–33.
Settergren B, Ahlm C, Alexeyev O, Billheden J, Stegmayr B. Pathogenetic and clinical aspects of the renal involvement in hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Ren Fail. 1997;19:1–14.
Romberger DJ. Fibronectin. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1997;29:939–43.
Mosher DF. Plasma fibronectin concentration: a risk factor for arterial thrombosis? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:1193–5.
Orem C, Celik S, Orem A, Calapoğlu M, Erdöl C. Increased plasma fibronectin levels in patients with acute myocardial infarction complicated with left ventricular thrombus. Thromb Res. 2002;105:37–41.
Ruiz Martín G, Prieto Prieto J, Veiga de Cabo J, Gomez Lus L, Barberán J, González Landa JM, et al. Plasma fibronectin as a marker of sepsis. Int J Infect Dis. 2004;8:236–43.
Rubli E, Büssard S, Frei E, Lundsgaard-Hansen P, Pappova E. Plasma fibronectin and associated variables in surgical intensive care patients. Ann Surg. 1983;197:310–7.
Liu Z, Zhao Q, Han Q, Gao M, Zhang N. Serum thrombospondin-1 is altered in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. J Med Virol. 2008;80:1799–803.
Mosher DF. Fibronectin. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1980;5:111–51.
Liu Z, Han Q, Zhang L, Zhao Q, Chen J, Lou S. Low levels of serum vitronectin associated with clinical phases in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Clin Exp Med. 2009. doi:10.1007/s10238-009-0050-4 (Epub ahead of print).
Bilato C, Curto KA, Monticone RE, Pauly RR, White AJ, Crow MT. The inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell migration by peptide and antibody antagonists of the alphavbeta3 integrin complex is reversed by activated calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. J Clin Invest. 1997;100:693–704.
Wu X, Mogford JE, Platts SH, Davis GE, Meininger GA, Davis MJ. Modulation of calcium current in arteriolar smooth muscle by alphav beta3 and alpha5 beta1 integrin ligands. J Cell Biol. 1998;143:241–52.
Cho J, Mosher DF. Enhancement of thrombogenesis by plasma fibronectin cross-linked to fibrin and assembled in platelet thrombi. Blood. 2006;107:3555–63.
Alexeyev OA, Ahlm C, Billheden J, Settergren B, Wadell G, Juto P. Elevated levels of total and Puumala virus-specific immunoglobulin E in the Scandinavian type of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1994;1:269–72.
Wang W. Effect of type I allergy on the pathogenesis of epidemic hemorrhagic fever. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Chin Med J). 1987;67:253–5. (in Chinese).
Yasuda M, Hasunuma Y, Adachi H, Sekine C, Sakanishi T, Hashimoto H, et al. Expression and function of fibronectin binding integrins on rat mast cells. Int Immunol. 1995;7:251–8.
Ra C, Yasuda M, Yagita H, Okumura K. Fibronectin receptor integrins are involved in mast cell activation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1994;94:625–8.
Lam V, Kalesnikoff J, Lee CW, Hernandez-Hansen V, Wilson BS, Oliver JM, et al. IgE alone stimulates mast cell adhesion to fibronectin via pathways similar to those used by IgE + antigen but distinct from those used by Steel factor. Blood. 2003;102:1405–13.
Bergijk EC, Baelde HJ, De Heer E, Killen PD, Bruijn JA. Specific accumulation of exogenous fibronectin in experimental glomerulosclerosis. J Pathol. 1995;176:191–9.
Rostagno AA, Gallo G, Gold LI. Binding of polymeric IgG to fibronectin in extracellular matrices: an in vitro paradigm for immune-complex deposition. Mol Immunol. 2002;38:1101–11.
Liu YF, Yang SJ, Yan PS, Liu YY. Characteristics of immunocomplex in autopsy tissues of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Chin Med J (Engl). 1994;107:444–9.
Penttinen K, Lähdevirta J, Kekomäki R, Ziola B, Salmi A, Hautanen A, et al. Circulating immune complexes, immunoconglutinins, and rheumatoid factors in nephropathia epidemica. J Infect Dis. 1981;143:15–21.
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor David Pintel (Department of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology, University of Missouri-Columbia, Missouri) for his critical reading and careful revising of this manuscript. This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number: 30271176) and the Shaanxi Provincial Scientific and Technological Program (Grant number: 2004 K172G8).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: C. Kasserra.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Q., Kang, W., Zhang, L. et al. Increased serum fibronectin levels in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Inflamm. Res. 59, 135–139 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-009-0080-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-009-0080-0